SLUS696C June 2006 – February 2019
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5
Programming
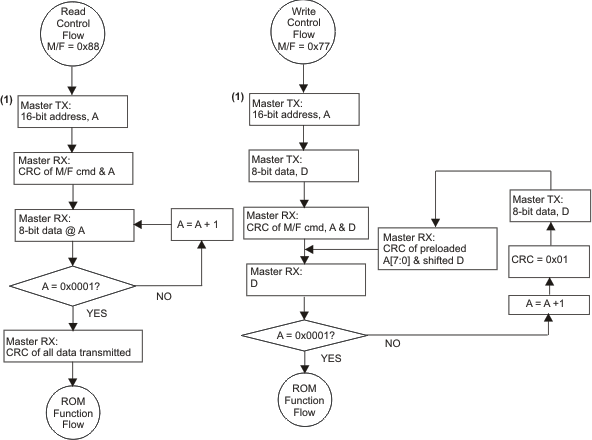
- 7.5.1 Communicating with the bq26100 Device
- 7.5.2 Memory Descriptions
- 7.5.3 SHA-1 Description
- 7.5.4 Key Programming Description
- 7.6 Register Maps
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.6.1.2.1 CTRL Register (address = 0001h) [reset = 1h]
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W |
| 0h | 0h | 0h | 0h | 0h | 1h | 0h | 0h |
Table 9. Control Register Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | PROGK1 | R/W | 0h |
If LOCKK1 is 1 (see Status Register), writing this bit to 1 enables the programming of Device Key 1. Further information about the programming of the keys is found in the SHA-1 section. |
| 6 | PROGK0 | R/W | 0h |
If the LOCKK0 bit is 1 (see Status Register), writing this bit to 1 enables the programming of Device Key 0. Further information about the programming of the keys is found in the SHA-1 section. |
| 5 | RSVD | R/W | 0h |
These bits are reserved for future use. They should always be written to 0. |
| 4 | CLEAR | R/W | 0h |
Writing this bit to 1 clears the message/digest registers. This can be done before the message is written to ensure that all data values are known or after the digest is read to clear the HMAC calculation output. The bq26100 device resets the bit back to 0. |
| 3 | RSVD | R/W | 0h |
Reserved |
| 2 | POR | R/W | 1h |
This bit is set when the device comes out of a POR condition. The bit can be written to 0 to clear the flag. Writing the bit to 1 has no effect on device operation. |
| 1 | DONE | R/W | 0h |
This bit is set when the device completes the HMAC calculation. The host should poll for this bit to determine when the digest is available for reading. This bit is automatically cleared when the AUTH bit is written to 1. This bit is also cleared at POR. |
| 0 | AUTH | R/W | 0h |
This bit is set to initiate the HMAC calculation. This bit is automatically cleared when the DONE bit is written to 1. |