ZHCSHE9J June 2010 – January 2018 TPS7A80
PRODUCTION DATA.
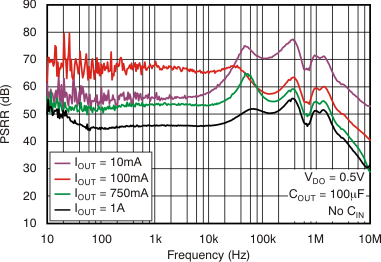
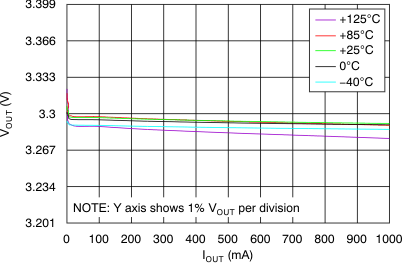
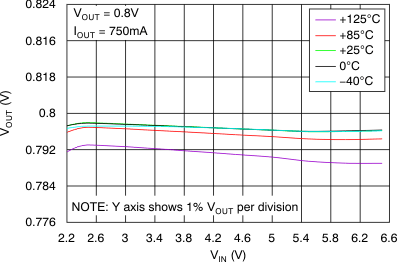
6.6 Typical Characteristics
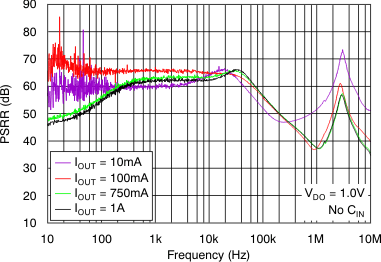
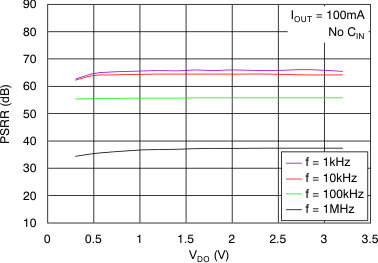
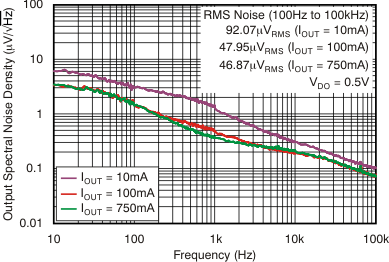
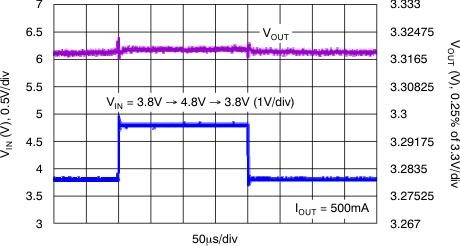
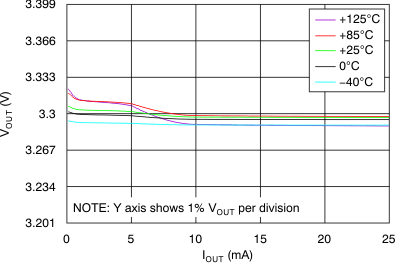
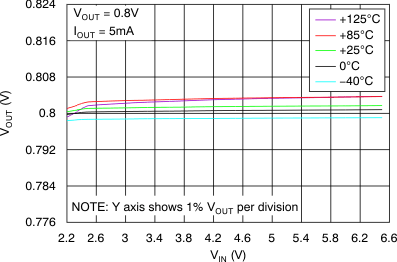
At VOUT(TYP) = 3.3 V, VIN = VOUT(TYP) + 0.5 V or 2.2 V (whichever is greater), IOUT = 100 mA, VEN = VIN, CIN = 1 μF,COUT = 4.7 μF, and CNR = 0.01 μF, all temperature values refer to TJ (unless otherwise noted).
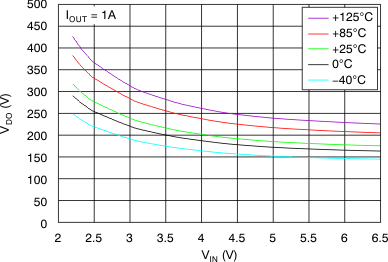
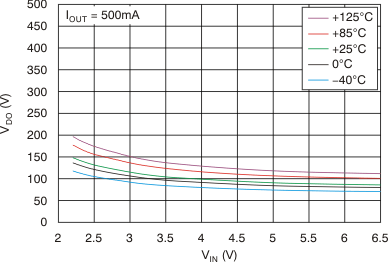
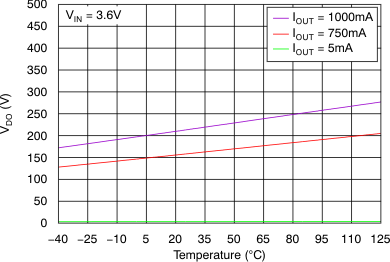
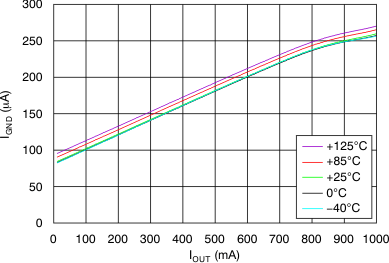
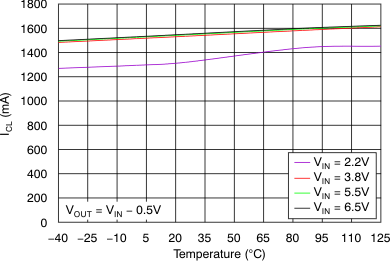
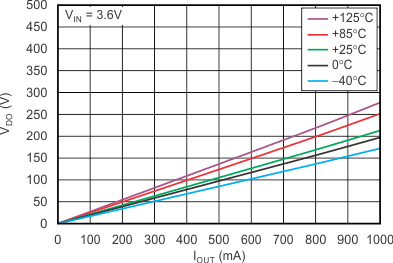
vs Dropout Voltage
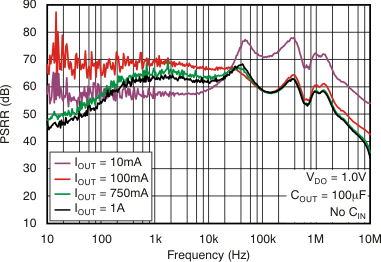
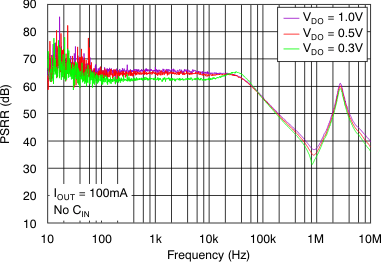
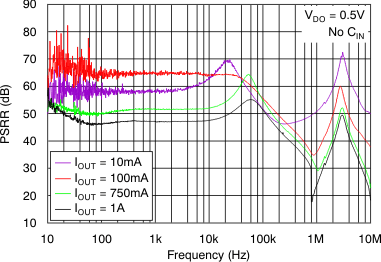
vs Frequency
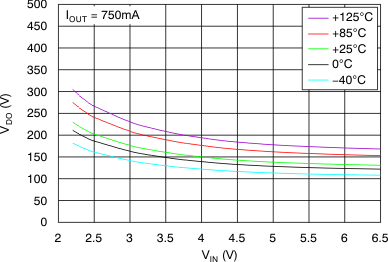
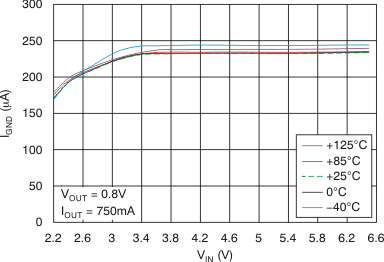
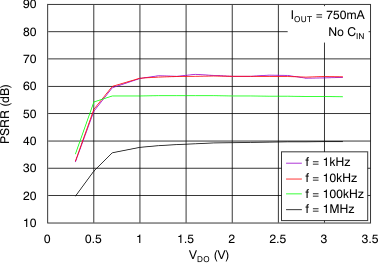
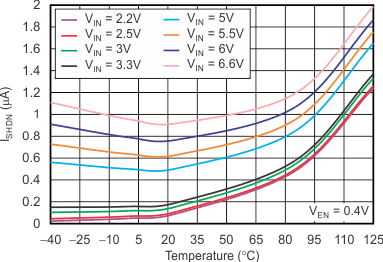
vs Dropout Voltage
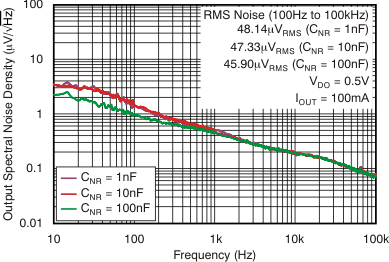
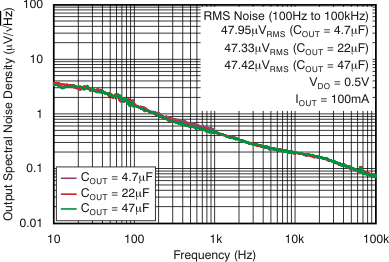
vs Frequency
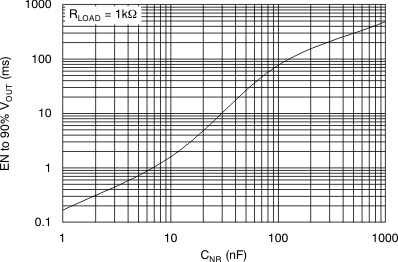
vs Noise Reduction Capacitance
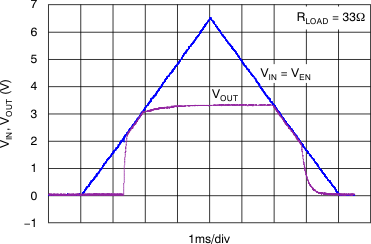
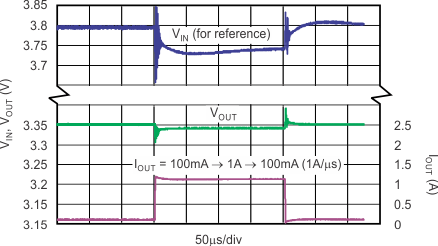
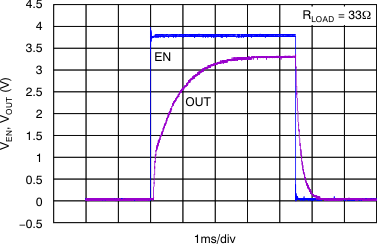
| The internal reference requires approximately 2 ms of rampup time (see Start-Up); therefore, VOUT fully reaches the target output voltage of 3.3 V in 2 ms from start-up. |