ZHCSBR3C December 2013 – May 2018 OPA355-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
9.2.3 Driving ADCs
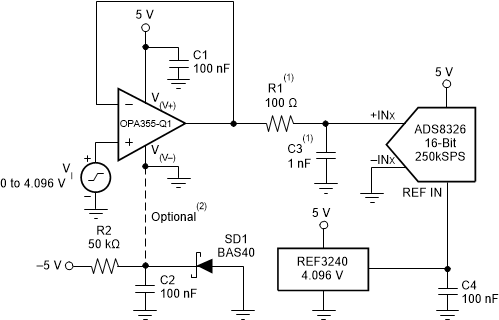
The OPA355-Q1 op amps are designed for driving sampling analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) with sampling speeds up to 1 MSPS. The zero-crossover distortion input stage topology allows the OPA355-Q1 device to drive ADCs without degradation of differential linearity and THD.
The OPA355-Q1 device can be used to buffer the ADC switched input capacitance and resulting charge injection while providing signal gain. Figure 35 shows the OPA355-Q1 device configured to drive the ADS8326.
1.
NOINDENT:
Suggested value; may require adjustment based on specific application.2.
Figure 35. Driving the ADS8326 NOINDENT:
Single-supply applications lose a small number of ADC codes near ground as a result of op amp output swing limitation. If a negative power supply is available, this simple circuit creates a –0.3-V supply to allow output swing to true ground potential.