SNVA966 July 2020 – MONTH LP8864-Q1 , LP8864S-Q1 , LP8866-Q1 , LP8866S-Q1
- Trademarks
- 1Fault Handling Routine
- 2Different Fault and Diagnostic Handling Method Recommendation
- 3Summary
-
A Fault-Related
Functions
-
A.1 Protection and Fault Detections
- A.1.1 Supply Faults
-
A.1.2 Boost Faults
- A.1.2.1 Boost Overvoltage Faults (BSTOVPL, BSTOVPH)
- A.1.2.2 Boost Overcurrent Faults (BSTOCP)
- A.1.2.3 LEDSET Resistor Missing Faults (LEDSET)
- A.1.2.4 MODE Resistor Missing Faults (MODESEL)
- A.1.2.5 FSET Resistor Missing Faults (FSET)
- A.1.2.6 ISET Resistor Out of Range Faults (ISET)
- A.1.2.7 Thermal Shutdown Faults (TSD)
- A.1.3 LED Faults
- A.1.4 Overview of the Fault and Protection Schemes
- A.2 Programming Examples
-
A.1 Protection and Fault Detections
1 Fault Handling Routine
The LP8864-Q1, LP8864S-Q1, LP8866-Q1, and LP8866S-Q1 (hereafter, LP886XX-Q1) devices have a huge variety of fault detections and diagnostic features. The system could make use of all these features to better evaluate the current system condition, making the most suitable decision. It will help to avoid both overacting under minor faults and underacting under critical faults.
However, to fully leverage all those features, a well-organized fault handling routine is needed. The following figure is the recommended software handling routine which works with the LP886XX-Q1 devices.
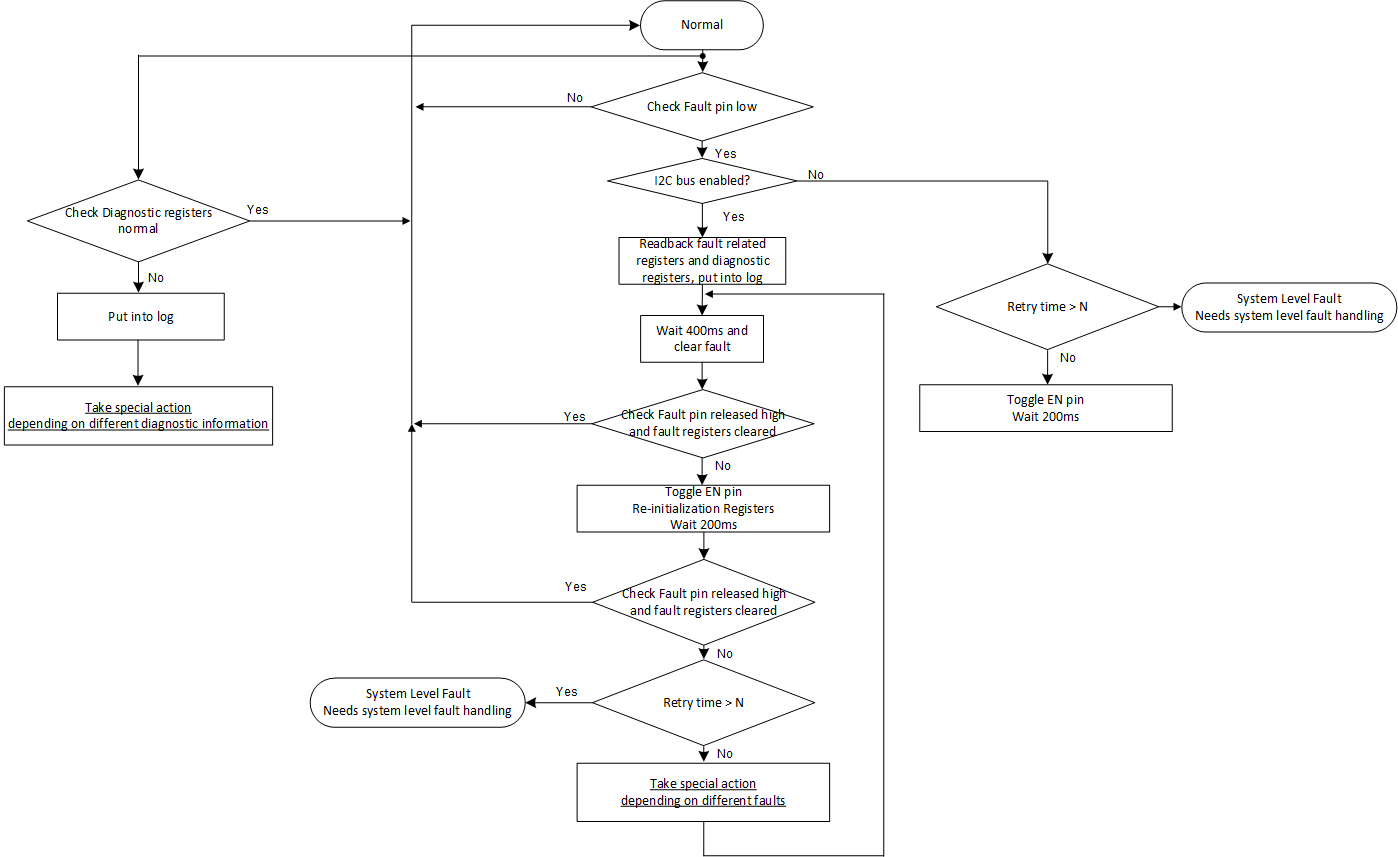 Figure 1-1 Software Recommended Fault Handling Routine
Figure 1-1 Software Recommended Fault Handling RoutineWhen a fault is detected through the FAULT pin, the software needs to take related action.
Faults can be resolved in the following ways by the fault handling routine:
- Automatically recovered by the internal fault recovery mechanism of the chip
- Recovered by powering cycle the chip
- Recovered by taking corresponding system-level action
- A fault which cannot be recovered by the previous three methods
Higher critical level actions are taken if current level actions do not solve the issue. The details of those specific actions are described in Section 2. The corresponding system-level action to handle faults and incorrect diagnostic information will differ based on different faults detected.