ZHCSG38A March 2017 – November 2022 TPS65263-1Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Adjusting the Output Voltage
- 7.3.2 Enable and Adjusting UVLO
- 7.3.3 Soft-Start Time
- 7.3.4 Power-Up Sequencing
- 7.3.5 V7V Low-Dropout Regulator and Bootstrap
- 7.3.6 Out-of-Phase Operation
- 7.3.7 Output Overvoltage Protection (OVP)
- 7.3.8 PSM
- 7.3.9 Slope Compensation
- 7.3.10 Overcurrent Protection
- 7.3.11 Power Good
- 7.3.12 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Register Maps
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.3.8 PSM
The TPS65263-1Q1 can enter high-efficiency PSM operation at light load current. To enable PSM operation, set the VOUTx_COM register bit 1 to '1' through I2C interface.
When a controller is enabled for PSM operation, the peak inductor current is sensed and compared with 310-mA current typically. Because the integrated current comparator catches the peak inductor current only, the average load current entering PSM varies with the applications and external output filters. In PSM, the sensed peak inductor current is clamped at 310 mA, shown in Figure 7-10.
When a controller operates in PSM, the inductor current is not allowed to reverse. The reverse current comparator turns off the low-side MOSFET when the inductor current reaches 0, preventing it from reversing and going negative.
Due to the delay in the circuit and current comparator, tdly (typical 50 nS at Vin = 12 V), the real peak inductor current threshold to turn off high-side power MOSFET can shift higher depending on inductor inductance and input, output voltages. Calculate the threshold of peak inductor current to turn off high-side power MOSFET with Equation 6.
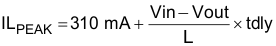
After the charge accumulated on the Vout capacitor is more than loading need, the COMP pin voltage drops to a low voltage driven by the error amplifier. There is an internal comparator at COMP pin. If the comp voltage is <0.35 V, the power stage stops switching to save power.
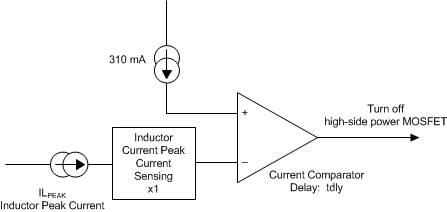 Figure 7-10 PSM Current Comparator
Figure 7-10 PSM Current Comparator