TIDUDT4A May 2018 – November 2021 AM3351 , AM3352 , AM3354 , AM3356 , AM3357 , AM3358 , AM3358-EP , AM3359
- Description
- Resources
- Features
- Applications
- 5
- 1System Description
- 2System Overview
- 3Hardware, Software, Testing Requirements, and Test Results
- 4Design Files
- 5Software Files
- 6Related Documentation
- 7About the Author
- 8Revision History
3.1.2.2 How to Customize the Processor SDK for This Reference Design
An operating system is necessary in most applications to manage hardware and software resources, while the released kernel carries rich features or low-level drivers that may not fit the user's hardware. For this reference design, run the fit kernel on board by applying a patch to processor SDK. Figure 3-2 shows the instructions used for this process.
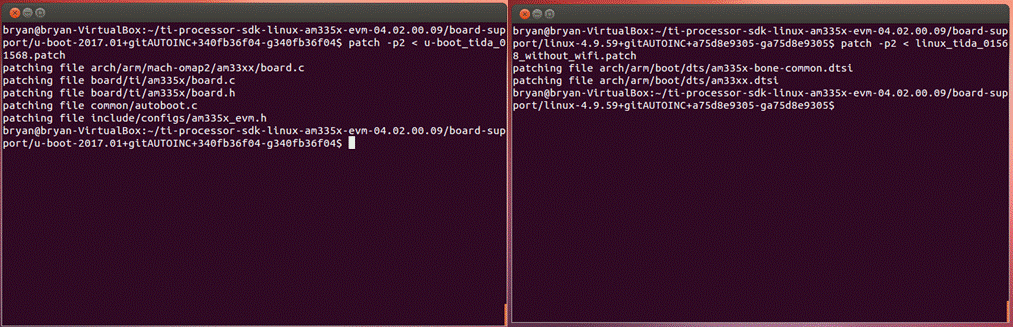 Figure 3-2 How to Apply a Patch to the Processor SDK
Figure 3-2 How to Apply a Patch to the Processor SDKComparing to the AM335x EVM or Beagle Bone family, the differences in hardware are:
- The EEPROM on this board does not contain the information of board ID.
- This board does not support the internal RTC.
- This board does not support the PMIC IC for power management.
The brief principle of modified codes behind the patch files:
- U-Boot: Disable the board detect function and enforce the return value for "am335x-boneblack".
- U-Boot: Disable the I2C communication with PMIC.
- U-Boot: Disable the RTC related function.
- U-Boot: Disable the "BOOTCOUNT_LIMIT" configuration during auto booting.
- Kernel: Remove the RTC node, PMIC node and related codes in device tree (DTS file).
- Kernel: Disable the "RTC Real Time Clocking" configuration.
- Kernel: Add WL1837MOD driver configuration.