ZHCSL68C April 2017 – December 2020 TPS7A84A
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics: General
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics: TPS7A8400A
- 6.7 Electrical Characteristics: TPS7A8401A
- 6.8 Typical Characteristics: TPS7A8400A
- 6.9 Typical Characteristics: TPS7A8401A
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1
Application Information
- 8.1.1
External Component Selection
- 8.1.1.1 Adjustable Operation
- 8.1.1.2 ANY-OUT Programmable Output Voltage
- 8.1.1.3 ANY-OUT Operation
- 8.1.1.4 Increasing ANY-OUT Resolution for LILO Conditions
- 8.1.1.5 Current Sharing
- 8.1.1.6 Recommended Capacitor Types
- 8.1.1.7 Input and Output Capacitor Requirements (CIN and COUT)
- 8.1.1.8 Feed-Forward Capacitor (CFF)
- 8.1.1.9 Noise-Reduction and Soft-Start Capacitor (CNR/SS)
- 8.1.2 Start-Up
- 8.1.3 AC and Transient Performance
- 8.1.4 DC Performance
- 8.1.5 Sequencing Requirements
- 8.1.6 Negatively Biased Output
- 8.1.7 Reverse Current Protection
- 8.1.8 Power Dissipation (PD)
- 8.1.1
External Component Selection
- 8.2 Typical Applications
- 8.1
Application Information
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
8.1.8.1 Estimating Junction Temperature
The JEDEC standard now recommends the use of psi (Ψ) thermal metrics to estimate the junction temperatures of the LDO when in-circuit on a typical PCB board application. These metrics are not strictly speaking thermal resistances, but rather offer practical and relative means of estimating junction temperatures. These psi metrics are determined to be significantly independent of the copper-spreading area. The key thermal metrics (ΨJT and ΨJB) are given in the Thermal Information table in the Section 6 section and are used in accordance with Equation 14.
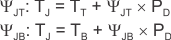
where:
- PD is the power dissipated as explained in Equation 11
- TT is the temperature at the center-top of the device package, and
- TB is the PCB surface temperature measured 1 mm from the device package and centered on the package edge