SPRABA5D January 2014 – January 2019 AM1802 , AM1802 , AM1806 , AM1806 , AM1808 , AM1808 , AM1810 , AM1810
-
Using the AM18xx Bootloader
- Trademarks
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Boot Modes
- 3 Non-AIS Boot Modes
- 4
Application Image Script (AIS) Boot
- 4.1 Section Load Command (0x58535901)
- 4.2 Section Fill Command (0x5853590A)
- 4.3 Enable CRC Command (0x58535903)
- 4.4 Disable CRC Command (0x58535904)
- 4.5 Validate CRC Command (0x58535902)
- 4.6 Jump & Close Command (0x58535906)
- 4.7 Jump Command (0x58535905)
- 4.8 Sequential Read Enable Command (0x58535963)
- 4.9 Function Execute Command (0x5853590D)
- 4.10 Boot Table Command (0x58535907)
- 5
AISgen: Tool to Generate Boot Script (AIS Image)
- 5.1 Installation
- 5.2 Getting Started
- 5.3
Generating AIS
- 5.3.1 Boot Mode and Boot Peripheral Setup
- 5.3.2 Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) Setup
- 5.3.3 Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory (SDRAM) Setup
- 5.3.4 DDR Setup
- 5.3.5 PSC Setup
- 5.3.6 Pin Multiplexing Setup
- 5.3.7 Application File Selection
- 5.3.8 AIS File Selection
- 5.3.9 Status and Messages
- 5.3.10 Additional AIS Options
- 5.3.11 Command Line Usage
- 6 Master Boot – Booting From a Slave Memory Device
- 7 Slave Boot – Booting From an External Master Host
- 8 UART Boot Host - Using Your PC as a UART Boot Master
- 9 Boot Requirements, Constraints and Default Settings
- 10 References
- A Boot Mode Selection Table
- B Details of Supported NAND Devices
- C CRC Computation Algorithm
-
D Details of Pre-Defined ROM Functions
- D.1 PLL0 Configuration (Index = 0, Argument Count = 2)
- D.2 PLL1 Configuration (Index = 1, Argument Count = 2)
- D.3 Clock Configuration (Index = 2, Argument Count = 1)
- D.4 mDDR/DDR2 Controller Configuration (Index = 3, Argument Count = 8)
- D.5 EMIFA SDRAM Configuration (Index = 4, Argument Count = 5)
- D.6 EMIFA Async Configuration (Index = 5, Argument Count = 5)
- D.7 PLL and Clock Configuration (Index = 6, Argument Count = 3)
- D.8 Power and Sleep Configuration (PSC) (Index = 7, Argument Count = 1)
- D.9 Pinmux Configuration (Index = 8, Argument Count = 3)
- E ROM Revision History
- Revision History
7.4 Opcode Synchronization (OS)
As the bootloader may take an indeterminate amount of time to execute an AIS command, a handshake mechanism is needed between the host and the bootloader before the host can send any command to the bootloader. The opcode synchronization method is used for this purpose.
All opcodes, including PING_DEVICE, that are transmitted by the host to the bootloader are of the form 0x585359##, where ## varies for individual opcodes. The bootloader acknowledges each opcode with a corresponding RECV opcode. The RECV opcodes are generated from the original opcodes by changing the most significant byte to 0x52. Thus, they are of the form 0x525359##.
Not getting a correct response (RECV opcode) from the bootloader indicates that the bootloader is busy executing the previous command. The host should continue sending the opcode until it is successfully acknowledged by the bootloader. Figure 24 shows the flowchart of how the OS should be implemented on the host:
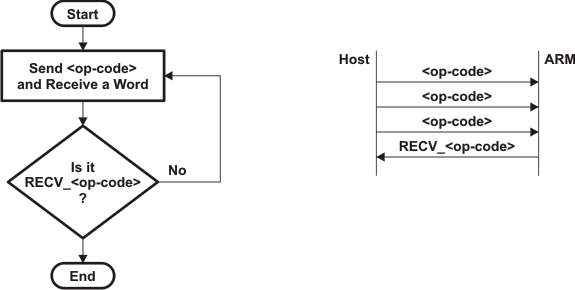 Figure 24. Flowchart: Op-Code Synchronization
Figure 24. Flowchart: Op-Code Synchronization The host is required to understand each command and supply the required arguments and data to the bootloader.