SLUAAG7 October 2021 BQ25720
- Trademarks
- 1Introduction
-
2Design Considerations for Notebook
Applications
- 2.1 Vmin Active Protection (VAP)
- 2.2 Fast Role Swap (FRS)
- 2.3 Processor Hot Indication
- 2.4 Two-Level Battery Discharge Current Limit
- 2.5 Pass Through Mode (PTM) Operation
- 2.6 Seamless Mode Transition
- 2.7 Current and Power Monitor
- 2.8 Input Source Dynamic Power Management
- 2.9 Power Up USB Port From Battery (USB OTG)
- 3Test Results
- 4Summary
- 5References
2.1 Vmin Active Protection (VAP)
The BQ25720 integrates latest the Intel Vmin Active Protection (VAP) feature which the device charges up the VBUS voltage from the battery to store some energy in the input decoupling capacitors and releases it to the system during a system peak power demand. The high system peak power can cause the VSYS to drop below the minimum system voltage due to impedance from the battery to the system, and then limits the power that can be drawn without crashing the system.
When only the battery powers the system and no external load is connected to the USB OTG port, the charger can be configured to store energy in the input capacitors by charging them up to a programmable voltage level. This VAP supplements the system during periods of high demand to improve system turbo performance that is strongly recommended by Intel.
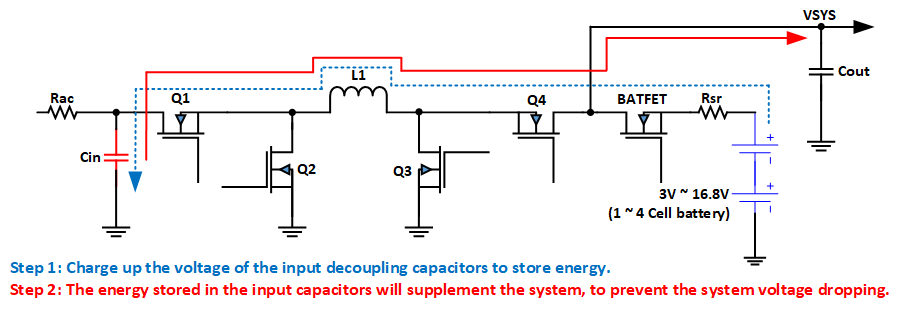 Figure 2-1 Energy Flow in Supplement Mode
Figure 2-1 Energy Flow in Supplement Mode