ZHCSJQ2A May 2019 – August 2019 TPS2596
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 器件比较表
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Application
- 9.2.1 Precision Current Limiting and Protection for White Goods
- 9.2.2 Design Requirements
- 9.2.3 Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.4 Support Component Selection: RFLT and CIN
- 9.2.5 Application Curves
- 9.3 System Examples
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12器件和文档支持
- 13机械、封装和可订购信息
9.2.3.2 Undervoltage and Overvoltage Lockout Set Point
The undervoltage lockout (UVLO) and overvoltage lockout (OVLO) trip point is adjusted using the external voltage divider network of R1, R2 and R3as connected between IN, EN/UVLO, OVLO and GND pins of the device. The values required for setting the undervoltage and overvoltage are calculated solving Equation 8 and Equation 9.
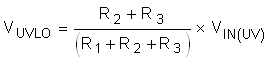

Where VUVLO(R) is UVLO rising threshold (1.2 V). Because R1, R2 and R3 leak the current from input supply VIN, these resistors must be selected based on the acceptable leakage current from input power supply VIN.
The current drawn by R1, R2 and R3 from the power supply is IR123 = VIN / (R1 + R2 + R3).
However, leakage currents due to external active components connected to the resistor string can add error to these calculations. So, the resistor string current, IR123 must be chosen to be 20 times greater than the leakage current expected.
From the device electrical specifications, VOVLO = 1.2 V and VUVLO = 1.2 V. For design requirements, VOV = 13.7 V and VUV = 8 V. To solve the equation, first choose the value of R3 = 47 kΩ and use Equation 9 to solve for (R1 + R2) = 489.58 kΩ. Use Equation 8 and value of (R1 + R2) to solve for R2 = 33.48 kΩ and finally R1= 456.1 kΩ. Using the closest standard 1% resistor values gives R1 = 464 kΩ, R2 = 33.2 kΩ, and R3 = 47.5 kΩ.