TIDT272 April 2022
3.5 Shutdown Sequence
Shutdown behavior is shown in the following figure. An oscilloscope with isolated channels was used.
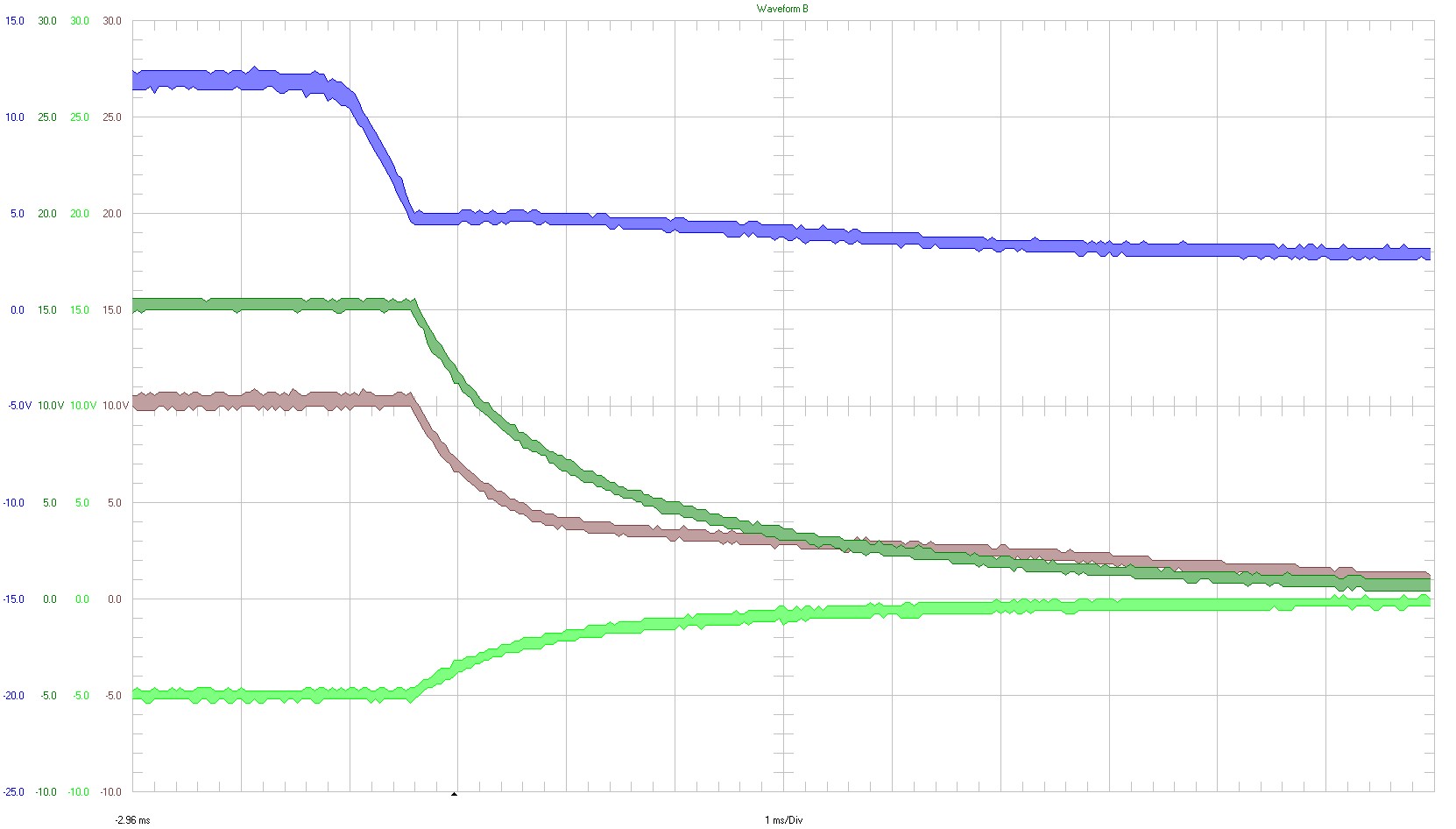
|
5 V / div Ch1 ⇒ Input Ch2 ⇒ +15 Vout (3) Ch3 ⇒ +10 Vout (aux) Ch4 ⇒ -5 Vout (3) 20 MHz bandwidth 1 ms / div |