SLOA101B August 2002 – May 2016 SN55HVD233-SEP , SN65HVDA1040A-Q1 , SN65HVDA1050A-Q1 , SN65HVDA540-5-Q1 , SN65HVDA540-Q1 , SN65HVDA541-5-Q1 , SN65HVDA541-Q1 , SN65HVDA542-5-Q1 , SN65HVDA542-Q1
-
Introduction to the Controller Area Network (CAN)
- Trademarks
- 1 Introduction
- 2 The CAN Standard
- 3 Standard CAN or Extended CAN
- 4 A CAN Message
- 5
The CAN Bus
- 5.1
CAN Transceiver Features
- 5.1.1 3.3-V Supply Voltage
- 5.1.2 ESD Protection
- 5.1.3 Common-Mode Voltage Operating Range
- 5.1.4 Common-Mode Noise Rejection
- 5.1.5 Controlled Driver Output Transition Times
- 5.1.6 Low-Current Bus Monitor, Standby and Sleep Modes
- 5.1.7 Bus Pin Short-Circuit Protection
- 5.1.8 Thermal Shutdown Protection
- 5.1.9 Bus Input Impedance
- 5.1.10 Glitch-Free Power Up and Power Down
- 5.1.11 Unpowered Node Protection
- 5.1.12 Reference Voltage
- 5.1.13 V-Split
- 5.1.14 Loopback
- 5.1.15 Autobaud Loopback
- 5.2 CAN Transceiver Selection Guide
- 5.1
CAN Transceiver Features
- 6 Conclusion
- 7 Additional Reading
- Revision History
5.1.13 V-Split
V-split is a fortified Vcc/2 Vref pin with the same ESD protection rating, short-circuit protection, and common-mode operating range as the bus pins. It is used to stabilize bus voltage at Vcc/2 and prevent it from drifting to a high common-mode voltage during periods of inactivity.
It also filters unwanted high-frequency noise from bus lines with the termination technique of Figure 12. This is accomplished with a coupling capacitor between two ~60 Ω ±1% termination resistors to couple high-frequency noise to a solid ground potential. Care must be taken to match the two resistors carefully so as not to reduce the effective immunity. This technique improves the electromagnetic compatibility of a network. A typical value of CL for a high-speed CAN is 4.7 nF, which generates a 3-dB point at 1.1 Mbps. This, of course, is a signaling-rate-dependant value.
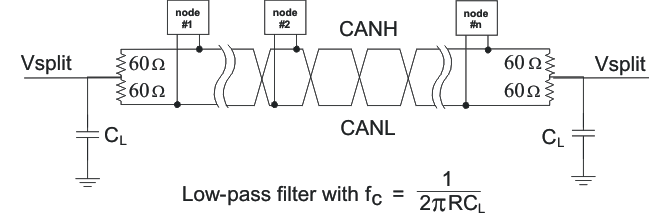 Figure 12. Split Termination
Figure 12. Split Termination