TIDUDT4A May 2018 – November 2021 AM3351 , AM3352 , AM3354 , AM3356 , AM3357 , AM3358 , AM3358-EP , AM3359
- Description
- Resources
- Features
- Applications
- 5
- 1System Description
- 2System Overview
- 3Hardware, Software, Testing Requirements, and Test Results
- 4Design Files
- 5Software Files
- 6Related Documentation
- 7About the Author
- 8Revision History
3.2.2.2 Typical Characteristics of DC-DCs
Figure 3-8 shows the efficiency of the 5 voltage rails with 5-V DC supply.
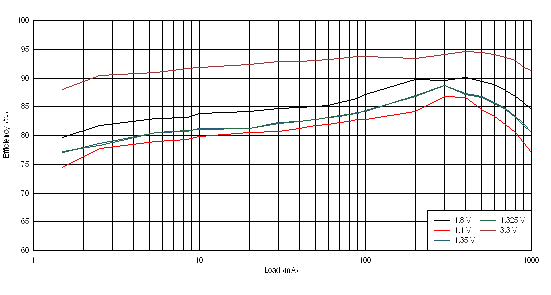 Figure 3-8 Efficiency of 5 Voltage Rails
Figure 3-8 Efficiency of 5 Voltage RailsTo test the efficiency, four multimeters are used: two are set up as voltmeters to measure the input and output voltages, and two are set up as ammeters to measure the input and output currents. In addition, an electronic load is used to achieve different currents.
Table 3-4, Table 3-5, Table 3-6, Table 3-7, and Table 3-8 list the details of the efficiency curves shown in Figure 3-8.
| VIN(V) | IIN(mA) | VOUT(V) | IOUT(V) | η(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.972 | 4.55 | 1.807 | 10.49 | 83.79 |
| 4.949 | 8.52 | 1.806 | 19.67 | 84.25 |
| 4.924 | 12.97 | 1.804 | 29.97 | 84.66 |
| 4.899 | 17.28 | 1.802 | 39.91 | 84.95 |
| 4.876 | 21.38 | 1.802 | 49.23 | 85.10 |
| 4.85 | 25.95 | 1.802 | 59.52 | 85.22 |
| 4.823 | 30.66 | 1.802 | 70.3 | 85.67 |
| 4.798 | 34.91 | 1.801 | 80.13 | 86.16 |
| 4.773 | 39.31 | 1.796 | 90.36 | 86.49 |
| 4.749 | 43.53 | 1.796 | 100.2 | 87.05 |
| 4.491 | 88.58 | 1.789 | 199.55 | 89.74 |
| 4.911 | 121.1 | 1.785 | 298.65 | 89.64 |
| 4.883 | 160.1 | 1.78 | 396 | 90.16 |
| 4.85 | 206.68 | 1.775 | 505.3 | 89.48 |
| 4.822 | 245.64 | 1.77 | 594.23 | 88.80 |
| 4.786 | 295.55 | 1.765 | 703.75 | 87.81 |
| 4.754 | 339.95 | 1.76 | 797.25 | 86.82 |
| 4.718 | 388.68 | 1.756 | 896.17 | 85.82 |
| 4.718 | 440.6 | 1.75 | 1003 | 84.44 |
| VIN(V) | IIN(mA) | VOUT(V) | IOUT(V) | η(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5.02 | 2.74 | 1.0883 | 10.08 | 79.75 |
| 5 | 5.52 | 1.09 | 20.4 | 80.57 |
| 4.988 | 8.22 | 1.09 | 30.37 | 80.74 |
| 4.974 | 10.73 | 1.089 | 39.82 | 81.25 |
| 4.958 | 13.53 | 1.087 | 50.39 | 81.65 |
| 4.942 | 16.23 | 1.086 | 60.54 | 81.97 |
| 4.927 | 18.95 | 1.085 | 70.74 | 82.21 |
| 4.913 | 21.36 | 1.084 | 79.78 | 82.41 |
| 4.896 | 24.24 | 1.083 | 90.64 | 82.71 |
| 4.881 | 26.99 | 1.082 | 100.88 | 82.86 |
| 4.715 | 55.97 | 1.073 | 206.93 | 84.14 |
| 4.574 | 80.63 | 1.0688 | 299.54 | 86.81 |
| 4.395 | 111.8 | 1.064 | 399.9 | 86.59 |
| 4.944 | 126.74 | 1.0595 | 500.17 | 84.57 |
| 4.924 | 154.4 | 1.055 | 600.9 | 83.39 |
| 4.904 | 182.63 | 1.05 | 699.15 | 81.97 |
| 4.881 | 213.6 | 1.046 | 802 | 80.46 |
| 4.858 | 245.66 | 1.04 | 903.47 | 78.73 |
| 4.834 | 278.5 | 1.036 | 1002 | 77.11 |
| VIN(V) | IIN(mA) | VOUT(V) | IOUT(V) | η(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.968 | 7.6 | 3.319 | 10.45 | 91.86 |
| 4.93 | 14.18 | 3.318 | 19.46 | 92.36 |
| 4.885 | 21.9 | 3.317 | 29.94 | 92.83 |
| 4.846 | 28.69 | 3.314 | 38.95 | 92.84 |
| 4.8 | 36.67 | 3.313 | 49.42 | 93.02 |
| 4.753 | 44.79 | 3.31 | 59.91 | 93.15 |
| 4.712 | 51.88 | 3.31 | 68.92 | 93.32 |
| 4.663 | 60.28 | 3.31 | 79.4 | 93.50 |
| 4.613 | 68.85 | 3.31 | 89.88 | 93.67 |
| 4.57 | 76.37 | 3.31 | 98.9 | 93.80 |
| 4.898 | 143.46 | 3.296 | 199.21 | 93.44 |
| 4.84 | 216.12 | 3.2866 | 299.6 | 94.13 |
| 4.78 | 289.16 | 3.2823 | 398.51 | 94.63 |
| 4.715 | 367.1 | 3.2778 | 498.89 | 94.48 |
| 4.643 | 448.84 | 3.2736 | 599.17 | 94.12 |
| 4.565 | 534.06 | 3.2695 | 698.05 | 93.61 |
| 4.472 | 626.51 | 3.2655 | 798.38 | 93.05 |
| 4.276 | 746 | 3.262 | 898.72 | 91.90 |
| 4.18 | 853.2 | 3.2585 | 1000 | 91.37 |
| VIN(V) | IIN(mA) | VOUT(V) | IOUT(V) | η(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.992 | 3.57 | 1.353 | 10.7 | 81.23 |
| 4.974 | 6.66 | 1.356 | 19.85 | 81.25 |
| 4.955 | 10 | 1.3545 | 30.1 | 82.28 |
| 4.935 | 13.51 | 1.3531 | 40.64 | 82.48 |
| 4.917 | 16.59 | 1.352 | 49.97 | 82.82 |
| 4.898 | 20 | 1.3512 | 60.3 | 83.17 |
| 4.879 | 23.21 | 1.351 | 69.8 | 83.27 |
| 4.859 | 26.7 | 1.35 | 80.34 | 83.60 |
| 4.839 | 30.31 | 1.348 | 91.36 | 83.97 |
| 4.823 | 32.97 | 1.347 | 99.46 | 84.25 |
| 4.63 | 66.54 | 1.34 | 200 | 86.99 |
| 4.432 | 101.27 | 1.3344 | 298.44 | 88.73 |
| 4.923 | 122.96 | 1.3296 | 397.66 | 87.35 |
| 4.9 | 155.16 | 1.325 | 498.08 | 86.80 |
| 4.873 | 191.27 | 1.3196 | 605.8 | 85.77 |
| 4.848 | 225.04 | 1.315 | 702.2 | 84.64 |
| 4.823 | 260.34 | 1.31 | 798.94 | 83.35 |
| 4.793 | 300 | 1.305 | 905.32 | 82.16 |
| 4.764 | 340.2 | 1.3 | 1003 | 80.45 |
| VIN(V) | IIN(mA) | VOUT(V) | IOUT(V) | η(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.993 | 3.42 | 1.322 | 10.46 | 80.98 |
| 4.976 | 6.38 | 1.325 | 19.45 | 81.18 |
| 4.956 | 9.73 | 1.323 | 29.94 | 82.14 |
| 4.94 | 12.63 | 1.322 | 38.94 | 82.51 |
| 4.921 | 16 | 1.32 | 49.42 | 82.85 |
| 4.9 | 19.4 | 1.32 | 59.91 | 83.19 |
| 4.88 | 22.81 | 1.3187 | 70.4 | 83.40 |
| 4.865 | 25.72 | 1.318 | 79.4 | 83.63 |
| 4.846 | 29.1 | 1.3165 | 89.87 | 83.90 |
| 4.826 | 32.44 | 1.3146 | 100.4 | 84.31 |
| 4.64 | 64.65 | 1.3075 | 199.2 | 86.82 |
| 4.44 | 99.14 | 1.3027 | 299.59 | 88.66 |
| 4.924 | 120.48 | 1.298 | 398.5 | 87.19 |
| 4.9 | 152 | 1.2933 | 498.9 | 86.63 |
| 4.877 | 184.85 | 1.2886 | 599.2 | 85.65 |
| 4.852 | 218.66 | 1.284 | 698 | 84.48 |
| 4.825 | 254.5 | 1.279 | 798.37 | 83.16 |
| 4.798 | 291.96 | 1.274 | 898.7 | 81.73 |
| 4.769 | 330.6 | 1.2696 | 1000 | 80.53 |
Figure 3-9 shows the output voltage ripple of the 1.8-V rails at 4 different loads.
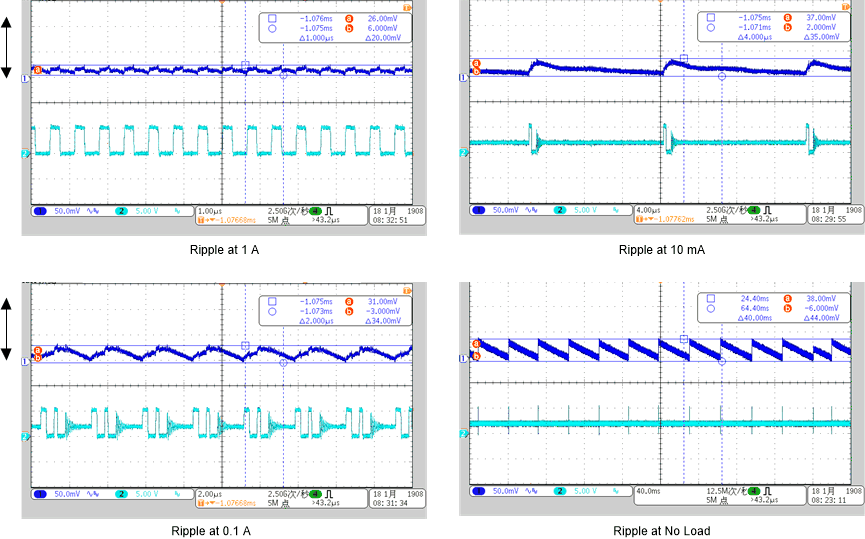 Figure 3-9 Output Voltage Ripple of 1.8 V at 4 Different Output Load
Figure 3-9 Output Voltage Ripple of 1.8 V at 4 Different Output LoadThe output voltage ripple remains below 30 mVpp under a full load (1 A), light load (10 mA), 100mA and no load. This test result has a large margin, comparing the 5% requirement. The device automatically enters PSM to improve efficiency at light load when the inductor current becomes discontinuous. In PSM, the converter reduces switching frequency and minimizes current consumption.
The other power supply rails' ripple are similar to the 1.8-V rail, refer to the TLV62568/9's data sheet for more details.