SNLS289D April 2008 – September 2015 LMH1982
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6
Register Maps
- 7.6.1
I2C Interface Control Register Definitions
- 7.6.1.1 Genlock and Input Reference Control Registers
- 7.6.1.2 Genlock Status And Lock Control Register
- 7.6.1.3 Input Control Register
- 7.6.1.4 PLL 1 Divider Register
- 7.6.1.5 PLL 4 Charge Pump Current Control Register
- 7.6.1.6 Output Clock and TOF Control Register
- 7.6.1.7 TOF Configuration Registers
- 7.6.1.8 PLL 1, 2, 3 Charge Pump Current Control Registers
- 7.6.1.9 Reserved Registers
- 7.6.1
I2C Interface Control Register Definitions
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1
Application Information
- 8.1.1 148.35 MHz PLL Initialization Sequence
- 8.1.2 Enabling Genlock Mode
- 8.1.3 Output Disturbance While Output Alignment Mode Enabled
- 8.1.4 Evaluating the LMH1982
- 8.1.5 Input Reference
- 8.1.6 Output Clocks and TOF
- 8.1.7 Reference And Pll Lock Status
- 8.1.8 Loop Response
- 8.2 Typical Applications
- 8.1
Application Information
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
10 Layout
10.1 Layout Guidelines
These are some of the guidelines used in producing the LMH1982 dedicated EVM, for the user’s reference:
- The LMH1982 requires that 3.3 V and 2.5 V be regulated to within ±5% and have low noise to ensure optimal output jitter performance. The 27-MHz VCXO also requires a clean 3.3-V supply and proper supply bypassing for optimal performance. Use close-by low noise linear regulators to produce clean 3.3 V and 2.5 V for the application board.
- Route the LVDS output SD and HD clocks from the LMH1982 through controlled 100-Ω differential impedance lines to either edge-mount SMA connectors or to the following stage(s). If a differential probe will be used to measure the clocks directly on the board, then the differential lines should be terminated with 100 Ω.
- Keep the loop filter components (R8, C10, C27, and C28) next to the LMH1982 with a tight layout as shown in Figure 19.
Please consult the LMH1982 EVM for more information.
10.2 Layout Example
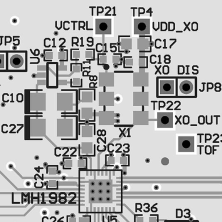 Figure 19. PCB Layout Showing Loop Filter and VCXO
Figure 19. PCB Layout Showing Loop Filter and VCXO