SLAU646F September 2015 – June 2020
- Read This First
- 1Introduction
- 2Installing MSP430 GCC Toolchain
-
3Using MSP430 GCC Within CCS
- 3.1 Create New Project
- 3.2 Debug Using MSP-FET, MSPFET430UIF, eZ-FET, eZ430
- 3.3
Build Options for MSP430 GCC
- 3.3.1 GNU Compiler
- 3.3.2 GNU Compiler: Runtime
- 3.3.3 GNU Compiler: Symbols
- 3.3.4 GNU Compiler: Directories
- 3.3.5 GNU Compiler: Optimization
- 3.3.6 GNU Compiler: Preprocessor
- 3.3.7 GNU Compiler: Assembler
- 3.3.8 GNU Compiler: Debugging
- 3.3.9 GNU Compiler: Diagnostic Options
- 3.3.10 GNU Compiler: Miscellaneous
- 3.3.11 GNU Linker
- 3.3.12 GNU Linker: Basic
- 3.3.13 GNU Linker: Libraries
- 3.3.14 GNU Linker: Symbols
- 3.3.15 GNU Linker: Miscellaneous
- 3.3.16 GNU Objcopy Utility
- 3.4 CCS Compared to MSP430 GCC
-
4MSP430 GCC Stand-Alone Package
- 4.1 MSP430 GCC Stand-Alone Package Folder Structure
- 4.2 Package Content
- 4.3 MSP430 GCC Options
- 4.4 MSP430 Built-in Functions
- 4.5 Using MSP430 GCC Support Files
- 4.6 Quick Start: Blink the LED
- 4.7 GDB Settings
- 5MSP430 GCC Features
- 6Building MSP430 GCC From Sources
- 7MSP430 GCC and MSPGCC
- 8Appendix
- 9References
- Revision History
3.3.12 GNU Linker: Basic
Figure 3-14 shows the MSP430 GCC Linker Basic settings window.
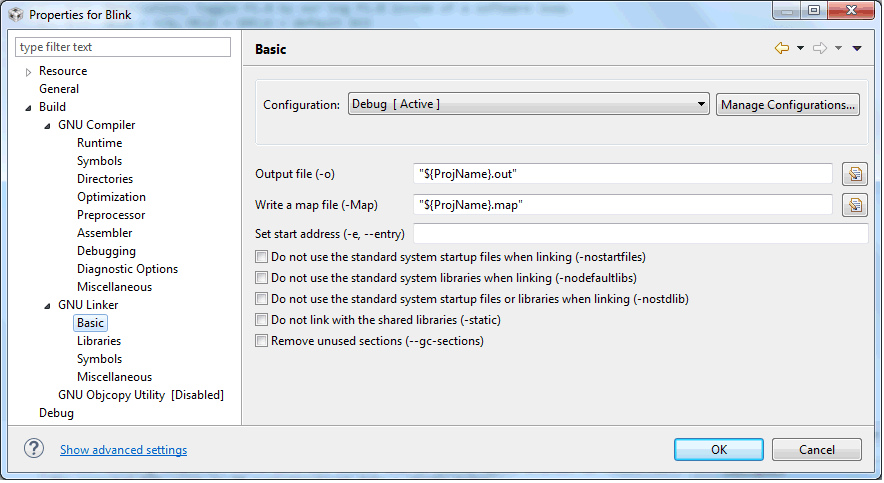 Figure 3-14 MSP430 GCC Linker Basic Settings
Figure 3-14 MSP430 GCC Linker Basic SettingsTable 3-12 describes the options that are available for MSP430 GCC Linker Basic settings.
Table 3-12 MSP430 GCC Linker Basic Settings
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Output file (-o) | Use output as the name for the file produced by ld; if this option is not specified, the name 'a.out' is used by default. The script command OUTPUT can also specify the output file name. |
| Write a map file (-Map) | Print to the file mapfile a link map, which contains diagnostic information about where symbols are mapped by Id and information on global common storage allocation. |
| Set start address (-e, --entry) | Use entry as the explicit symbol for beginning program execution, rather than the default entry point. |
| Do not use the
standard system startup files when linking (-nostartfiles) |
Do not use the standard system startup files when linking. The standard system libraries are used unless -nostdlib or -nodefaultlibs is used. |
| Do not use the
standard system libraries when linking (-nodefaultlibs) |
Do not use the standard system libraries when linking. Only the specified libraries are passed to the linker, and options specifying linkage of the system libraries, such as ‑static‑libgcc or ‑shared‑libgcc, are ignored. The standard startup files are used unless -nostartfiles is used. The compiler may generate calls to memcmp, memset, memcpy, and memmove. These entries are usually resolved by entries in libc. These entry points should be supplied through some other mechanism when this option is specified. |
| Do not use the standard system startup files or libraries when linking (-nostdlib) | Do not use the standard system startup files or libraries when linking. |
| Do not link with the shared libraries (-static) | On systems that support dynamic linking, this prevents linking with the shared libraries. On other systems, this option has no effect. |
| Remove unused
sections (--gc-sections) |
Enable garbage collection of unused input sections. Ignored on targets that do not support this option. |