SWRU271I October 2010 – January 2020 CC2540 , CC2540T , CC2541 , CC2541-Q1 , CC2640R2F
- Preface
- 1Overview
- 2The TI Bluetooth Low Energy Software Development Platform
- 3The Operating System Abstraction Layer (OSAL)
- 4The Application and Profiles
-
5The Bluetooth Low Energy Protocol Stack
- 5.1 Overview
- 5.2 Generic Access Profile (GAP)
- 5.3 GAPRole Task
- 5.4 Gap Bond Manager (GAPBondMgr)
- 5.5
Generic Attribute Profile (GATT)
- 5.5.1 GATT Characteristics and Attributes
- 5.5.2 GATT Services and Profile
- 5.5.3 GATT Client Abstraction
- 5.5.4 GATT Server Abstraction
- 5.6 L2CAP
- 5.7 HCI
- 5.8 Library Files
- 6Drivers
- 7Creating a Custom Bluetooth Low Energy Application
- 8Development and Debugging
-
9General Information
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Porting From BLE-Stack 1.5.0 to 1.5.1
- 9.3 Porting From BLE-Stack 1.4.2 to 1.5.0
- 9.4
Porting From Earlier BLE-Stack Versions
- 9.4.1 Porting BLEv1.4.1 Projects to BLEv1.4.2
- 9.4.2 Porting BLEv1.4.0 Projects to BLEv1.4.1
- 9.4.3 Porting BLEv1.3.2 Projects to BLEv1.4.0
- 9.4.4 Porting BLEv1.2 Projects to BLEv1.3
- 9.4.5 Porting From CC2540 to CC2541 Project
- 9.5 Release Notes History
- 9.6 Document History
- A GAP API
- B GAPRole Peripheral Role API
- C GAPRole Central Role API
- D GATT/ATT API
- E GATTServApp API
- F GAPBondMgr API
- G HCI Extension API
- Revision History
5.2.1.1 Connection Parameters
This section describes the connection parameters sent by the initiating device with the connection request. These parameters can be modified by either device when the connection is established.
These parameters are the following:
- Connection Interval – Bluetooth Low Energy connections use a frequency-hopping scheme. The devices send and receive data on a specific channel at a specific time and meet at a new channel later. The link layer of the Bluetooth Low Energy protocol stack handles the channel switching. This meeting, where the two devices send and receive data, is a connection event. If there is no application data sent or received, the devices exchange link layer data to maintain the connection. The connection interval is the time between two connection events in units of 1.25 ms. The connection interval can range from a minimum value of 6 (7.5 ms) to a maximum of 3200 (4.0 seconds).
- Slave Latency – This parameter lets the slave (peripheral) device skip several connection events. If the device has no data to send, it can skip connection events and deactivate its radio during the connection event, which saves power. The slave latency value represents the maximum number of events that can be skipped. This value ranges from a minimum value of 0 (no connection events)) to a maximum of 499. The maximum value must create an effective connection interval less than 16 seconds. For an overview of this parameter, see Figure 5-3.
- Supervision Time-out – This parameter is the maximum time period between two successful connection events. If this time period passes without a successful connection event, the device considers the connection lost and returns to an unconnected state. This parameter value is represented in units of 10 ms. The supervision time-out value can range from a minimum of 10 (100 ms) to 3200 (32 seconds). The time-out must be larger than the effective connection interval. For more details, see Section 5.2.1.2.
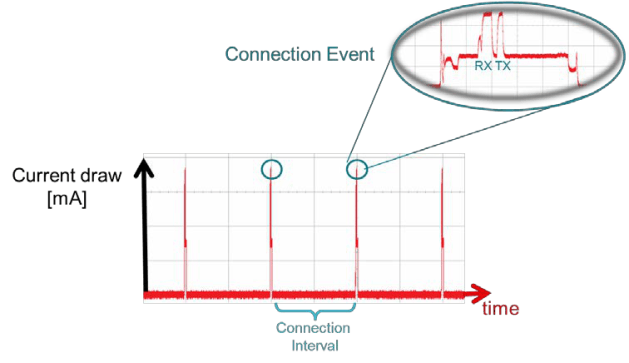 Figure 5-2 Connection Event and Interval
Figure 5-2 Connection Event and Interval Applications may require different connection intervals. This difference affects the power consumption of the device. For more detailed information on power consumption, see the Measuring Power Consumption.
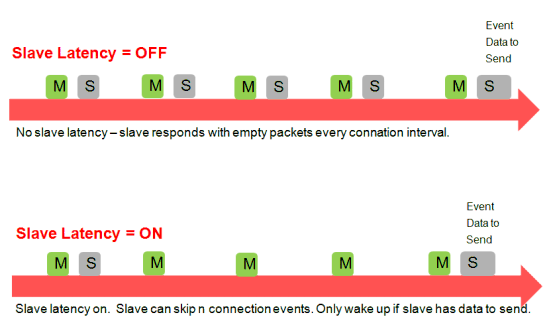 Figure 5-3 Slave Latency
Figure 5-3 Slave Latency