SLAA457B September 2013 – October 2018 MSP430F5500 , MSP430F5501 , MSP430F5502 , MSP430F5503 , MSP430F5504 , MSP430F5505 , MSP430F5506 , MSP430F5507 , MSP430F5508 , MSP430F5509 , MSP430F5510 , MSP430F5513 , MSP430F5514 , MSP430F5515 , MSP430F5517 , MSP430F5519 , MSP430F5521 , MSP430F5522 , MSP430F5524 , MSP430F5525 , MSP430F5526 , MSP430F5527 , MSP430F5528 , MSP430F5529 , MSP430F5630 , MSP430F5631 , MSP430F5632 , MSP430F5633 , MSP430F5634 , MSP430F5635 , MSP430F5636 , MSP430F5637 , MSP430F5638 , MSP430F5658 , MSP430F5659 , MSP430F6630 , MSP430F6631 , MSP430F6632 , MSP430F6633 , MSP430F6634 , MSP430F6635 , MSP430F6636 , MSP430F6637 , MSP430F6638 , MSP430F6658 , MSP430F6659 , MSP430FG6425 , MSP430FG6426 , MSP430FG6625 , MSP430FG6626
6.2 F5529 LaunchPad™ Development Kit
The MSP-EXP430F5529LP LaunchPad Development Kit is an inexpensive evaluation module for the MSP430F5529 USB microcontroller. It is an easy way to start developing on the MSP430 MCU, having on-board emulation for programming and debugging, as well as buttons and LEDs for simple user interface.
Rapid prototyping is simple, thanks to 40-pin expansion headers on the LaunchPad development kit that connect to a wide range of available BoosterPack™ plug-in modules. You can quickly add features like wireless, displays, sensors, and much more. You can either design your own BoosterPack plug-in module or choose among many already available from TI and elsewhere. The 40-pin interface is compatible with any 20-pin BoosterPack plug-in module that complies with the standard.
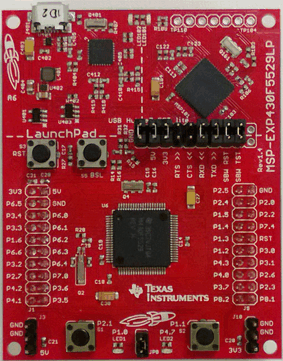 Figure 12. MSP430F5529 LaunchPad Development Kit
Figure 12. MSP430F5529 LaunchPad Development Kit Features of the F5529 LaunchPad development kit include:
- USB-enabled MSP430F5529 16-bit MCU
- Up to 25-MHz system clock; 1.8-V to 3.6-V operation
- 128KB flash; 8KB RAM
- Five timers
- Up to four serial interfaces (SPI, UART, I2C)
- 12-bit analog-to-digital converter
- Analog comparator
- Integrated USB, with a complete set of USB tools, libraries, examples, and reference guides
- Integrated eZ-FET lite emulator, with an application ("backchannel") UART.
- Ability to emulate and develop USB applications with a single USB cable, made possible with an on-board USB hub.
- Power sourced from the USB host. The 5-V bus power is reduced to 3.3 V, using an on-board dc/dc converter.
- Both male and female 40-pin BoosterPack plug-in module headers, configured for stacking. 20-pin BoosterPack plug-in modules can also be attached.
- Compatible with the 40-pin BoosterPack plug-in module standard.