ZHCSGW0E October 2017 – February 2020 OPA202 , OPA2202 , OPA4202
PRODUCTION DATA.
7.3.3 Noise Performance
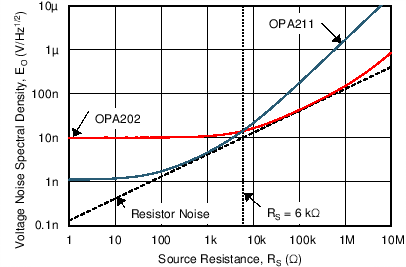
Figure 42 shows the total circuit noise for varying source impedances with the operational amplifier in a unity-gain configuration (with no feedback resistor network and therefore no additional noise contributions). The OPAx202 and OPA211 are shown with total circuit noise calculated. The op amp itself contributes a voltage noise component and a current noise component. The voltage noise is commonly modeled as a time-varying component of the offset voltage. The current noise is modeled as the time-varying component of the input bias current and reacts with the source resistance to create a voltage component of noise. Therefore, the lowest noise op amp for a given application depends on the source impedance. For low source impedance, current noise is negligible and voltage noise dominates. The OPAx202 have both low voltage noise and low current noise because of the super-beta bipolar junction transistor (super-β BJT) input of the op amp. As a result, the current noise contribution of the OPAx202 is negligible for most practical source impedances, which makes the series the better choice for applications with high source impedance.
The equation in Figure 42 shows the calculation of the total circuit noise with these parameters:
- en = voltage noise
- In = current noise
- RS = source impedance
- k = Boltzmann's constant = 1.38 × 10–23 J/K
- T = temperature in kelvins (K)
For more details on calculating noise, see Basic Noise Calculations.