ZHCSJC9G September 2006 – Jaunuary 2020 LM5069
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1
48-V, 10-A Hot Swap Design
- 8.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.1.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 8.2.1
48-V, 10-A Hot Swap Design
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
8.2.1.2.2 Selecting the Hot Swap FET(s)
It is critical to select the correct MOSFET for a hot swap design. The device must meet the following requirements:
- The VDS rating must be sufficient to handle the maximum system voltage along with any ringing caused by transients.
- The SOA of the FET must be sufficient to handle all usage cases: start-up, hot-short, start into short.
- RDSON must be sufficiently low to maintain the junction and case temperature below the maximum rating of the FET. In fact, TI recommends keeping the steady state FET temperature below 125°C to allow margin to handle transients.
- Maximum continuous current rating must be above the maximum load current and the pulsed drain current must be greater than the current threshold of the circuit breaker. Most MOSFETs that pass the first three requirements also pass these two.
For this design the SUM40N15-38 was selected. After selecting the MOSFET, the maximum steady state case temperature can be computed as Equation 4.
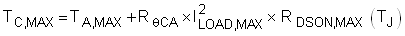
Note that the RDSON is a strong function of junction temperature, which for most MOSFETs is close to the case temperature. A few iterations of the above equations may be necessary to converge on the final RDSON and TC,MAX value. According to the CSD19536KTT datasheet, its RDSON is approximately 1.2× at 65°C. Equation 5 uses this RDSON value to compute the TC,MAX.
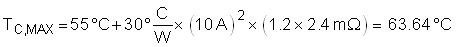
This maximum steady state case temperature does not indicate that a second MOSFET may be required to reduce and distribute power dissipation during normal operation.
As an aside, when using parallel MOSFETs, the maximum steady state case temperature can be computed in Equation 6.
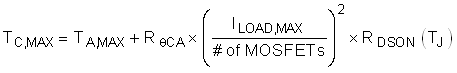
Iterate until the computed TC,MAX is using two parallel MOSFETs is less than to the junction temperature assumed for RDSON. Then, no further iterations are necessary.