ZHCSIU4A September 2018 – August 2019 ADS1284
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4
Device Functional Modes
- 8.4.1 Synchronization (SYNC PIN and SYNC Command)
- 8.4.2 Reset (RESET Pin and Reset Command)
- 8.4.3 Master Clock Input (CLK)
- 8.4.4 Power-Down (PWDN Pin and STANDBY Command)
- 8.4.5 Power-On Sequence
- 8.4.6 DVDD Power Supply
- 8.4.7 Serial Interface
- 8.4.8 Data Format
- 8.4.9 Reading Data
- 8.4.10 One-Shot Operation
- 8.4.11 Offset and Full-Scale Calibration Registers
- 8.4.12 Calibration Commands (OFSCAL and GANCAL)
- 8.4.13 User Calibration
- 8.5
Programming
- 8.5.1
Commands
- 8.5.1.1 SDATAC Requirements
- 8.5.1.2 WAKEUP: Wake-Up From Standby Mode
- 8.5.1.3 STANDBY: Standby Mode
- 8.5.1.4 SYNC: Synchronize the Analog-to-Digital Conversion
- 8.5.1.5 RESET: Reset the Device
- 8.5.1.6 RDATAC: Read Data Continuous
- 8.5.1.7 SDATAC: Stop Read Data Continuous
- 8.5.1.8 RDATA: Read Data by Command
- 8.5.1.9 RREG: Read Register Data
- 8.5.1.10 WREG: Write to Register
- 8.5.1.11 OFSCAL: Offset Calibration
- 8.5.1.12 GANCAL: Gain Calibration
- 8.5.1
Commands
- 8.6
Register Maps
- 8.6.1
Register Descriptions
- 8.6.1.1 ID_CFG: ID_Configuration Register (address = 00h) [reset =x0h]
- 8.6.1.2 CONFIG0: Configuration Register 0 (address = 01h) [reset = 52h]
- 8.6.1.3 CONFIG1: Configuration Register 1 (address = 02h) [reset = 08h]
- 8.6.1.4 HPF0 and HPF1 Registers
- 8.6.1.5 OFC0, OFC1, OFC2 Registers
- 8.6.1.6 FSC0, FSC1, FSC2 Registers
- 8.6.1
Register Descriptions
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10器件和文档支持
- 11机械、封装和可订购信息
8.3.3.1 Modulator
The low-noise modulator is an inherently-stable, fourth-order, ΔΣ, 2 + 2 pipelined structure, as Figure 38 shows. The modulator shifts the quantization noise to a higher frequency (out of the passband), where the noise is removed by the digital filter. The modulator data can either be completely filtered by the on-chip digital filter or partially filtered by use of the sinc filter section alone. Partial filtering provided by the sinc filter section is intended for use with an external FIR filter.
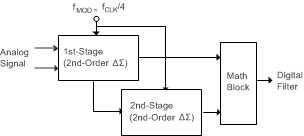 Figure 38. ADS1284 Fourth-Order Modulator
Figure 38. ADS1284 Fourth-Order Modulator Modulator performance is optimized for input signal frequencies over the range dc to 2 kHz. As Figure 39 shows, the effect of PGA and modulator chop result in spectral artifacts occurring at the chop frequency (4 kHz) and harmonics related of the chop frequency. When using the sinc filter output in conjunction with an external post-decimation filter, design the external filter to suppress the modulator chopping artifacts.
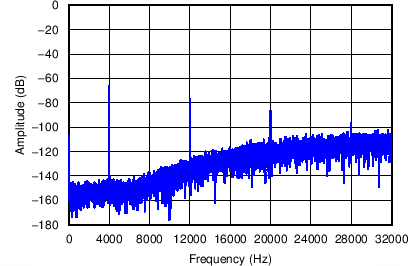 Figure 39. Sinc Output FFT (64 kSPS)
Figure 39. Sinc Output FFT (64 kSPS)