ZHCSTC5A October 2023 – March 2024 LM51772
ADVANCE INFORMATION
- 1
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 说明(续)
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Buck-Boost Control Scheme
- 8.3.2 Power Save Mode
- 8.3.3 Programmable Conduction Mode PCM
- 8.3.4 Reference System
- 8.3.5 Supply Voltage Selection – VMAX Switch and Selection Logic
- 8.3.6 Enable and Undervoltage Lockout
- 8.3.7 Internal VCC Regulator
- 8.3.8 Error Amplifier and Control
- 8.3.9 Short Circuit - Hiccup Protection
- 8.3.10 Current Monitor/Limiter
- 8.3.11 Oscillator Frequency Selection
- 8.3.12 Frequency Synchronization
- 8.3.13 Output Voltage Tracking
- 8.3.14 Slope Compensation
- 8.3.15 Configurable Soft Start
- 8.3.16 Drive Pin
- 8.3.17 Dual Random Spread Spectrum – DRSS
- 8.3.18 Gate Driver
- 8.3.19 Cable Drop Compensation (CDC)
- 8.3.20 CFG-pin and R2D Interface
- 8.3.21 Advanced Monitoring Features
- 8.3.22
Protection Features
- 8.3.22.1 Thermal Shutdown (TSD)
- 8.3.22.2 Over Current Protection
- 8.3.22.3 Output Over Voltage Protection 1 (OVP1)
- 8.3.22.4 Output Over Voltage Protection 2 (OVP2)
- 8.3.22.5 Input Voltage Protection (IVP)
- 8.3.22.6 Input Voltage Regulation (IVR)
- 8.3.22.7 Power Good
- 8.3.22.8 Boot-Strap Under Voltage Protection
- 8.3.22.9 Boot-strap Over Voltage Clamp
- 8.3.22.10 CRC - CHECK
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 9 LM51772 Registers
-
10Application and Implementation
- 10.1 Application Information
- 10.2
Typical Application
- 10.2.1 Design Requirements
- 10.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 10.2.2.1 Custom Design with WEBENCH Tools
- 10.2.2.2 Frequency
- 10.2.2.3 Feedback Divider
- 10.2.2.4 Inductor and Current Sense Resistor Selection
- 10.2.2.5 Output Capacitor
- 10.2.2.6 Input Capacitor
- 10.2.2.7 Slope Compensation
- 10.2.2.8 UVLO Divider
- 10.2.2.9 Soft-Start Capacitor
- 10.2.2.10 MOSFETs QH1 and QL1
- 10.2.2.11 MOSFETs QH2 and QL2
- 10.2.2.12 Loop Compensation
- 10.2.2.13 External Component Selection
- 10.2.3 Application Curves
- 10.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10.4 Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Revision History
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.3.1 Buck-Boost Control Scheme
The LM51772 buck-boost control algorithm ensure there is a seamless transition between the different operating modes, the fixed frequency operation, and the power stage protection features. The internal state machine controls the current flow using three active switching states:
State I: Transistors Q1 and Q3 are conducting. Q2 and Q4 are not conducting (boost mode magnetization state).
State II: Transistors Q1 and Q4 are conducting. Q2 and Q3 are not conducting (boost demagnetization or buck magnetization state).
State III: Transistors Q2 and Q4 are conducting. Q1 and Q3 are not conducting (buck demagnetization state).
| Switch | State I | State II | State III |
|---|---|---|---|
| Q1 | ON | ON | OFF |
| Q2 | OFF | OFF | ON |
| Q3 | ON | OFF | OFF |
| Q4 | OFF | ON | ON |
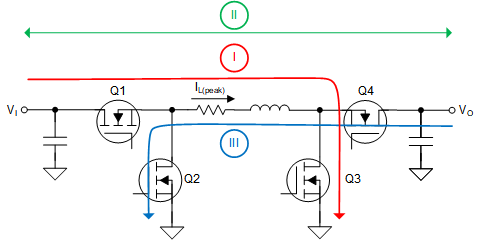
Figure 8-2 Buck-Boost Active Switching States