ZHCS767B January 2012 – April 2016 TPA2080D1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 器件比较表
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
- 9 Detailed Description
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13器件和文档支持
- 14机械、封装和可订购信息
9.3.5 Filter-Free Operation and Ferrite Bead Filters.
A ferrite bead filter can often be used if the design is failing radiated emissions without an LC filter and the frequency sensitive circuit is greater than 1 MHz. This filter functions well for circuits that just have to pass FCC and CE because FCC and CE only test radiated emissions greater than 30 MHz. When choosing a ferrite bead, choose one with high impedance at high frequencies, and very low impedance at low frequencies. In addition, select a ferrite bead with adequate current rating to prevent distortion of the output signal.
Use an LC output filter if there are low-frequency, (< 1 MHz) EMI-sensitive circuits or long leads from amplifier to speaker.
Figure 21 shows a typical ferrite bead output filters.
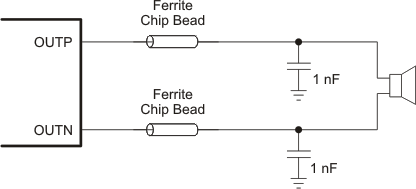 Figure 21. Typical Ferrite Chip Bead Filter
Figure 21. Typical Ferrite Chip Bead Filter
Table 1. Suggested Chip Ferrite Bead
| LOAD | VENDOR | PART NUMBER | SIZE |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8 Ω | Murata | BLM18EG121SN1 | 0603 |
| 4 Ω | TDK | MPZ2012S101A | 0805 |