ZHCSMV1 December 2020 TAS5822M
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming and Control
- 7.6 Register Maps
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.3.2 Device Clocking
The TAS5822M devices have flexible systems for clocking. Internally, the device requires a number of clocks, mostly at related clock rates to function correctly. All of these clocks can be derived from the Serial Audio Interface.
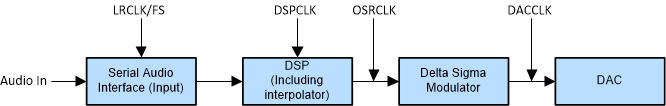 Figure 7-1 Audio Flow with Respective Clocks
Figure 7-1 Audio Flow with Respective ClocksFigure 7-1 shows the basic data flow and clock Distribution.
The Serial Audio Interface typically has 3 connection pins which are listed as follows:
- SCLK (Bit Clock)
- LRCLK/FS (Left Right Word Clock and Frame Sync)
- SDIN (Input Data)
The device has an internal PLL that is used to take SCLK and create the higher rate clocks required by the DSP and the DAC clock.
The device has an audio sampling rate detection circuit that automatically senses which frequency the sampling rate is operating. Common audio sampling frequencies of 32 kHz, 44.1kHz – 48 kHz, 88.2 kHz – 96 kHz are supported. The sampling frequency detector sets the clock for DAC and DSP automatically.