ZHCS834G June 2011 – March 2020 TPS7A63-Q1 , TPS7A6401-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagrams
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
封装选项
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
订购信息
7.3.1 Power Up, Reset Delay, and Reset Output
During power up, the regulator incorporates a protection scheme to limit the current through the pass element and output capacitor. When the input voltage exceeds a certain threshold (VIN(POWERUP)) level, the output voltage begins to ramp up as shown in Figure 16.
When starting up, and also when the output recovers from a negative voltage spike due to a load step or a dip in the input voltage for a specified duration, the device implements reset delay to indicate that output voltage is stable and in regulation.
When the output voltage reaches the power-on-reset threshold (VTH(POR)) level, that is, 93% of regulated output voltage (3.3 V or 5 V, or a programmed value), a constant output current charges an external capacitor (CDLY) to an internal threshold (VTH(RDELAY)) voltage level. Then, nRST asserts high and CDLY discharges through an internal load. This allows CDLY to charge from approximately 0 V during the next power cycle.
Program the reset delay time by connecting an external capacitor (CDLY ,100 pF to 100 nF) to the RDELAY pin. Equation 1 gives the delay time:
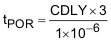
where
- tPOR = reset delay time in seconds
- CDLY = reset delay capacitor value in farads
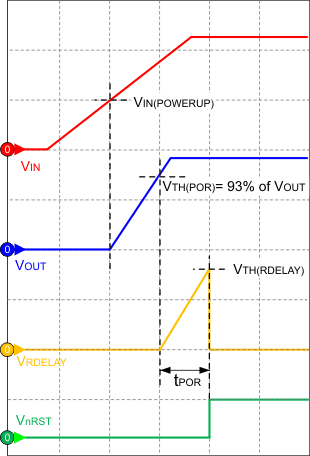 Figure 16. Power Up and Conditions for Activation of Reset
Figure 16. Power Up and Conditions for Activation of Reset 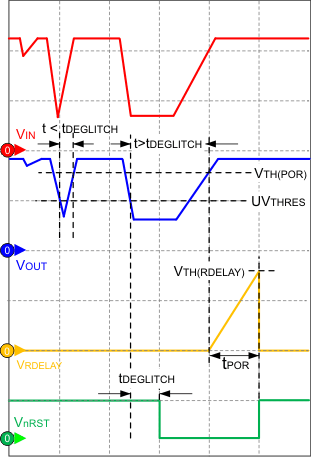 Figure 17. Reset Delay and Deglitch Filter
Figure 17. Reset Delay and Deglitch Filter As Figure 17 shows, if the regulated output voltage falls below 93% of the set level, nRST asserts low after a short de-glitch time of approximately 5.5 µs (typical). In case of negative transients in the input voltage (VIN), the reset signal asserts low only if the output (VOUT) drops and stays below the reset threshold level (VTH(POR)) for more than the deglitch time (tDEGLITCH), as Figure 17 and Figure 20 illustrate. While nRST is low, if the input voltage returns to the nominal operating voltage, the normal power-up sequence ensues. nRST asserts high only if the output voltage exceeds the reset threshold voltage (VTH(POR)) and the reset delay time (tPOR) has elapsed.