ZHCSQL8C June 2022 – October 2025 AM620-Q1 , AM623 , AM625 , AM625-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 器件比较
-
5 终端配置和功能
- 5.1 引脚图
- 5.2 引脚属性
- 5.3
信号说明
- 14
- 5.3.1 CPSW3G
- 5.3.2 CPTS
- 5.3.3 CSI-2
- 5.3.4 DDRSS
- 5.3.5 DSS
- 5.3.6 ECAP
- 5.3.7 仿真和调试
- 5.3.8 EPWM
- 5.3.9 EQEP
- 5.3.10 GPIO
- 5.3.11 GPMC
- 5.3.12 I2C
- 5.3.13 MCAN
- 5.3.14 MCASP
- 5.3.15 MCSPI
- 5.3.16 MDIO
- 5.3.17 MMC
- 5.3.18 OLDI
- 5.3.19 OSPI
- 5.3.20 电源
- 5.3.21 PRUSS
- 5.3.22 保留
- 5.3.23 系统和其他
- 5.3.24 计时器
- 5.3.25 UART
- 5.3.26 USB
- 5.4 引脚连接要求
-
6 规格
- 6.1 绝对最大额定值
- 6.2 未通过 AEC - Q100 认证的器件的 ESD 等级
- 6.3 符合 AEC - Q100 标准的器件的 ESD 等级
- 6.4 上电小时数 (POH)
- 6.5 建议运行条件
- 6.6 运行性能点
- 6.7 功耗摘要
- 6.8 电气特性
- 6.9 一次性可编程 (OTP) 电子保险丝的 VPP 规格
- 6.10 热阻特性
- 6.11 温度传感器特性
- 6.12
时序和开关特性
- 6.12.1 时序参数和信息
- 6.12.2 电源要求
- 6.12.3 系统时序
- 6.12.4 时钟规格
- 6.12.5
外设
- 6.12.5.1 CPSW3G
- 6.12.5.2 CPTS
- 6.12.5.3 CSI-2
- 6.12.5.4 DDRSS
- 6.12.5.5 DSS
- 6.12.5.6 ECAP
- 6.12.5.7 仿真和调试
- 6.12.5.8 EPWM
- 6.12.5.9 EQEP
- 6.12.5.10 GPIO
- 6.12.5.11 GPMC
- 6.12.5.12 I2C
- 6.12.5.13 MCAN
- 6.12.5.14 MCASP
- 6.12.5.15 MCSPI
- 6.12.5.16 MMCSD
- 6.12.5.17 OLDI
- 6.12.5.18 OSPI
- 6.12.5.19 PRUSS
- 6.12.5.20 计时器
- 6.12.5.21 UART
- 6.12.5.22 USB
-
7 详细说明
- 7.1 概述
- 7.2 处理器子系统
- 7.3 加速器和协处理器
- 7.4 其他子系统
- 7.5
外设
- 7.5.1 千兆位以太网交换机 (CPSW3G)
- 7.5.2 摄像头串行接口接收器 (CSI_RX_IF)
- 7.5.3 DDR 子系统 (DDRSS)
- 7.5.4 显示子系统 (DSS)
- 7.5.5 增强型捕获 (ECAP)
- 7.5.6 错误定位器模块 (ELM)
- 7.5.7 增强型脉宽调制 (EPWM)
- 7.5.8 错误信令模块 (ESM)
- 7.5.9 增强型正交编码器脉冲 (EQEP)
- 7.5.10 通用接口 (GPIO)
- 7.5.11 通用存储器控制器 (GPMC)
- 7.5.12 全局时基计数器 (GTC)
- 7.5.13 内部集成电路 (I2C)
- 7.5.14 模块化控制器局域网 (MCAN)
- 7.5.15 多通道音频串行端口 (MCASP)
- 7.5.16 多通道串行外设接口 (MCSPI)
- 7.5.17 多媒体卡安全数字 (MMCSD)
- 7.5.18 八进制串行外设接口 (OSPI)
- 7.5.19 计时器
- 7.5.20 通用异步收发器 (UART)
- 7.5.21 通用串行总线子系统 (USBSS)
- 8 应用、实现和布局
- 9 器件和文档支持
- 10修订历史记录
- 11机械、封装和可订购信息
6.12.5.11.1 GPMC 和 NOR 闪存 - 同步模式
表 6-65 和表 6-66 展示了 GPMC 和 NOR 闪存的时序要求和开关特性 - 同步模式。
表 6-65 GPMC 和 NOR 闪存时序要求 - 同步模式 请参阅图 6-46、图 6-47 和图 6-50
| 编号 | 参数 | 说明 | 最小值 | 最大值 | 单位 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F12 | tsu(dV-clkH) | 建立时间,GPMC_AD[15:0] 在 GPMC_CLK 高电平之前有效 | 0.92 | ns | |
| F13 | th(clkH-dV) | 保持时间,GPMC_AD[15:0] 在 GPMC_CLK 高电平之后有效 | 2.09 | ns | |
| F21 | tsu(waitV-clkH) | 建立时间,GPMC_WAIT[j](1)(2) 在 GPMC_CLK 高电平之前有效 | 0.92 | ns | |
| F22 | th(clkH-waitV) | 保持时间,GPMC_WAIT[j](1)(2) 在 GPMC_CLK 高电平之后有效 | 2.09 | ns |
(1) 在 GPMC_WAIT[j] 中,j 等于 0 或 1。
(2) 等待监视支持仅限于 WaitMonitoringTime 值 > 0。有关等待监视功能的完整说明,请参阅器件 TRM 中的通用存储器控制器 (GPMC) 一节。
表 6-66 GPMC 和 NOR 闪存开关特性 - 同步模式 请参阅图 6-46、图 6-47、图 6-48、图 6-49 和图 6-50
| 编号 | 参数 | 说明 | 最小值 | 最大值 | 单位 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F0 | tc(clk) | 周期时间,GPMC_CLK(16) | 7.52 | ns | |
| F1 | tw(clkH) | 典型脉冲持续时间,GPMC_CLK 高电平 | 0.475P(13) - 0.3 | ns | |
| F1 | tw(clkL) | 典型脉冲持续时间,GPMC_CLK 低电平 | 0.475P(13) - 0.3 | ns | |
| F2 | td(clkH-csnV) | 延迟时间,GPMC_CLK 上升沿到 GPMC_CSn[i] 转换(12) | F(5) - 2.2 | F(5) + 3.75 | ns |
| F3 | td(clkH-CSn[i]V) | 延迟时间,GPMC_CLK 上升沿到 GPMC_CSn[i] 无效(12) | D(4) - 2.2 | D(4) + 4.5 | ns |
| F4 | td(aV-clk) | 延迟时间,GPMC_A[27:1] 有效至 GPMC_CLK 第一个边沿 | B(2) - 2.3 | B(2) + 4.5 | ns |
| F5 | td(clkH-aIV) | 延迟时间,GPMC_CLK 上升沿到 GPMC_A[27:1] 无效 | -2.3 | 4.5 | ns |
| F6 | td(be[x]nV-clk) | 延迟时间,GPMC_BE0n_CLE、GPMC_BE1n 有效至 GPMC_CLK 第一个边沿 | B(2) - 2.3 | B(2) + 1.9 | ns |
| F7 | td(clkH-be[x]nIV) | 延迟时间,GPMC_CLK 上升沿到 GPMC_BE0n_CLE、GPMC_BE1n 无效 | D(4) - 2.3 | D(4) + 1.9 | ns |
| F8 | td(clkH-advn) | 延迟时间,GPMC_CLK 上升沿到 GPMC_ADVn_ALE 转换 | G(6) - 2.3 | G(6) + 4.5 | ns |
| F9 | td(clkH-advnIV) | 延迟时间,GPMC_CLK 上升沿到 GPMC_ADVn_ALE 无效 | D(4) - 2.3 | D(4) + 4.5 | ns |
| F10 | td(clkH-oen) | 延迟时间,GPMC_CLK 上升沿到 GPMC_OEn_REn 转换 | H(7) - 2.3 | H(7) + 3.5 | ns |
| F11 | td(clkH-oenIV) | 延迟时间,GPMC_CLK 上升沿到 GPMC_OEn_REn 无效 | D(4) - 2.3 | D(4) + 3.5 | ns |
| F14 | td(clkH-wen) | 延迟时间,GPMC_CLK 上升沿到 GPMC_WEn 转换 | I(8) - 2.3 | I(8) + 4.5 | ns |
| F15 | td(clkH-do) | 延迟时间,GPMC_CLK 上升沿到 GPMC_AD[15:0] 转换(9) | - 2.3 | + 2.7 | ns |
| F15 | td(clkL-do) | 延迟时间,GPMC_CLK 下降沿到 GPMC_AD[15:0] 数据总线转换(10) | - 2.3 | + 2.7 | ns |
| F15 | td(clkL-do) | 延迟时间,GPMC_CLK 下降沿到 GPMC_AD[15:0] 数据总线转换(11) | - 2.3 | + 2.7 | ns |
| F17 | td(clkH-be[x]n) | 延迟时间,GPMC_CLK 上升沿到 GPMC_BE0n_CLE、GPMC_BE1n 转换(9) | - 2.3 | + 1.9 | ns |
| F17 | td(clkL-be[x]n) | 延迟时间,GPMC_CLK 下降沿到 GPMC_BE0n_CLE、GPMC_BE1n 转换(10) | - 2.3 | + 1.9 | ns |
| F17 | td(clkL-be[x]n) | 延迟时间,GPMC_CLK 下降沿到 GPMC_BE0n_CLE、GPMC_BE1n 转换(11) | - 2.3 | + 1.9 | ns |
| F18 | tw(csnV) | 脉冲持续时间,GPMC_CSn[i](12) 低电平 | A(1) | ns | |
| F19 | tw(be[x]nV) | 脉冲持续时间,GPMC_BE0n_CLE、GPMC_BE1n 低电平 | C(3) | ns | |
| F20 | tw(advnV) | 脉冲持续时间,GPMC_ADVn_ALE 低电平 | K(14) | ns |
(1) 对于单次读取:A = (CSRdOffTime - CSOnTime) × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) × GPMC_FCLK(15)
对于单次写入:A = (CSWrOffTime - CSOnTime) × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) × GPMC_FCLK(15)
对于突发读取:A = (CSRdOffTime - CSOnTime + (n - 1) × PageBurstAccessTime) × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) × GPMC_FCLK(15)
对于突发写入:A = (CSWrOffTime - CSOnTime + (n - 1) × PageBurstAccessTime) × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) × GPMC_FCLK(15)
n 是页面突发访问编号。
对于单次写入:A = (CSWrOffTime - CSOnTime) × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) × GPMC_FCLK(15)
对于突发读取:A = (CSRdOffTime - CSOnTime + (n - 1) × PageBurstAccessTime) × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) × GPMC_FCLK(15)
对于突发写入:A = (CSWrOffTime - CSOnTime + (n - 1) × PageBurstAccessTime) × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) × GPMC_FCLK(15)
n 是页面突发访问编号。
(2) 地址总线/字节使能在周期开始时有效,GPMC_CLK 激活时间可能在周期开始之后延迟 B = ClkActivationTime×GPMC_FCLK(15)
(3) 对于单次读取:C = RdCycleTime × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) × GPMC_FCLK(15)
对于单次写入:C = WrCycleTime × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) × GPMC_FCLK(15)
对于突发读取:C = (RdCycleTime + (n - 1) × PageBurstAccessTime) × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) × GPMC_FCLK(15)
对于突发写入:C = (WrCycleTime + (n - 1) × PageBurstAccessTime) × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) × GPMC_FCLK(15)
n 是页面突发访问编号。
对于单次写入:C = WrCycleTime × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) × GPMC_FCLK(15)
对于突发读取:C = (RdCycleTime + (n - 1) × PageBurstAccessTime) × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) × GPMC_FCLK(15)
对于突发写入:C = (WrCycleTime + (n - 1) × PageBurstAccessTime) × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) × GPMC_FCLK(15)
n 是页面突发访问编号。
(4) 对于单次读取:D = (RdCycleTime - RdAccessTime) × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) × GPMC_FCLK(15)
对单次于写入:D = (WrCycleTime - WrAccessTime) × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) × GPMC_FCLK(15)
对于突发读取:D = (RdCycleTime - RdAccessTime + (n - 1) × PageBurstAccessTime) × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) × GPMC_FCLK(15)
对于突发写入:D = (WrCycleTime - WrAccessTime + (n - 1) × PageBurstAccessTime) × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) × GPMC_FCLK(15)
n 是页面突发访问编号。
对单次于写入:D = (WrCycleTime - WrAccessTime) × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) × GPMC_FCLK(15)
对于突发读取:D = (RdCycleTime - RdAccessTime + (n - 1) × PageBurstAccessTime) × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) × GPMC_FCLK(15)
对于突发写入:D = (WrCycleTime - WrAccessTime + (n - 1) × PageBurstAccessTime) × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) × GPMC_FCLK(15)
n 是页面突发访问编号。
(5) 对于 CSn 下降沿(CS 激活):
对于读取模式下的 CSn 上升沿(CS 停用):
对于写入模式下的 CSn 上升沿(CS 停用):
- 如果 GPMCFCLKDIVIDER = 0:
- F = 0.5 × CSExtraDelay × GPMC_FCLK(15)
- 如果 GPMCFCLKDIVIDER = 1:
- 如果 GPMCFCLKDIVIDER = 2:
对于读取模式下的 CSn 上升沿(CS 停用):
- 如果 GPMCFCLKDIVIDER = 0:
- F = 0.5 × CSExtraDelay × GPMC_FCLK(15)
- 如果 GPMCFCLKDIVIDER = 1:
- 如果 GPMCFCLKDIVIDER = 2:
对于写入模式下的 CSn 上升沿(CS 停用):
- 如果 GPMCFCLKDIVIDER = 0:
- F = 0.5 × CSExtraDelay × GPMC_FCLK(15)
- 如果 GPMCFCLKDIVIDER = 1:
- 如果 GPMCFCLKDIVIDER = 2:
(6) 对于 ADV 下降沿(ADV 激活):
对于读取模式下的 ADV 上升沿(ADV 停用):
对于写入模式下的 ADV 上升沿(ADV 停用):
- 如果 GPMCFCLKDIVIDER = 0:
- G = 0.5 × ADVExtraDelay × GPMC_FCLK(15)
- 如果 GPMCFCLKDIVIDER = 1:
- 如果 GPMCFCLKDIVIDER = 2:
对于读取模式下的 ADV 上升沿(ADV 停用):
- 如果 GPMCFCLKDIVIDER = 0:
- G = 0.5 × ADVExtraDelay × GPMC_FCLK(15)
- 如果 GPMCFCLKDIVIDER = 1:
- 如果 GPMCFCLKDIVIDER = 2:
对于写入模式下的 ADV 上升沿(ADV 停用):
- 如果 GPMCFCLKDIVIDER = 0:
- G = 0.5 × ADVExtraDelay × GPMC_FCLK(15)
- 如果 GPMCFCLKDIVIDER = 1:
- 如果 GPMCFCLKDIVIDER = 2:
(7) 对于 OE 下降沿(OE 激活)和 IO DIR 上升沿(数据总线输入方向):
对于 OE 上升沿(OE 停用):
- 如果 GPMCFCLKDIVIDER = 0:
- H = 0.5 × OEExtraDelay × GPMC_FCLK(15)
- 如果 GPMCFCLKDIVIDER = 1:
- 如果 GPMCFCLKDIVIDER = 2:
对于 OE 上升沿(OE 停用):
- 如果 GPMCFCLKDIVIDER = 0:
- H = 0.5 × OEExtraDelay × GPMC_FCLK(15)
- 如果 GPMCFCLKDIVIDER = 1:
- 如果 GPMCFCLKDIVIDER = 2:
(8) 对于 WE 下降沿(WE 激活):
对于 WE 上升沿(WE 停用):
- 如果 GPMCFCLKDIVIDER = 0:
- I = 0.5 × WEExtraDelay × GPMC_FCLK(15)
- 如果 GPMCFCLKDIVIDER = 1:
- 如果 GPMCFCLKDIVIDER = 2:
对于 WE 上升沿(WE 停用):
- 如果 GPMCFCLKDIVIDER = 0:
- I = 0.5 × WEExtraDelay × GPMC_FCLK(13)
- 如果 GPMCFCLKDIVIDER = 1:
- 如果 GPMCFCLKDIVIDER = 2:
(9) 如果使用 CLK DIV 1 模式,仅限第一次传输:数据和字节使能信号在 GPMC_CLK 上升沿转换
- 非多路复用模式:数据在周期开始时转换
- 多路复用模式:数据在 WRDATAONADMUXBUS × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) × GPMC_FCLK 处转换(15)
(10) CLK DIV 1 模式情况,初始传输后的所有数据信号和字节使能信号:数据和字节使能信号在 GPMC_CLK 的下降沿(GPMC_CLK 的半个周期)转换
(11) 非 CLK DIV 1 模式的情况(GPMC_CLK 从 GPMC_FCLK 进行分频):所有数据与字节使能信号均在 GPMC_CLK 的下降沿(GPMC_CLK 的半个周期)转换。必须配置 ClkActivationTime、GPMCFCLKDIVIDER、RDACCESSTIME/WRACCESSTIME 和 PAGEBURSTACCESSTIME 配置,以在 GPMC_CLK 的下降沿强制执行数据和字节使能信号转换(以便在 GPMC_CLK 上升沿锁存)
(12) 在 GPMC_CSn[i] 中,i 等于 0、1、2 或 3。
(13) P = 以 ns 为单位的 GPMC_CLK 周期
(14) 对于读取:K = (ADVRdOffTime - ADVOnTime) × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) × GPMC_FCLK(15)
对于写入:K = (ADVWrOffTime - ADVOnTime) × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) × GPMC_FCLK(15)
对于写入:K = (ADVWrOffTime - ADVOnTime) × (TimeParaGranularity + 1) × GPMC_FCLK(15)
(15) GPMC_FCLK 是通用存储器控制器内部功能时钟周期(以 ns 为单位)。
(16) 与 GPMC_CLK 输出时钟相关的最大和最小频率可在 GPMC 模块中通过设置 GPMC_CONFIG1_i 配置寄存器位字段 GPMCFCLKDIVIDER 进行编程。
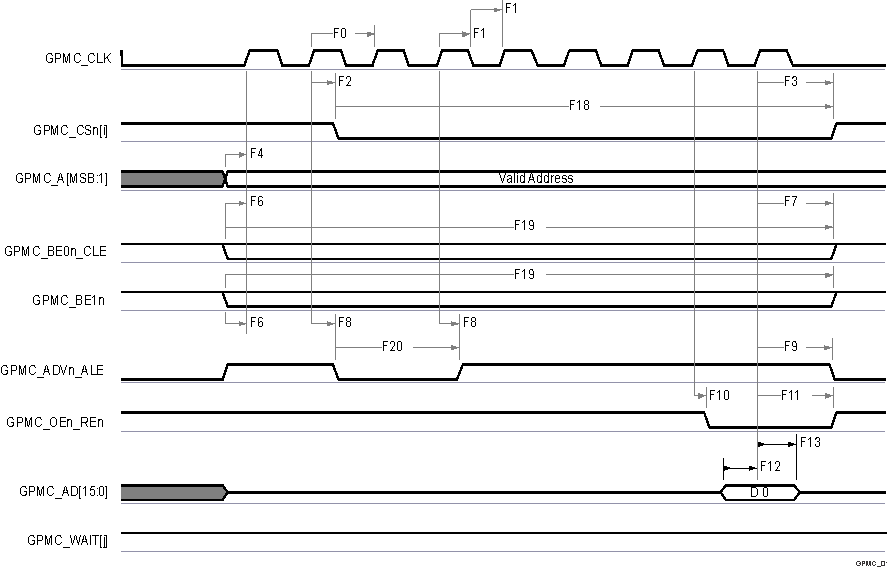
A. 在 GPMC_CSn[i] 中,i 等于 0、1、2 或 3。
B. 在 GPMC_WAIT[j] 中,j 等于 0 或 1。
图 6-46 GPMC 和 NOR 闪存 - 同步单次读取 (GPMCFCLKDIVIDER = 0)
A. 在 GPMC_CSn[i] 中,i 等于 0、1、2 或 3。
B. 在 GPMC_WAIT[j] 中,j 等于 0 或 1。
图 6-47 GPMC 和 NOR 闪存 - 同步突发读取 - 4x16 位 (GPMCFCLKDIVIDER = 0)
A. 在 GPMC_CSn[i] 中,i 等于 0、1、2 或 3。
B. 在 GPMC_WAIT[j] 中,j 等于 0 或 1。
图 6-48 GPMC 和 NOR 闪存 - 同步突发写入 (GPMCFCLKDIVIDER = 0)
A. 在 GPMC_CSn[i] 中,i 等于 0、1、2 或 3。
B. 在 GPMC_WAIT[j] 中,j 等于 0 或 1。
图 6-49 GPMC 和多路复用 NOR 闪存 - 同步突发读取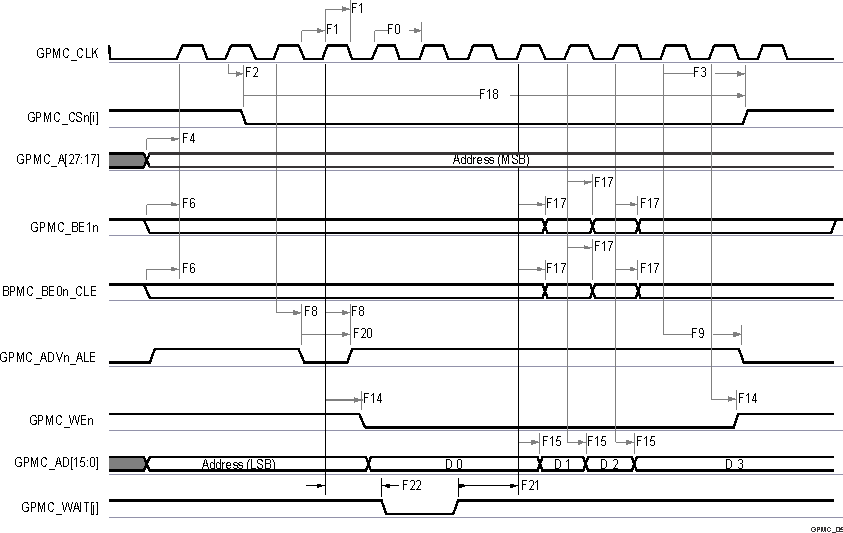
A. 在 GPMC_CSn[i] 中,i 等于 0、1、2 或 3。
B. 在 GPMC_WAIT[j] 中,j 等于 0 或 1。
图 6-50 GPMC 和多路复用 NOR 闪存 - 同步突发写入