ZHCSF32E February 2016 – December 2019 MSP430FR2310 , MSP430FR2311
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1器件概述
- 2修订历史记录
- 3Device Comparison
- 4Terminal Configuration and Functions
-
5Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings
- 5.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.4 Active Mode Supply Current Into VCC Excluding External Current
- 5.5 Active Mode Supply Current Per MHz
- 5.6 Low-Power Mode LPM0 Supply Currents Into VCC Excluding External Current
- 5.7 Low-Power Mode LPM3 and LPM4 Supply Currents (Into VCC) Excluding External Current
- 5.8 Low-Power Mode LPMx.5 Supply Currents (Into VCC) Excluding External Current
- 5.9 Production Distribution of LPM Supply Currents
- 5.10 Typical Characteristics – Current Consumption Per Module
- 5.11 Thermal Resistance Characteristics
- 5.12
Timing and Switching Characteristics
- 5.12.1 Power Supply Sequencing
- 5.12.2 Reset Timing
- 5.12.3 Clock Specifications
- 5.12.4 Digital I/Os
- 5.12.5 VREF+ Built-in Reference
- 5.12.6 Timer_B
- 5.12.7
eUSCI
- Table 5-14 eUSCI (UART Mode) Clock Frequency
- Table 5-15 eUSCI (UART Mode) Switching Characteristics
- Table 5-16 eUSCI (SPI Master Mode) Clock Frequency
- Table 5-17 eUSCI (SPI Master Mode) Switching Characteristics
- Table 5-18 eUSCI (SPI Slave Mode) Switching Characteristics
- Table 5-19 eUSCI (I2C Mode) Switching Characteristics
- 5.12.8 ADC
- 5.12.9 Enhanced Comparator (eCOMP)
- 5.12.10 Smart Analog Combo (SAC)
- 5.12.11 Transimpedance Amplifier (TIA)
- 5.12.12 FRAM
- 5.12.13 Emulation and Debug
-
6Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 CPU
- 6.3 Operating Modes
- 6.4 Interrupt Vector Addresses
- 6.5 Memory Organization
- 6.6 Bootloader (BSL)
- 6.7 JTAG Standard Interface
- 6.8 Spy-Bi-Wire Interface (SBW)
- 6.9 FRAM
- 6.10 Memory Protection
- 6.11
Peripherals
- 6.11.1 Power-Management Module (PMM) and On-chip Reference Voltages
- 6.11.2 Clock System (CS) and Clock Distribution
- 6.11.3 General-Purpose Input/Output Port (I/O)
- 6.11.4 Watchdog Timer (WDT)
- 6.11.5 System Module (SYS)
- 6.11.6 Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC)
- 6.11.7 Enhanced Universal Serial Communication Interface (eUSCI_A0, eUSCI_B0)
- 6.11.8 Timers (Timer0_B3, Timer1_B3)
- 6.11.9 Backup Memory (BAKMEM)
- 6.11.10 Real-Time Clock (RTC) Counter
- 6.11.11 10-Bit Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
- 6.11.12 eCOMP0
- 6.11.13 SAC0
- 6.11.14 TIA0
- 6.11.15 eCOMP0, SAC0, TIA0, and ADC in SOC Interconnection
- 6.11.16 Embedded Emulation Module (EEM)
- 6.11.17 Peripheral File Map
- 6.12 Input/Output Diagrams
- 6.13 Device Descriptors (TLV)
- 6.14 Identification
- 7Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 8器件和文档支持
- 9机械、封装和可订购信息
8.2 器件命名规则
为了标示产品开发周期所处的阶段,TI 为所有 MSP MCU 器件的部件号分配了前缀。每个 MSP MCU 商用系列产品成员都具有以下两个前缀之一:MSP 或 XMS。这些前缀代表了产品开发的发展阶段,即从工程原型 (XMS) 直到完全合格的生产器件 (MSP)。
XMS - 实验器件,不一定代表最终器件的电气规格
MSP - 完全合格的生产器件
XMS 器件在供货时附带如下免责声明:
“开发中的产品用于内部评估用途。”
MSP 器件的特性已经全部明确,并且器件的质量和可靠性已经完全论证。TI 的标准保修证书对该器件适用。
预测显示原型器件 (XMS) 的故障率大于标准生产器件。由于这些器件的预计最终使用故障率尚不确定,德州仪器 (TI) 建议不要将它们用于任何生产系统。请仅使用合格的生产器件。
TI 器件的命名规则还包括一个带有器件系列名称的后缀。此后缀表示温度范围、封装类型和配送形式。Figure 8-1 提供了解读完整器件名称的图例。
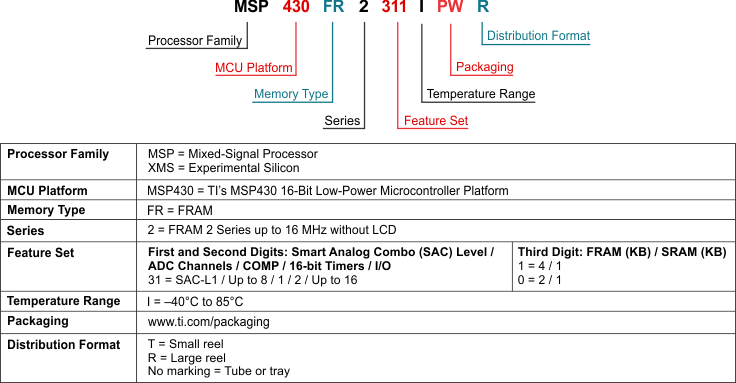 Figure 8-1 器件命名规则
Figure 8-1 器件命名规则