SLAA126B April 2001 – September 2018 MSP430F149 , MSP430F149 , TLC3544 , TLC3544 , TLC3548 , TLC3548
5.1 Initializing the ADC
Initializing the ADC is a relatively straightforward task. After power up, EOC/INT is high and the data registers are set to zero. The user has the option of setting a default hardware mode, or programmed mode. Each mode requires two 16-bit initialization cycles. Data output from the power up initialization phase should be ignored. For the purpose of this application report, the initialization cycle consists of chip select being held low through two 8-bit SCLK cycles.
Hardware mode is defined by the status of the SDI pin. After power up, two consecutive initialization cycles put the device into hardware mode if the SDI pin is tied to DVDD. This loads the ADC’s configuration register with 0x0800h.
To enter the programmed mode, the host processor must write 0xA000h (WRITE CFR + 000h) to the SDI pin during the first initialization cycle, followed by a WRITE CFR + DATA command during the second.
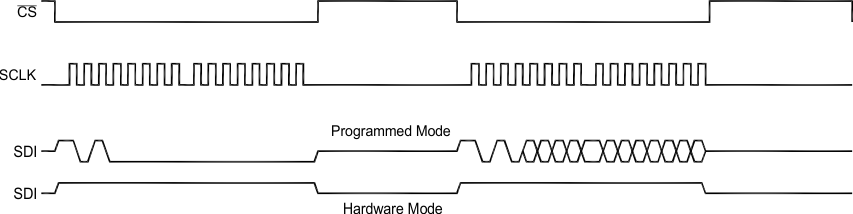 Figure 2. ADC Initialization Cycle
Figure 2. ADC Initialization Cycle