TIDUDT4A May 2018 – November 2021 AM3351 , AM3352 , AM3354 , AM3356 , AM3357 , AM3358 , AM3358-EP , AM3359
- Description
- Resources
- Features
- Applications
- 5
- 1System Description
- 2System Overview
- 3Hardware, Software, Testing Requirements, and Test Results
- 4Design Files
- 5Software Files
- 6Related Documentation
- 7About the Author
- 8Revision History
2.3.2 LM3881
The LM3881 Simple Power Sequencer provides a simple solution for sequencing multiple rails in a controlled manner. An established clock signal facilitates control of the power up and power down of three open-drain FET output flags. These flags permit a connection to the shutdown or enable pins of the linear regulators or switching regulators to control the operation of the power supplies. This allows the design of a complete power system without the concern of large inrush currents or latch-up conditions that can occur during an uncontrolled startup. An invert (INV) pin reverses the logic of the output flags. This pin should be tied to a logic output high or low, and not be allowed to remain an open circuit. The following sections assume that the INV pin is held low such that the flag output is active high.
Figure 2-5 shows the functional block diagram of the LM3881.
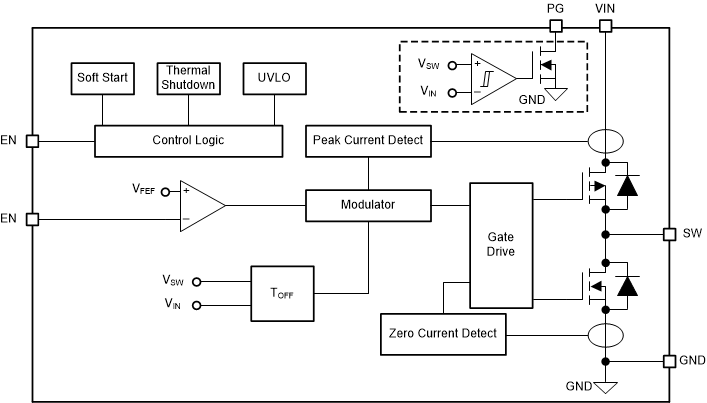 Figure 2-5 LM38881 Functional Block Diagram
Figure 2-5 LM38881 Functional Block DiagramFeatures:
- Easy Method to Sequence Rails
- Power-Up and Power-Down Control
- Tiny Footprint
- Low Quiescent Current of 80 µA
- Input Voltage Range of 2.7 V to 5.5 V
- Output Invert Feature
- Timing Controlled by Small Value External Capacitor