ZHCSBN3F August 2013 – March 2019
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
7.3.5 Push-Pull Multiplexer Drivers
There are two push-pull drivers intended to mulitplex between a primary nonrechargeable connected at VBAT_PRI and secondary storage element connected on VBAT_SEC based on the VBAT_OK signal. When the VBAT_OK signal goes high, indicating that the secondary rechargeable battery at VBAT_SEC is above the VBAT_OK_HYST threshold, the VB_PRI_ON output goes high followed by the VB_SEC_ON signal going low in order to connect VBAT_SEC to the system output (referred to as the VOR node). When VBAT_OK goes low, indicating that the secondary rechargeable battery at VBAT_SEC is below the VBAT_OK threshold, the VB_SEC_ON output goes high followed by the VB_PRI_ON signal going low in order to connect VBAT_PRI to the system. The drivers are powered by an ideal diode OR of the secondary battery at VBAT_SEC and the primary battery at VBAT_PRI, even during cold-start, giving each enough drive for up to 2 nF of gate capacitance of external back-to-back PMOS FETs. The switching characteristics follows a break-before-make model, wherein during a transition, the drivers both go high for a typical dead time of 5 us before one of the signals goes low. The figure below shows the FET gate voltages for the transition from the secondary battery being connected to the system to the primary battery being connected.
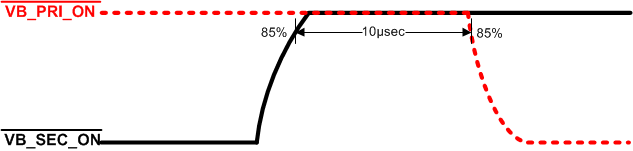 Figure 13. Break-Before-Make Operation of VB_PRI_ON and VB_SEC_ON
Figure 13. Break-Before-Make Operation of VB_PRI_ON and VB_SEC_ON