ZHCSMT4C October 2021 – November 2022 LMR51420
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.3.4 Minimum On Time, Minimum Off Time, and Frequency Foldback
Minimum on time (tON_MIN) is the shortest duration of time that the high-side switch can be turned on. tON_MIN is typically 70 ns for the LMR51420. Minimum off time (tOFF_MIN) is the shortest duration of time that the high-side switch can be off. tOFF_MIN is typically 150 ns. In CCM operation, tON_MIN and tOFF_MIN limit the voltage conversion range without switching frequency foldback.
The minimum duty cycle without frequency foldback allowed is:
The maximum duty cycle without frequency foldback allowed is:
Given a required output voltage, the maximum VIN without frequency foldback can be found by:
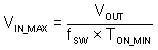
The minimum VIN without frequency foldback can be calculated by:
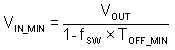
In the LMR51420, a frequency foldback scheme is employed after tON_MIN or tOFF_MIN is triggered, which can extend the maximum duty cycle or lower the minimum duty cycle.
The on time decreases while VIN voltage increases. After the on time decreases to tON_MIN, the switching frequency starts to decrease while VIN continues to increase, which lowers the duty cycle further to keep VOUT in regulation according to Equation 4.
The frequency foldback scheme also works after larger duty cycle is needed under low VIN condition. The frequency decreases after the device reaches tOFF_MIN, which extends the maximum duty cycle according to Equation 5. In such condition, the frequency can be as low as approximately 133 kHz. A wide range of frequency foldback allows for the LMR51420 output voltage to stay in regulation with a much lower supply voltage VIN, which leads to a lower effective dropout.
With frequency foldback while maintaining a regulated output voltage, VIN_MAX is raised, and VIN_MIN is lowered by decreased fSW.
| VOUT = 1.8 V | fSW = 1.1 MHz | IOUT = 2.0 A |
| VOUT = 5.0 V | fSW = 1.1 MHz | IOUT = 2.0 A |