SLAU646F September 2015 – June 2020
- Read This First
- 1Introduction
- 2Installing MSP430 GCC Toolchain
-
3Using MSP430 GCC Within CCS
- 3.1 Create New Project
- 3.2 Debug Using MSP-FET, MSPFET430UIF, eZ-FET, eZ430
- 3.3
Build Options for MSP430 GCC
- 3.3.1 GNU Compiler
- 3.3.2 GNU Compiler: Runtime
- 3.3.3 GNU Compiler: Symbols
- 3.3.4 GNU Compiler: Directories
- 3.3.5 GNU Compiler: Optimization
- 3.3.6 GNU Compiler: Preprocessor
- 3.3.7 GNU Compiler: Assembler
- 3.3.8 GNU Compiler: Debugging
- 3.3.9 GNU Compiler: Diagnostic Options
- 3.3.10 GNU Compiler: Miscellaneous
- 3.3.11 GNU Linker
- 3.3.12 GNU Linker: Basic
- 3.3.13 GNU Linker: Libraries
- 3.3.14 GNU Linker: Symbols
- 3.3.15 GNU Linker: Miscellaneous
- 3.3.16 GNU Objcopy Utility
- 3.4 CCS Compared to MSP430 GCC
-
4MSP430 GCC Stand-Alone Package
- 4.1 MSP430 GCC Stand-Alone Package Folder Structure
- 4.2 Package Content
- 4.3 MSP430 GCC Options
- 4.4 MSP430 Built-in Functions
- 4.5 Using MSP430 GCC Support Files
- 4.6 Quick Start: Blink the LED
- 4.7 GDB Settings
- 5MSP430 GCC Features
- 6Building MSP430 GCC From Sources
- 7MSP430 GCC and MSPGCC
- 8Appendix
- 9References
- Revision History
3.3.16 GNU Objcopy Utility
Figure 3-18 shows the MSP430 GCC GNU Objcopy Utility settings window.
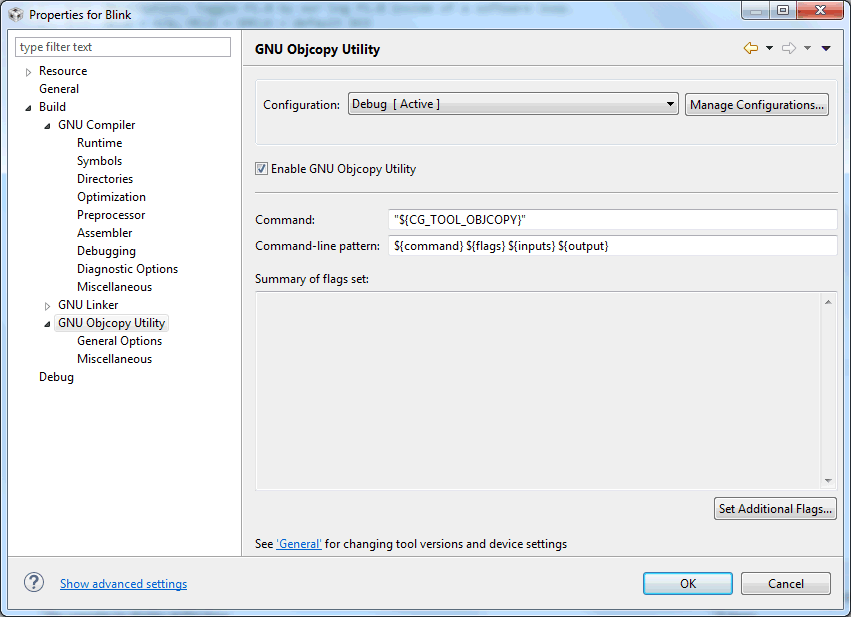 Figure 3-18 MSP430 GCC GNU Objcopy Utility Settings
Figure 3-18 MSP430 GCC GNU Objcopy Utility SettingsTable 3-16 describes the options that are available for GNU Objcopy Utility.
Table 3-16 MSP430 GCC GNU Objcopy Utility Settings
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Enable GNU Objcopy Utility | Enable this option to enable the GNU Objcopy Utility. It is disabled by default. |
| Command | GNU Objcopy location |
| Command-line pattern | Command line parameters |
| Summary of flags set | Command line with which the GNU Objcopy is called. Displays all the flags passed to the Objcopy command. |
Figure 3-19 shows the MSP430 GCC GNU Objcopy Utility General Options settings window.
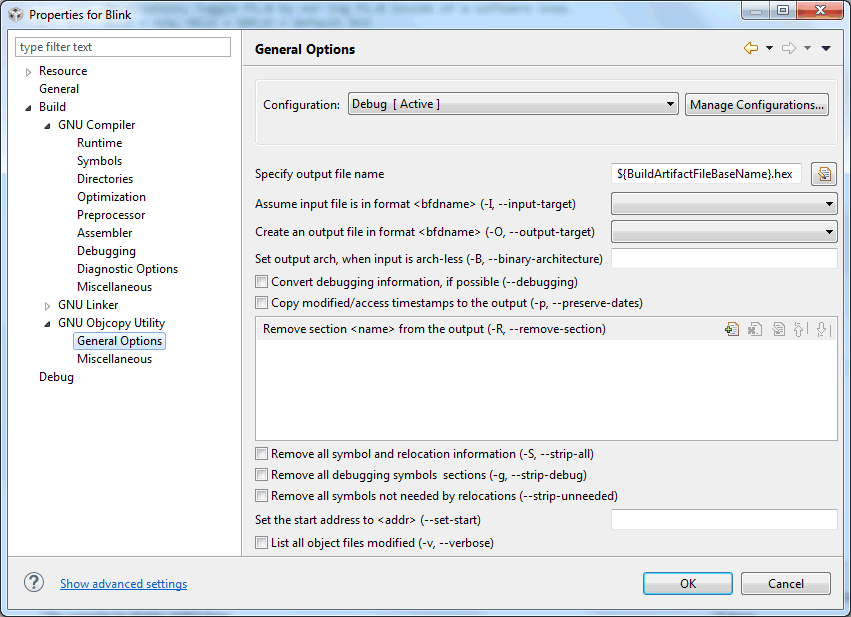 Figure 3-19 MSP430 GCC GNU Objcopy Utility General Options Settings
Figure 3-19 MSP430 GCC GNU Objcopy Utility General Options SettingsTable 3-17 describes the options that are available for GNU Objcopy Utility General Options.
Table 3-17 MSP430 GCC GNU Objcopy Utility General Options Settings
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Specify output file name | Specifies the output file name |
| Assume input file is in format
<bfdname> -I bfdname --input-target=bfdname | Consider the source file's object format to be bfdname, rather than attempting to deduce it. |
| Create an output file in
format <bfdname> -O bfdname --output-target=bfdname | Write the output file using the object format bfdname. |
| Set output arch when input is
arch-less -B bfdarch --binary-architecture=bfdarch | Useful when transforming an architecture-less input file into an object file. In this case the output architecture can be set to bfdarch. |
| Convert debugging information, if possible (--debugging) | Convert debugging information, if possible. This is not the default because only certain debugging formats are supported, and the conversion process can be time consuming. |
| Copy modified/access timestamps to the output (-p, --preserve-dates) | Set the access and modification dates of the output file to be the same as those of the input file. |
| Remove section <name>
from the output -R sectionpattern --remove-section=sectionpattern | Remove any section matching sectionpattern from the output file. This option may be given more than once. Note that using this option inappropriately may make the output file unusable. Wildcard characters are accepted in sectionpattern. Using the -j and -R options together results in undefined behavior. |
| Remove all symbol and relocation information (-S, --strip-all) | Do not copy relocation and symbol information from the source file. |
| Remove all debugging symbols sections (-g, --strip-debug) | Do not copy debugging symbols or sections from the source file. |
| Remove all symbols not needed by relocations (--strip-unneeded) | Strip all symbols that are not needed for relocation processing. |
| Set the start address to <addr> (--set-start) | Set the start address of the new file to the specified value. Not all object file formats support setting the start address. |
| List all object files modified (-v, --verbose) | Verbose output: list all object files modified. In the case of archives, 'objcopy -V' lists all members of the archive. |
Figure 3-20 shows the MSP430 GCC GNU Objcopy Utility Miscellaneous settings window.
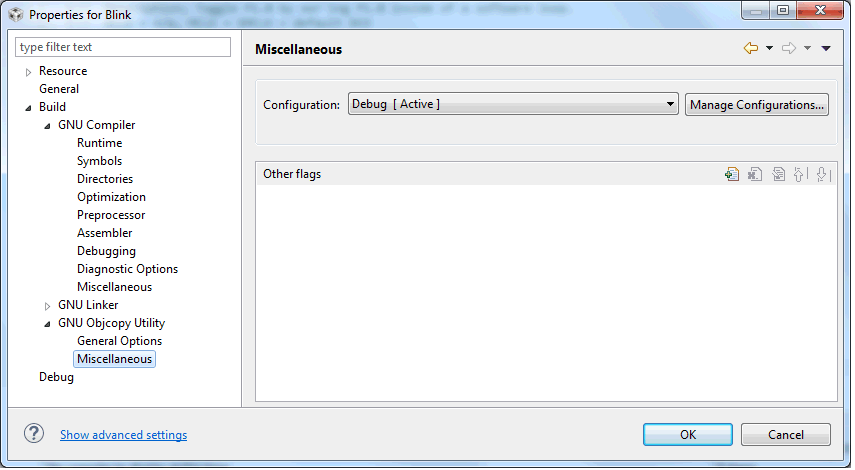 Figure 3-20 MSP430 GCC GNU Objcopy Utility Miscellaneous Settings
Figure 3-20 MSP430 GCC GNU Objcopy Utility Miscellaneous SettingsTable 3-18 describes the options that are available for GNU Objcopy Utility Miscellaneous.
Table 3-18 MSP430 GCC GNU Objcopy Utility Miscellaneous Settings
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Other flags | Specifies individual flags based on the user requirements. |