TIDT369A November 2023 – April 2024
2.3.3 Input AC Voltage Sensing
The line and the neutral voltages are sensed by resistor divider to the ground of the board as shown in Figure 2-4. The two readings are subtracted on the controller to get the Vac sensing.
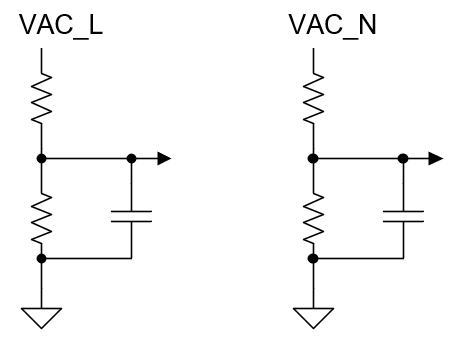 Figure 2-4 Input AC Voltage
Sensing
Figure 2-4 Input AC Voltage
Sensing