SLUUCO2 August 2022
- Abstract
- Trademarks
- 1 Description
- 2 Electrical Performance Specifications
- 3 Schematic
- 4 Test Setup
- 5 EVM Configuration Using the Fusion GUI
- 6 Test Procedure
- 7 Performance Data and Typical Characteristic Curves
- 8 EVM Assembly Drawing and PCB Layout
- 9 Bill of Materials
- 10Using the Fusion GUI
10.2 General Settings
Figure 10-2 shows the General Settings that can be used to configure the following:
- VOUT settings, power-good limits, and margin voltages
- OC fault, OC warn, and fault response
- OT fault, OT warn (die temperature), and fault response
- VIN on and off UVLO
- On and off configurations
- Soft start (output rise time), other turn-on timing and turn-off timing
- Switching frequency
- Compensation
After clicking Write to Hardware to make changes to one or more configurable parameters, the changes can be committed to nonvolatile memory by clicking Store Config to NVM. This action prompts a pop-up, and if confirmed, the changes are committed to nonvolatile memory to store all the modifications in nonvolatile memory.
Both the loop controller device and the loop follower device are tied to same bus interface. In a two-phase stacking system, the loop controller device receives and responds to all PMBus communication and loop follower devices do not need to be connected to the PMBus. If the controller receives commands that require updates to the PMBus registers of the follower, the controller relays these commands to the followers. All commands on this tab are for PHASE = 0xFF.
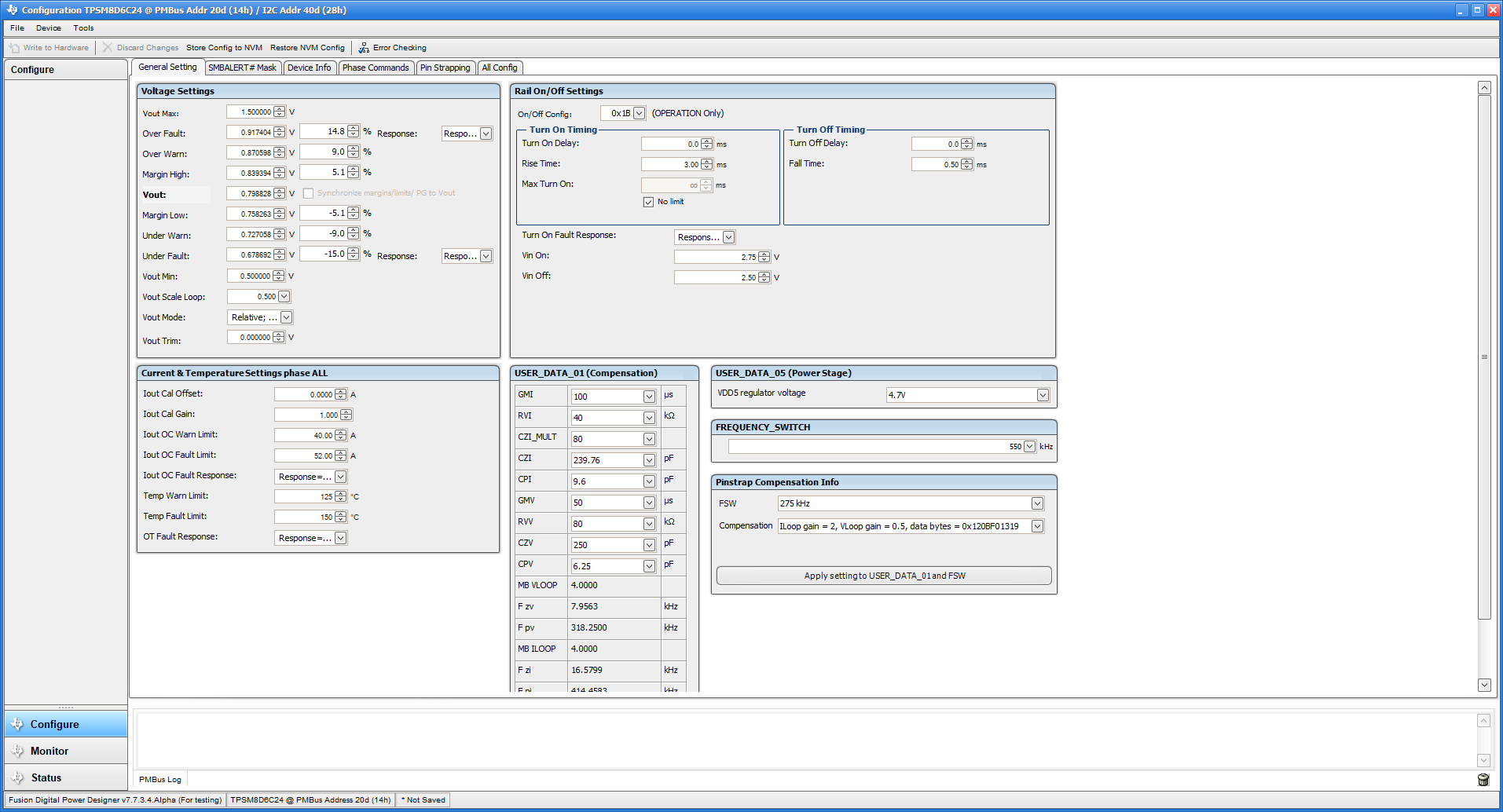 Figure 10-2 General
Settings
Figure 10-2 General
Settings