ZHCSPH5C June 2022 – March 2023 UCC28C50 , UCC28C51 , UCC28C52 , UCC28C53 , UCC28C54 , UCC28C55 , UCC28C56H , UCC28C56L , UCC28C57H , UCC28C57L , UCC28C58 , UCC28C59 , UCC38C50 , UCC38C51 , UCC38C52 , UCC38C53 , UCC38C54 , UCC38C55
PRODUCTION DATA
8.3.8 启用和禁用
根据所需的重启类型,可以通过几种方法来启用或禁用 UCC28C5x 器件。这两项基本技术使用外部晶体管将误差放大器输出拉至低电平 (<2VBE) 或将电流检测输入拉至高电平 (>1.1V)。施加禁用信号会导致 PWM 比较器的输出为高电平。PWM 锁存器采用复位优先原则,因此在 COMP 或 CS 引脚上的关断条件解除后,输出会一直保持低电平,直到下一个时钟周期。无软启动周期的另一种重启选择是将电流检测输入拉至高于逐周期电流限制阈值。可以使用从基准电压到电流检测输入的逻辑电平 P 沟道 FET。
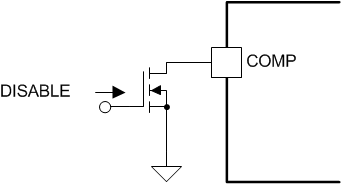 图 8-7 禁用电路
图 8-7 禁用电路