SNVS118F december 1999 – may 2023 LM2594 , LM2594HV
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Electrical Characteristics – 3.3 V
- 7.6 Electrical Characteristics – 5 V
- 7.7 Electrical Characteristics – 12 V
- 7.8 Electrical Characteristics – Adjustable
- 7.9 Electrical Characteristics – All Output Voltage Versions
- 7.10 Typical Characteristics
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.3.2 Undervoltage Lockout
Some applications require the regulator to remain off until the input voltage reaches a predetermined voltage. Figure 8-2 shows an undervoltage lockout feature applied to a buck regulator, while Figure 8-3 and Figure 8-4 apply the same feature to an inverting circuit. The circuit in Figure 8-3 features a constant threshold voltage for turnon and turnoff (Zener voltage plus approximately 1 V). If hysteresis is needed, the circuit in Figure 8-4 has a turnon voltage which is different than the turnoff voltage. The amount of hysteresis is approximately equal to the value of the output voltage. If Zener voltages greater than 25 V are used, an additional 47-kΩ resistor is needed from the ON/OFF pin to the ground pin to stay within the 25 V maximum limit of the ON/OFF pin.
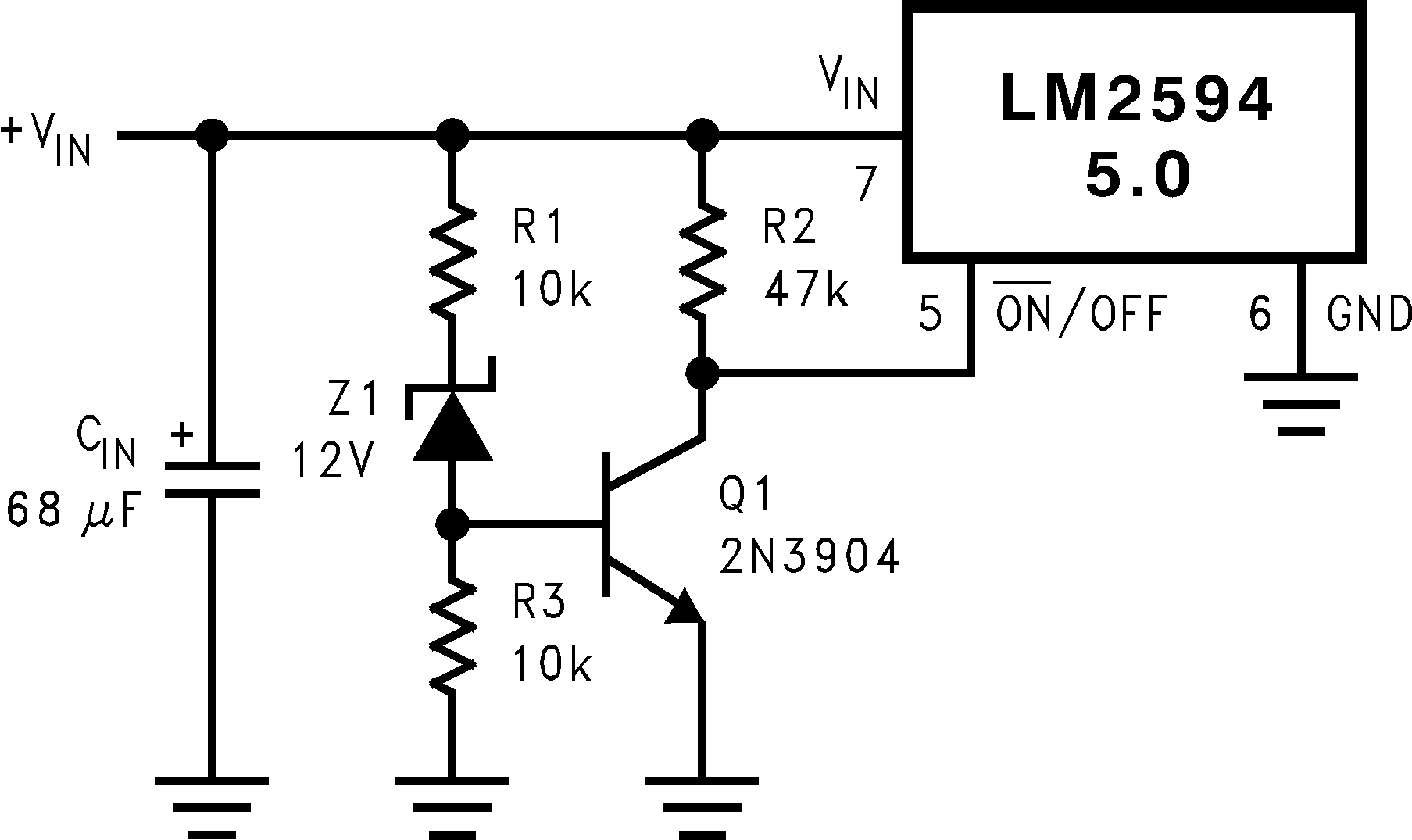 Figure 8-2 Undervoltage Lockout for Buck Regulator
Figure 8-2 Undervoltage Lockout for Buck Regulator