ZHCSR80A June 2009 – January 2023 AMC6821-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 说明(续)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.2 Feature Description
- 8.3 Device Functional Modes
- 8.4 Programming
- 8.5 Register Map
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
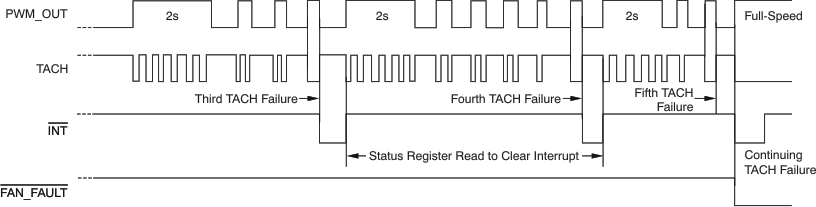
8.2.6 Fan Failure Detection
When the TACH data are larger than the TACH low limit, the fan runs at a speed below the predefined minimum RPM. When this condition occurs, a spin-up process is applied to start the fan again when spin-up is enabled. Bits [STIME2:STIME0] of the Fan Characteristics Register define this time period. Figure 8-9 shows the function of the fan failure detection. Refer to the Fan Spin-Up section.
The fan speed is measured immediately after spin-up; the TACH-FAST bit of Configuration Register 4 determines the monitoring rate. If the fan does not return to a normal range after five consecutive spin-ups, a FAN-FAILURE occurs; the FAN-FAULT pin goes low when it is enabled (the FAN-FAULT-EN bit of Configuration Register 1 is set), and the spin-up process continues. If the fan returns to a normal speed range before the fifth spin-up, the FAN-FAULT pin does not go low even though the FANS bit is still set to '1'. No FANS (fan-slow) detections are performed during spin-up. After the FAN-FAULT pin goes low, spin-up is performed indefinitely until the RPM reading returns to within normal range or the spin-up is disabled.
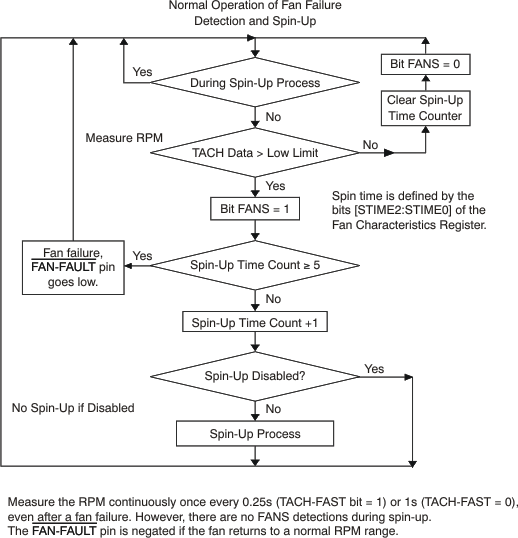 Figure 8-9 Fan Failure Detection and Spin-Up
Figure 8-9 Fan Failure Detection and Spin-UpThe SMBALERT pin continues to generate interrupts after the assertion of the FAN-FAULT pin because the tach measurement continues even after a fan failure. Should the fan recover from the failure condition, the FAN-FAULT pin signal is negated and the fan returns to normal operating speed. Figure 8-10 shows the operation of a FANS interrupt.