ZHCSH76C October 2017 – March 2024 TLV757P
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Detailed Description
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
封装选项
请参考 PDF 数据表获取器件具体的封装图。
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
- DYD|5
- DBV|5
- DRV|6
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
- DRV|6
订购信息
7.1.4 Reverse Current
As with most LDOs, excessive reverse current potentially damages this device.
Reverse current flows through the body diode on the pass transistor instead of the normal conducting channel. At high magnitudes, this current flow degrades the long-term reliability of the device, as a result of one of the following conditions:
- Degradation caused by electromigration
- Excessive heat dissipation
- Potential for a latch-up condition
Conditions where reverse current occurs are outlined in this section, all of which exceed the absolute maximum rating of VOUT > VIN + 0.3V:
- If the device has a large COUT and the input supply collapses with little or no load current
- The output is biased when the input supply is not established
- The output is biased above the input supply
If reverse current flow is expected in the application, use external protection to protect the device. Figure 7-3 shows one approach of protecting the device.
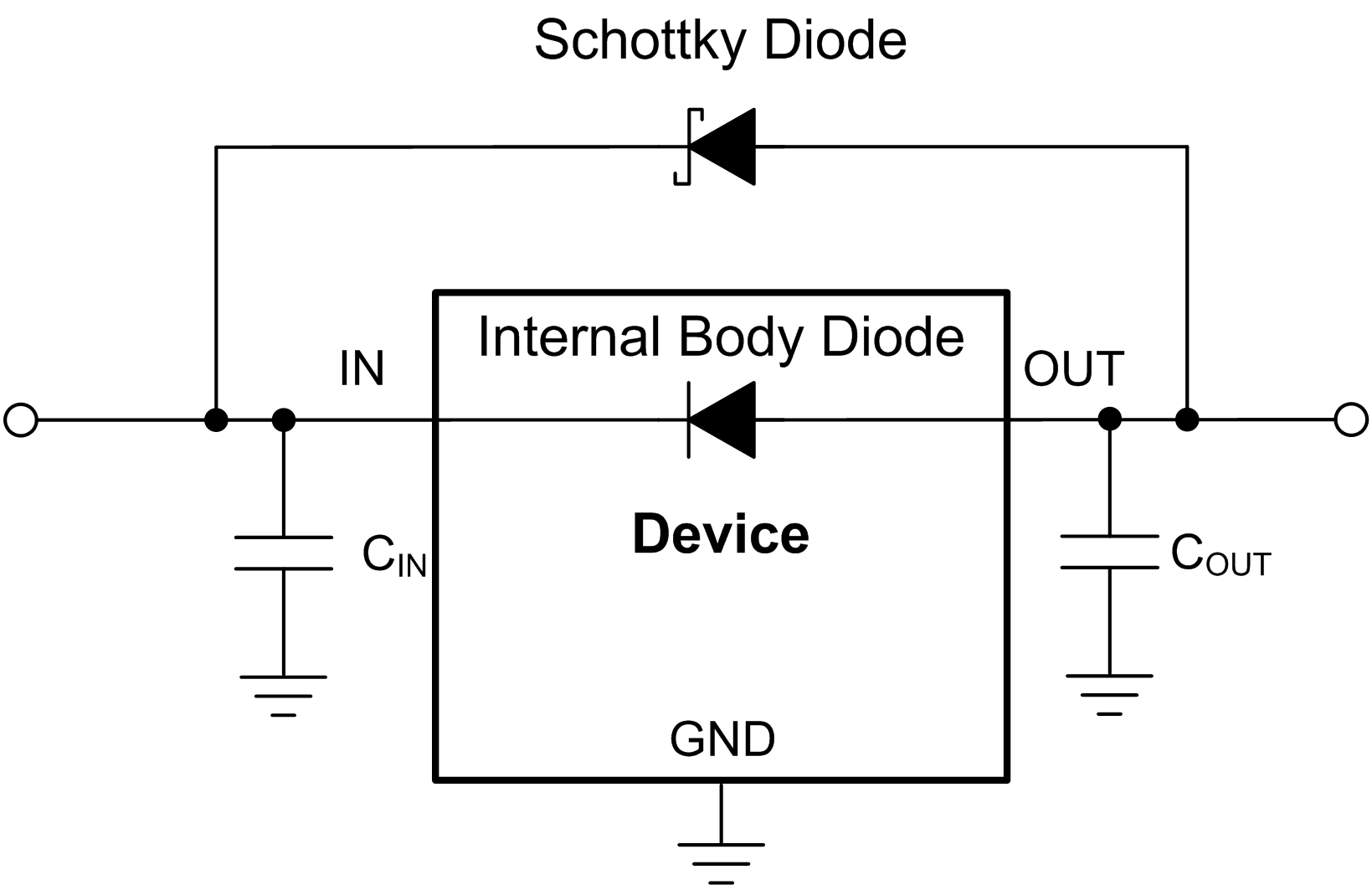 Figure 7-3 Example Circuit for Reverse Current Protection Using a Schottky Diode
Figure 7-3 Example Circuit for Reverse Current Protection Using a Schottky Diode