SLUSDW0B May 2020 – May 2020 UCC28065
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (Continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Principles of Operation
- 8.3.2 Natural Interleaving
- 8.3.3 On-Time Control, Maximum Frequency Limiting, Restart Timer and Input Voltage Feed-Forward compensation
- 8.3.4 Zero-Current Detection and Valley Switching
- 8.3.5 Phase Management and Light-Load Operation
- 8.3.6 Burst Mode Operation
- 8.3.7 External Disable
- 8.3.8 Improved Error Amplifier
- 8.3.9 Soft Start
- 8.3.10 Brownout Protection
- 8.3.11 Line Dropout Detection
- 8.3.12 VREF
- 8.3.13 VCC
- 8.3.14
System Level Protections
- 8.3.14.1 Failsafe OVP - Output Over-voltage Protection
- 8.3.14.2 Overcurrent Protection
- 8.3.14.3 Open-Loop Protection
- 8.3.14.4 VCC Undervoltage Lock-Out (UVLO) Protection
- 8.3.14.5 Phase-Fail Protection
- 8.3.14.6 CS - Open, TSET - Open and Short Protection
- 8.3.14.7 Thermal Shutdown Protection
- 8.3.14.8 Fault Logic Diagram
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Application
- 9.2.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.2.1 Inductor Selection
- 9.2.2.2 ZCD Resistor Selection RZA, RZB
- 9.2.2.3 HVSEN
- 9.2.2.4 Output Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.2.5 Selecting RS For Peak Current Limiting
- 9.2.2.6 Power Semiconductor Selection (Q1, Q2, D1, D2)
- 9.2.2.7 Brownout Protection
- 9.2.2.8 Converter Timing
- 9.2.2.9 Programming VOUT
- 9.2.2.10 Voltage Loop Compensation
- 9.2.3 Application Curves
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.3.1 Principles of Operation
The UCC28065 device contains the control circuits for two parallel-connected boost pulse-width modulated (PWM) power converters. The boost PWM power converters ramp current in the boost inductors for a time period proportional to the voltage on the error amplifier output (COMP pin). Each power converter then turns off the power MOSFET until current in the boost inductor decays to zero (as sensed on the zero current detection inputs, ZCD_A and ZCD_B). After the inductor demagnetizes, the power converter starts another cycle. This cycle process produces a triangular waveform of current, with peak current set by the on-time and the instantaneous power mains input voltage, VIN(t) value, as shown in Equation 1.
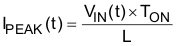
The average line current is exactly equal to half of the peak line current, as shown in Equation 2.
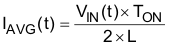
When the tON and L values are essentially constant during an AC-line period, the resulting triangular current waveform during each switching cycle has an average value proportional to the instantaneous value of the rectified AC-line voltage. This architecture results in a resistive input impedance characteristic at the line frequency and a near-unity power factor.