ZHCSFX3A April 2016 – November 2016 CC2564C
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1器件概述
- 2修订历史记录
- 3Device Comparison
- 4Terminal Configuration and Functions
-
5Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings
- 5.3 Power-On Hours
- 5.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.5 Power Consumption Summary
- 5.6 Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7 Thermal Resistance Characteristics for VQFN-MR (RVM) Package
- 5.8
Timing and Switching Characteristics
- 5.8.1 Device Power Supply
- 5.8.2 Clock Specifications
- 5.8.3 Peripherals
- 5.8.4
RF Performance
- 5.8.4.1
Bluetooth BR and EDR RF Performance
- 5.8.4.1.1 Bluetooth Receiver—In-Band Signals
- 5.8.4.1.2 Bluetooth Receiver—General Blocking
- 5.8.4.1.3 Bluetooth Transmitter—GFSK
- 5.8.4.1.4 Bluetooth Transmitter—EDR
- 5.8.4.1.5 Bluetooth Modulation—GFSK
- 5.8.4.1.6 Bluetooth Modulation—EDR
- 5.8.4.1.7 Bluetooth Transmitter—Out-of-Band and Spurious Emissions
- 5.8.4.2 Bluetooth low energy RF Performance
- 5.8.4.1
Bluetooth BR and EDR RF Performance
-
6Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 6.3 Clock Inputs
- 6.4 Functional Blocks
- 6.5 Bluetooth BR and EDR Features
- 6.6 Bluetooth low energy Description
- 6.7 Bluetooth Transport Layers
- 6.8 Changes from the CC2564B Device to the CC2564C Device
- 7Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 8器件和文档支持
- 9机械、封装和可订购信息
7 Applications, Implementation, and Layout
NOTE
Information in the following Applications section is not part of the TI component specification, and TI does not warrant its accuracy or completeness. TI’s customers are responsible for determining suitability of components for their purposes. Customers should validate and test their design implementation to confirm system functionality.
7.1 Reference Design Schematics and BOM for Power and Radio Connections
Figure 7-1 shows the reference schematics for the VQFN-MR package. For complete schematics and PCB layout guidelines, contact your TI representative.
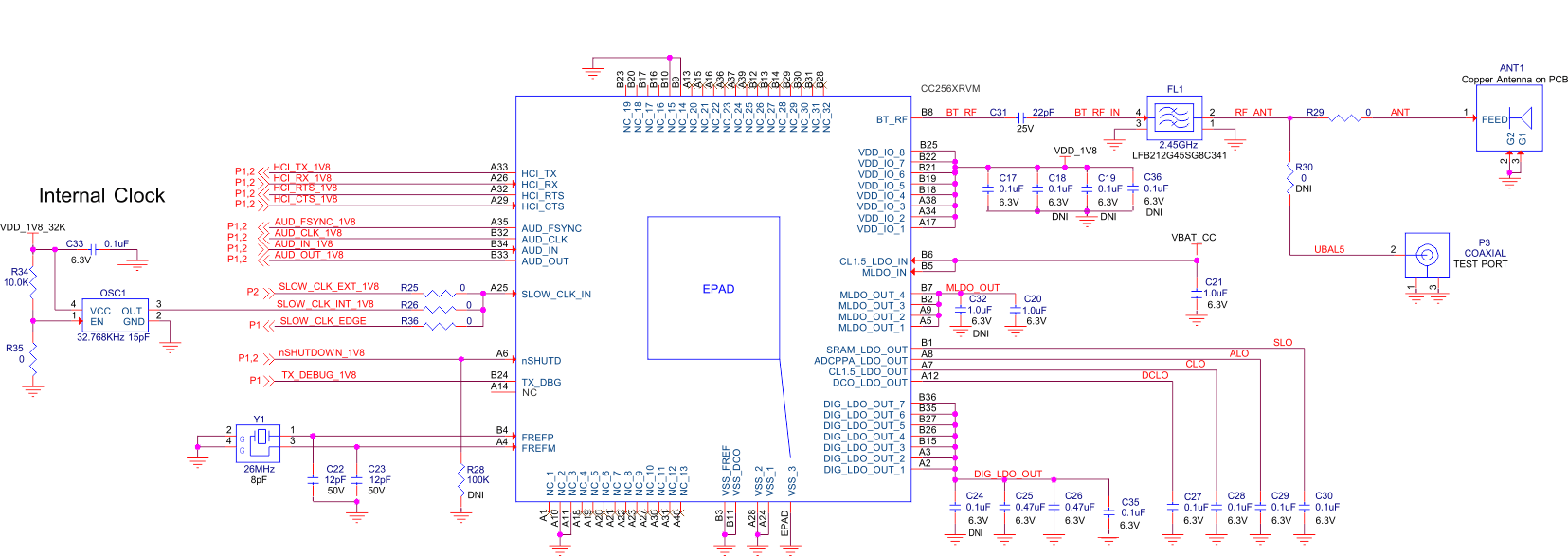 Figure 7-1 Reference Schematics
Figure 7-1 Reference Schematics
Table 7-1 lists the BOM for the VQFN-MR package.
Table 7-1 Bill of Materials
| QTY | REF. DES. |
VALUE | DESCRIPTION | MANUFACTURER | MANUFACTURER PART NUMBER |
ALT PART |
NOTES |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ANT1 | NA | ANT_IIFA_CC2420_32mil_MIR | NA | IIFA_CC2420 | Chip antenna | Copper antenna on PCB |
| 6 | Capacitor | 0.1 µF | Capacitor, ceramic; 0.1-µF 6.3-V 10% X7R 0402 |
Kemet | C0402C104K9RACTU | ||
| 2 | Capacitor | 1.0 µF | Capacitor, ceramic; 1.0-µF 6.3-V 10% X5R 0402 |
Taiyo Yuden | JMK105BJ105KV-F | ||
| 2 | Capacitor | 12 pF | Capacitor, ceramic; 12 pF 6.3-V X5R 10% 0402 |
Murata Electronics | GRM1555C1H120JZ01D | ||
| 2 | Capacitor | 0.47 µF | Capacitor, ceramic; 0.47-µF 6.3-V X5R ±10% 0402 |
Taiyo Yuden | JMK105BJ474KV-F | ||
| 1 | FL1 | 2.45 GHz | Filter, ceramic bandpass, 2.45-GHz SMD |
Murata Electronics | LFB212G45SG8C341 | DEA162450BT_1260B3 (TDK) | Place brown marking up |
| 1 | OSC1 | 32.768 kHz 15 pF | Oscillator; 32.768-kHz 15-pF 1.5-V 3.3-V SMD | Abracon Corporation | ASH7K-32.768KHZ-T | Optional | |
| 1 | U5 | CC2564CRVM | CC2564C dual-mode Bluetooth controller | Texas Instruments | CC2564CRVM | ||
| 1 | Y1 | 26 MHz | Crystal, 26 MHz | NDK | NX2016SA | TZ1325D (Tai-Saw TST) |
|
| 1 | C31 | 22 pF | Capacitor, ceramic; 22-pF 25-V 5% NP0 0201 |
Murata Electronics North America | GRM0335C1E220JD01D (EXS00A-CS06025) |
7.2 PCB Layout Guidelines
This section describes the PCB guidelines to speed up the PCB design using the CC256x VQFN device. Following these guidelines ensures that the design will pass Bluetooth SIG certification and also minimizes risk for regulatory certifications including FCC, ETSI, and CE. For more information, see CC256x QFN PCB Guidelines.
7.2.1 General PCB Guidelines
General PCB guidelines follow:
- You must verify the recommended PCB stackup in the PCB Design guidelines.
- You must verify the dimensions of the QFN PCB footprint in the QFN Package Information section of CC256x QFN PCB Guidelines and in Section 6.
- The decoupling capacitors must be as close as possible to the QFN device.
7.2.2 Power Supply Guidelines
Guidelines for the power supply follow:
- The trace width must be at least 10 mils for the VBAT and VIO traces.
- The length of the traces must be as short as possible (pin to pin).
- Decoupling capacitors must be as close as possible to the QFN device:
- The MLDO_IN capacitor must be close to pin B5.
- The VDD_IO capacitor must be close to pins B18 and A17.
Guidelines for the LDOs follow:
- The trace width for the trace between x_LDO_x pins and decoupling capacitors is at least 5 mils; where possible, the recommended trace width is 10 mils.
- Place the decoupling capacitor of MLDO_OUT (C20) as close as possible to pin A5.
- These capacitors must close to the following pins:
- The DIG_LDO_OUT capacitor must be close to ball B15.
- The DIG_LDO_OUT capacitor must be close to ball B27.
- The DIG_LDO_OUT capacitor must be close to ball B36.
- The DIG_LDO_OUT capacitor connected to ball B36 must be isolated from the top layer GND (see the Low-Dropout Capacitors section in CC256x QFN PCB Guidelines).
- The decoupling capacitors for SRAM, ADCPPA, and CL1.5 LDO_OUT must be as close as possible to their corresponding pins on the CC256x device.
- Place the device and capacitors together on the top side.
- The ground connection of each capacitor must be directly connected to solid ground layer (layer 2).
- The capacitor that is directly connected to pin A12 should be close to the device.
- Connect the DCO_LDO_OUT capacitor isolated from layer 1 ground directly to layer 2 solid ground.
Guidelines for the ground layer follow:
- Layer 2 must be a solid ground plane.
- Isolate VSS_FREF from ground on the top layer and route it directly to ground on the second layer (see the Key VSS Ball section in CC256x QFN PCB Guidelines).
- Isolate VSS_DCO (ball B11) from ground. Include VSS_DCO in the illustration of the DCO_LDO_OUT capacitor (see the DCO_LDO_OUT section in CC256x QFN PCB Guidelines).
- A minimum of 13 vias on the thermal pad are required to increase ground coupling.
- Connect VSS_FREF (ball B3) directly to solid ground, not to the thermal pad.
7.2.3 User Interfaces
Guidelines for the UART follow:
- The trace width for the UART must be at least 5 mils.
- Run the four UART lines as a bus interface.
- Determine if clocks, DC supply, or RF traces are not near these UART traces.
- The ground plane on layer 2 is solid below these lines and there is ground around these traces on the top layer.
Guidelines for the PCM follow:
- The trace width for the PCM must be at least 5 mils.
- Run the four PCM lines as a bus interface and approximately the same length.
- Determine if clocks, DC supply, RF traces, and LDO capacitors are not near these PCM traces.
- The ground plane on layer 2 is solid below these lines and there is ground around these traces on the top layer.
Guidelines for TX_DBG follow:
- Check for an accessible test point on the board from TX_DBG pin B24.
7.2.4 Clock Interfaces
Guidelines for the slow clock follow:
- The trace width for the slow clock must be at least 5 mils.
- The signal lines for the slow clock must be as short as possible.
- The ground plane on layer 2 is solid below these lines and there is ground around these traces on the top layer.
Guidelines for the fast clock follow:
- The trace width for the fast clock must be at least 5 mils.
- Ensure that crystal tuning capacitors are close to crystal pads.
- Make both traces (XTALM and XTALP) parallel as much as possible and approximately the same length.
- The ground plane on layer 2 is solid below these lines and there is ground around these traces on the top layer.
7.2.5 RF Interface
Guidelines for the RF Interface follow:
- TI recommends using an RF shield (not mandatory).
- Verify that RF traces are routed on the top layer and matched at 50 Ω with reference to ground.
- Route the RF line between these NC pins:
- NC_2 (A10)
- NC_3 (A11)
- NC_14 (B9)
- NC_15 (B10)
- Ensure the area underneath the BPF pads is grounded on layer 1 and layer 2.
- Keep RF_IN and RF_OUT of the BPF pads clear of any ground fill (see the RF Trace section in CC256x QFN PCB Guidelines).
- Follow guidelines specified in the vendor-specific antenna design guides (including placement of antenna).
- Follow guidelines specified in the vendor-specific BPF design guides.
- Verify that the Bluetooth RF trace is a 50-Ω, impedance-controlled trace with reference to solid ground.
- Ensure that the RF trace length is as short as possible.
These NC pins are grounded for better RF isolation.
NOTE
These pins are NC at the chip level, but TI recommends grounding them on the PCB layout for better RF isolation.