ZHCSAB9E September 2012 – June 2019 DP83848-EP
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 器件概述
- 2 修订历史记录
- 3 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
4 Specifications
- 4.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 4.2 ESD Ratings
- 4.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 4.4 Thermal Information
- 4.5 DC Specifications
- 4.6
AC Specifications
- 4.6.1 Power Up Timing
- 4.6.2 Reset Timing
- 4.6.3 MII Serial Management Timing
- 4.6.4 100-Mbps MII Transmit Timing
- 4.6.5 100-Mbps MII Receive Timing
- 4.6.6 100BASE-TX Transmit Packet Latency Timing
- 4.6.7 100BASE-TX Transmit Packet Deassertion Timing
- 4.6.8 100BASE-TX Transmit Timing (tR/F and Jitter)
- 4.6.9 100BASE-TX Receive Packet Latency Timing
- 4.6.10 100BASE-TX Receive Packet Deassertion Timing
- 4.6.11 10-Mbps MII Transmit Timing
- 4.6.12 10-Mbps MII Receive Timing
- 4.6.13 10-Mbps Serial Mode Transmit Timing
- 4.6.14 10-Mbps Serial Mode Receive Timing
- 4.6.15 10BASE-T Transmit Timing (Start of Packet)
- 4.6.16 10BASE-T Transmit Timing (End of Packet)
- 4.6.17 10BASE-T Receive Timing (Start of Packet)
- 4.6.18 10BASE-T Receive Timing (End of Packet)
- 4.6.19 10-Mbps Heartbeat Timing
- 4.6.20 10-Mbps Jabber Timing
- 4.6.21 10BASE-T Normal Link Pulse Timing
- 4.6.22 Auto-Negotiation Fast Link Pulse (FLP) Timing
- 4.6.23 100BASE-TX Signal Detect Timing
- 4.6.24 100-Mbps Internal Loopback Timing
- 4.6.25 10-Mbps Internal Loopback Timing
- 4.6.26 RMII Transmit Timing
- 4.6.27 RMII Receive Timing
- 4.6.28 Isolation Timing
- 4.6.29 25MHz_OUT Timing
-
5 Detailed Description
- 5.1 Overview
- 5.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 5.3 Feature Description
- 5.4 Device Functional Modes
- 5.5
Programming
- 5.5.1
Architecture
- 5.5.1.1 100BASE-TX Transmitter
- 5.5.1.2
100BASE-TX Receiver
- 5.5.1.2.1 Analog Front End
- 5.5.1.2.2 Digital Signal Processor
- 5.5.1.2.3 Signal Detect
- 5.5.1.2.4 MLT-3 to NRZI Decoder
- 5.5.1.2.5 NRZI to NRZ
- 5.5.1.2.6 Serial to Parallel
- 5.5.1.2.7 Descrambler
- 5.5.1.2.8 Code-group Alignment
- 5.5.1.2.9 4B/5B Decoder
- 5.5.1.2.10 100BASE-TX Link Integrity Monitor
- 5.5.1.2.11 Bad SSD Detection
- 5.5.1.3
10BASE-T Transceiver Module
- 5.5.1.3.1 Operational Modes
- 5.5.1.3.2 Smart Squelch
- 5.5.1.3.3 Collision Detection and SQE
- 5.5.1.3.4 Carrier Sense
- 5.5.1.3.5 Normal Link Pulse Detection and Generation
- 5.5.1.3.6 Jabber Function
- 5.5.1.3.7 Automatic Link Polarity Detection and Correction
- 5.5.1.3.8 Transmit and Receive Filtering
- 5.5.1.3.9 Transmitter
- 5.5.1.3.10 Receiver
- 5.5.1
Architecture
- 5.6
Memory
- 5.6.1
Register Definition
- 5.6.1.1 Basic Mode Control Register (BMCR)
- 5.6.1.2 Basic Mode Status Register (BMSR)
- 5.6.1.3 PHY Identifier Register #1 (PHYIDR1)
- 5.6.1.4 PHY Identifier Register #2 (PHYIDR2)
- 5.6.1.5 Auto-Negotiation Advertisement Register (ANAR)
- 5.6.1.6 Auto-Negotiation Link Partner Ability Register (ANLPAR) (BASE Page)
- 5.6.1.7 Auto-Negotiation Link Partner Ability Register (ANLPAR) (Next Page)
- 5.6.1.8 Auto-Negotiate Expansion Register (ANER)
- 5.6.1.9 Auto-Negotiation Next Page Transmit Register (ANNPTR)
- 5.6.2
Extended Registers
- 5.6.2.1 PHY Status Register (PHYSTS)
- 5.6.2.2 MII Interrupt Control Register (MICR)
- 5.6.2.3 MII Interrupt Status and Miscellaneous Control Register (MISR)
- 5.6.2.4 False Carrier Sense Counter Register (FCSCR)
- 5.6.2.5 Receiver Error Counter Register (RECR)
- 5.6.2.6 100 Mbps PCS Configuration and Status Register (PCSR)
- 5.6.2.7 RMII and Bypass Register (RBR)
- 5.6.2.8 LED Direct Control Register (LEDCR)
- 5.6.2.9 PHY Control Register (PHYCR)
- 5.6.2.10 10Base-T Status/Control Register (10BTSCR)
- 5.6.2.11 CD Test and BIST Extensions Register (CDCTRL1)
- 5.6.2.12 Energy Detect Control (EDCR)
- 5.6.1
Register Definition
- 6 Application and Implementation
- 7 Power Supply Recommendations
- 8 Layout
- 9 器件和文档支持
- 10机械、封装和可订购信息
封装选项
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
订购信息
6.2.1.2 Clock IN (X1) Requirements
The DP83848-EP supports an external CMOS level oscillator source or a crystal resonator device.
Oscillator
If an external clock source is used, X1 should be tied to the clock source and X2 should be left floating.
Specifications for CMOS oscillators: 25 MHz in MII Mode and 50 MHz in RMII Mode are listed in Table 6-1 and Table 6-2.
Crystal
A 25-MHz, parallel, 20-pF load crystal resonator should be used if a crystal source is desired. Figure 6-4 shows a typical connection for a crystal resonator circuit. The load capacitor values will vary with the crystal vendors; check with the vendor for the recommended loads.
The oscillator circuit is designed to drive a parallel resonance AT cut crystal with a minimum drive level of 100 mW and a maximum of 500 µW. If a crystal is specified for a lower drive level, a current limiting resistor should be placed in series between X2 and the crystal.
As a starting point for evaluating an oscillator circuit, if the requirements for the crystal are not known, CL1 and CL2 should be set at 33 pF, and R1 should be set at 0 Ω.
Specification for 25-MHz crystal are listed in Table 6-3.
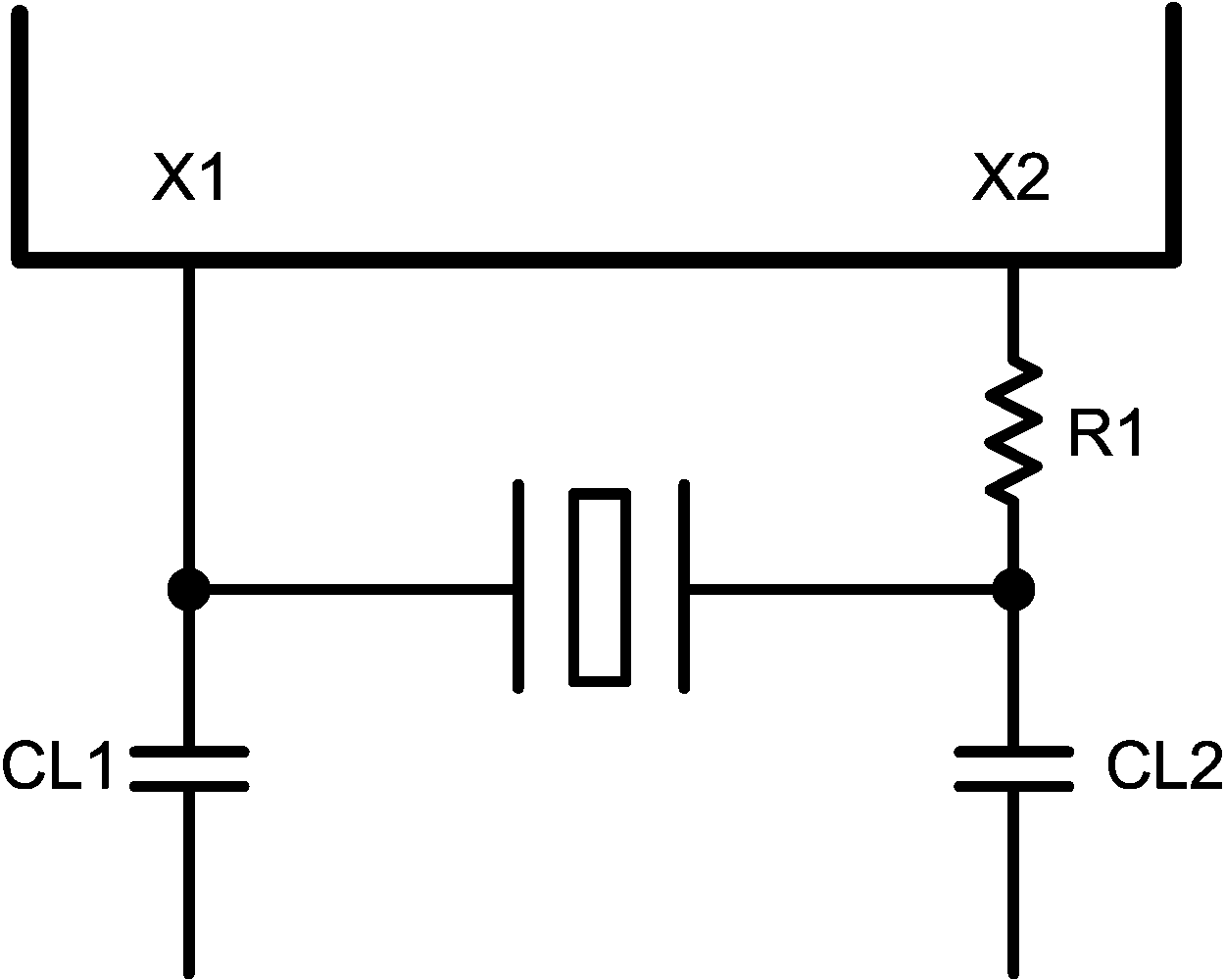 Figure 6-3 Crystal Oscillator Circuit
Figure 6-3 Crystal Oscillator Circuit Table 6-1 25-MHz Oscillator Specification
| PARAMETER | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | CONDITION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency | 25 | MHz | |||
| Frequency Tolerance | ±50 | ppm | Operational Temperature | ||
| Frequency Stability | ±50 | ppm | 1 year aging | ||
| Rise / Fall Time | 6 | nsec | 20% - 80% | ||
| Jitter | 800(1) | psec | Short term | ||
| Jitter | 800(1) | psec | Long term | ||
| Symmetry | 40% | 60% | Duty Cycle |
Table 6-2 50-MHz Oscillator Specification
| PARAMETER | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | CONDITION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency | 50 | MHz | |||
| Frequency Tolerance | ±50 | ppm | Operational Temperature | ||
| Frequency Stability | ±50 | ppm | Operational Temperature | ||
| Rise / Fall Time | 6 | nsec | 20% - 80% | ||
| Jitter | 800(1) | psec | Short term | ||
| Jitter | 800(1) | psec | Long term | ||
| Symmetry | 40% | 60% | Duty Cycle |
Table 6-3 25-MHz Crystal Specification
| PARAMETER | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | CONDITION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency | 25 | MHz | |||
| Frequency Tolerance | ±50 | ppm | Operational Temperature | ||
| Frequency Stability | ±50 | ppm | 1 year aging | ||
| Load Capacitance | 25 | 40 | pF |