ZHCSK74A August 2019 – April 2020 DRV425-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
8.2.1.2 Detailed Design Procedure
Use the following procedure to design a solution for a linear-position sensor based on the DRV425-Q1:
- Select the proper supply voltage, VDD, to support the desired magnetic field range (see Table 2 for reference).
- Select the proper reference voltage, VREFIN, to support the desired magnetic field range and to match the input voltage specifications of the desired ADC.
- Use the RangeCalculator tab in the DRV425 System Parameter Calculator to select the proper shunt resistor value of RSHUNT.
- The sensitivity drift performance of a DRV425-Q1 based linear position sensor is dominated by the temperature coefficient of the external shunt resistor. Select a low-drift shunt resistor for best sensor performance.
- Use the Problems Detected Table in DRV425 System Parameters tab in the DRV425 System Parameter Calculator to verify the system response.
The amplitude of the magnetic field is a function of distance to, and the shape of, the magnet, as shown in Figure 69. If the magnetic field to be measured exceeds 3.6 mT, see the magnet datasheet to calculate the appropriate minimum distance to the DRV425-Q1 to avoid saturating the fluxgate sensor.
The high sensitivity of the DRV425-Q1 may require shielding of the sensing area to avoid influence of undesired magnetic field sources (such as the earth magnetic field). Alternatively, an additional DRV425-Q1 can be used to perform difference measurement to cancel the influence of a static magnetic field source, as shown in Figure 68. Figure 70 shows the differential voltage generated by two DRV425-Q1 devices in such a circuit.
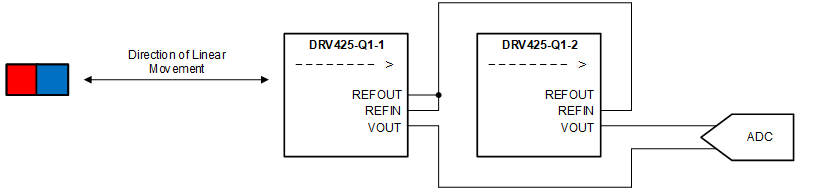 Figure 68. Differential Linear-Position Sensing Using Two DRV425-Q1 Devices
Figure 68. Differential Linear-Position Sensing Using Two DRV425-Q1 Devices