ZHCSEA7A June 2015 – September 2015 CDCEL824
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 说明(续)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
- 9 Detailed Description
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13器件和文档支持
- 14机械、封装和可订购信息
12 Layout
12.1 Layout Guidelines
When the CDCEL824 is used as a crystal buffer, any parasitics across the crystal affects the pulling range of the VCXO. Therefore, care must be taken in placing the crystal units on the board. Crystals should be placed as close to the device as possible, ensuring that the routing lines from the crystal terminals to XIN and XOUT have the same length.
If possible, cut out both ground plane and power plane under the area where the crystal and the routing to the device are placed. In this area, always avoid routing any other signal line, as it could be a source of noise coupling.
Additional discrete capacitors can be required to meet the load capacitance specification of certain crystal. For example, a 10.7-pF load capacitor is not fully programmable on the chip, because the internal capacitor can range from 0 pF to 20 pF with steps of 1 pF. The 0.7-pF capacitor therefore can be discretely added on top of an internal 10 pF.
To minimize the inductive influence of the trace, it is recommended to place this small capacitor as close to the device as possible and symmetrically with respect to XIN and XOUT.
Figure 16 shows a conceptual layout detailing recommended placement of power supply bypass capacitors. For component side mounting, use 0402 body size capacitors to facilitate signal routing. Keep the connections between the bypass capacitors and the power supply on the device as short as possible. Ground the other side of the capacitor using a low-impedance connection to the ground plane.
12.2 Layout Example
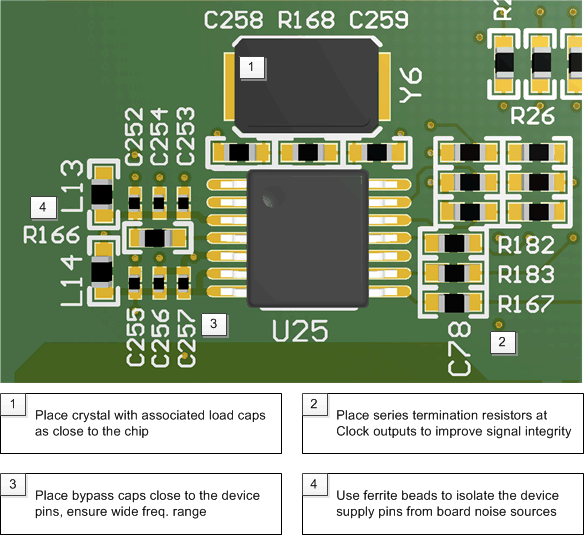 Figure 16. Board Layout
Figure 16. Board Layout