SLVAF84 September 2021 DRV8311 , DRV8312 , DRV8313 , DRV8316 , MCT8316Z
1 Introduction
For integrated MOSFET drivers, data sheets define propagation delay as the time it takes for changing input logic edges INHx and INLx (whichever changes first if MCU dead time is added) to change the half-bridge output voltage (OUTx) as Figure 1-1 shows. It includes an input deglitch delay, an analog driver, and a comparator delay resulting in a propagation delay time (tpd). The analog drivers insert automatic internal dead time (tdead) to avoid cross conduction of MOSFETs and shoot-through currents.
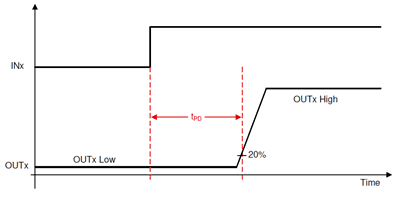 Figure 1-1 Propagation Delay Timing in Integrated MOSFET Drivers
Figure 1-1 Propagation Delay Timing in Integrated MOSFET DriversHowever, propagation delay and dead time can change based on many factors:
- Direction of current into or out of the phase
- Additional dead time from the MCU PWM inputs
- Delay Compensation to minimize duty cycle distortion
This application note investigates how each factor affects driver delay and dead time in integrated MOSFET drivers.