ZHCSOR9A November 2021 – April 2022 OPA4H014-SEP
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
6.6 Typical Characteristics
at TA = 25°C, VS = ±9 V, RL = 2 kΩ connected to midsupply, and VCM = VOUT = midsupply (unless otherwise noted)
Table 6-1 Table of Graphs
| DESCRIPTION | FIGURE |
|---|---|
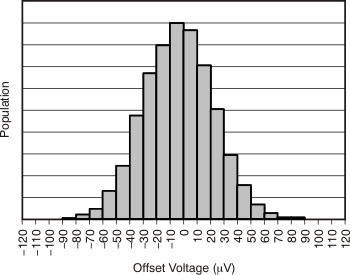
| Offset Voltage Production Distribution | Figure 6-1 |
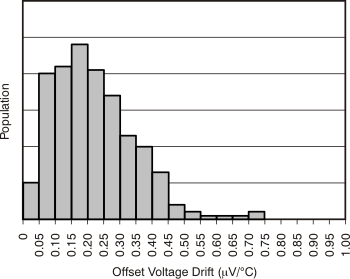
| Offset Voltage Drift Distribution | Figure 6-2 |
| Offset Voltage vs Common-Mode Voltage (Maximum Supply) | Figure 6-3 |
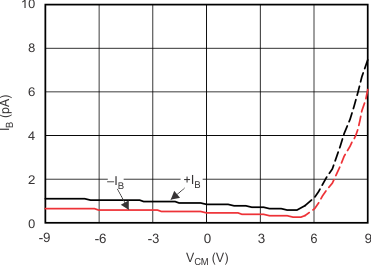
| IB vs Common-Mode Voltage | Figure 6-4 |
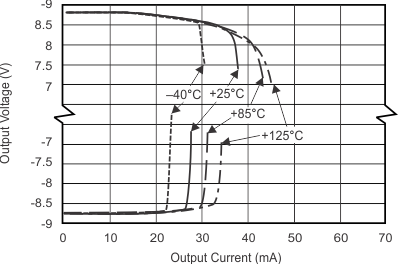
| Output Voltage Swing vs Output Current | Figure 6-5 |
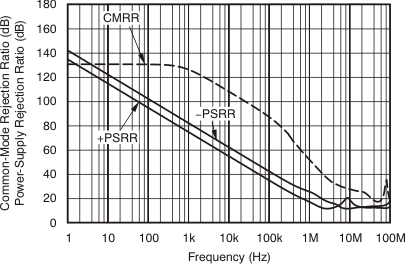
| CMRR and PSRR vs Frequency (RTI) | Figure 6-6 |
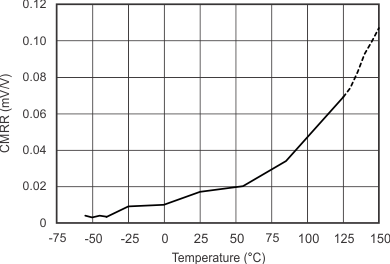
| Common-Mode Rejection Ratio vs Temperature | Figure 6-7 |
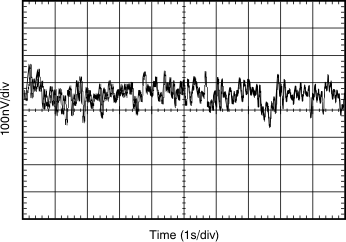
| 0.1-Hz to 10-Hz Noise | Figure 6-8 |
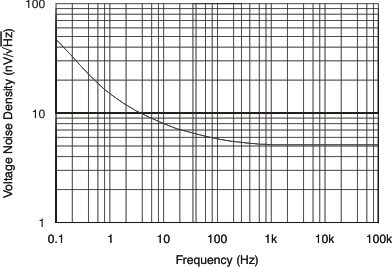
| Input Voltage Noise Density vs Frequency | Figure 6-9 |
| THD+N Ratio vs Frequency (80-kHz AP Bandwidth) | Figure 6-10 |
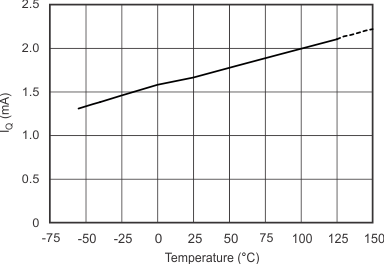
| Quiescent Current vs Temperature | Figure 6-11 |
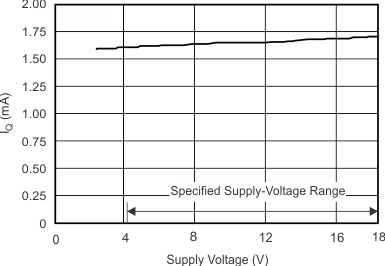
| Quiescent Current vs Supply Voltage | Figure 6-12 |
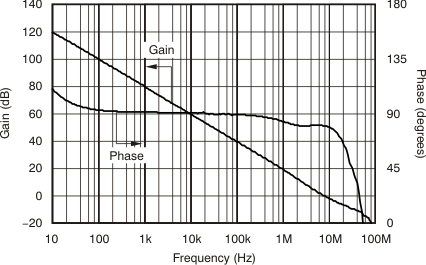
| Gain and Phase vs Frequency | Figure 6-13 |
| Closed-Loop Gain vs Frequency | Figure 6-14 |
| Open-Loop Gain vs Temperature | Figure 6-15 |
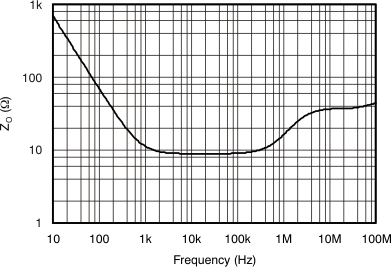
| Open-Loop Output Impedance vs Frequency | Figure 6-16 |
| Small-Signal Overshoot vs Capacitive Load (G = 1) | Figure 6-17 |
| Small-Signal Overshoot vs Capacitive Load (G = –1) | Figure 6-18 |
| No Phase Reversal | Figure 6-19 |
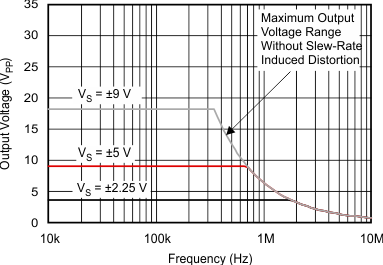
| Maximum Output Voltage vs Frequency | Figure 6-20 |
| Positive Overload Recovery | Figure 6-21 |
| Negative Overload Recovery | Figure 6-22 |
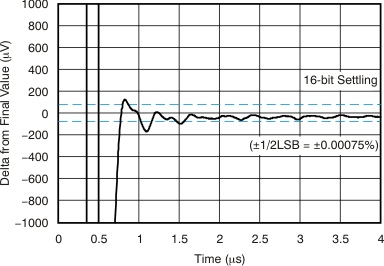
| Large-Signal Positive and Negative Settling Time | Figure 6-23, Figure 6-24 |
| Small-Signal Step Response (G = 1) | Figure 6-25 |
| Small-Signal Step Response (G = –1) | Figure 6-26 |
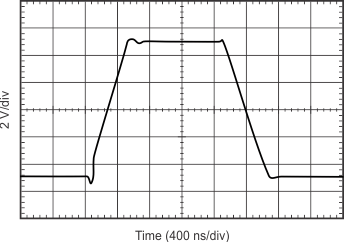
| Large-Signal Step Response (G = 1) | Figure 6-27 |
| Large-Signal Step Response (G = –1) | Figure 6-28 |
| Short-Circuit Current vs Temperature | Figure 6-29 |
| Channel Separation vs Frequency | Figure 6-30 |
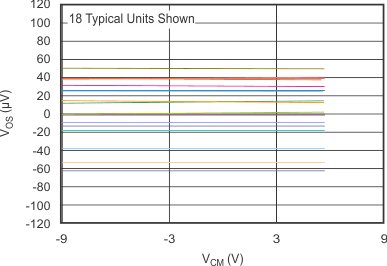
(Maximum Supply)
| G = +1 |
(100-mV Output Step)
| G = –10 |
| G = +1, CL = 100 pF |
| Short-circuiting may cause thermal shutdown; see Application Information section |
| VOUT = 3 VRMS, BW = 80 kHz, RL = 2 kΩ | ||
| CL = 30 pF |
| G = –1 |
(100-mV Output Step)
| G = –10 |
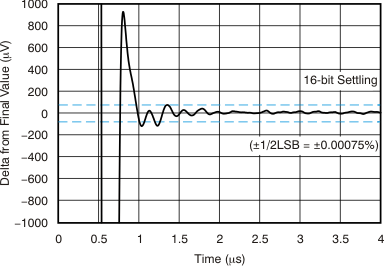
| G = –1, CL = 100 pF |
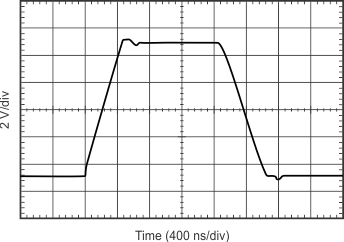
| VOUT = 3 VRMS | ||
| G = +1 |