SSZT838 January 2018 TAS6424-Q1 , TPA6404-Q1
Have you seen all of the latest technology that is being integrated into today’s new cars? Well, it’s quite impressive and some of these technologies are even being offered in entry-level and economy vehicles:
- A forward-collision warning with emergency braking system that automatically brakes your car to avoid a rear-end collision in case the car in front of you stops too suddenly.
- An advanced parking guidance system that will automatically back your car perfectly into a parallel parking spot.
- Lane-keeping assist technology vibrates your seat to alert you that you are drifting across the lane; it can even automatically control the steering to ensure that your car remains within the white lines.
New infotainment systems (Figure 1) handle the navigation, music, radio and streaming services inside today’s vehicles. As customers buy more mid-range or entry-level cars, it’s a natural expectation that their infotainment system have a large liquid crystal display (LCD) touchscreen, like on our smartphones and tablets. They also expect their cars to support Bluetooth® and/or Wi-Fi® so that they can stream music, podcasts or news.
 Figure 1 Automotive Infotainment
System
Figure 1 Automotive Infotainment
SystemIn this post, I’ll discuss several key design considerations for audio amplifiers in new automotive infotainment systems.
Size
Heat
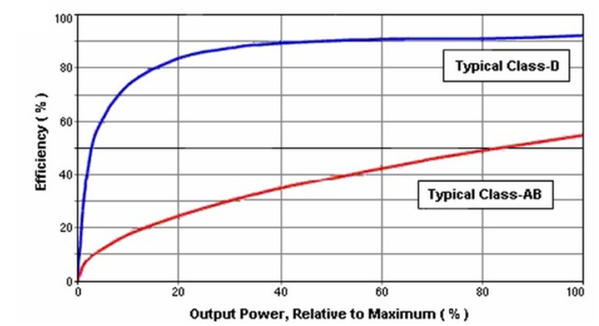 Figure 2 Class-AB vs. Class-D Efficiency (Image Courtesy of http://www.audioholics.com)
Figure 2 Class-AB vs. Class-D Efficiency (Image Courtesy of http://www.audioholics.com)At the 2018 Consumer Electronics Show (CES), Texas Instruments will be demonstrating the industry’s first 2.1MHz high switching frequency Class-D analog input automotive audio amplifier. We designed the TPA6404-Q1 to best address the issues related to infotainment head unit size and thermal load.
Class-D amplifiers typically switch the amplifier on and off at ~400kHz. A much higher 2.1MHz switching frequency in the TPA6404-Q1 Class-D amplifier design enables the use of a significantly lower inductance value for the output filter. You can see in Figure 3 that a 2.1MHz design using a newer 3.3µH metal alloy-type inductor (as opposed to the much larger 10µH/8.2µH needed for a 400kHz amplifier) allows all eight inductors for a four-channel solution to fit into the same footprint as just one 8.2µH inductor.
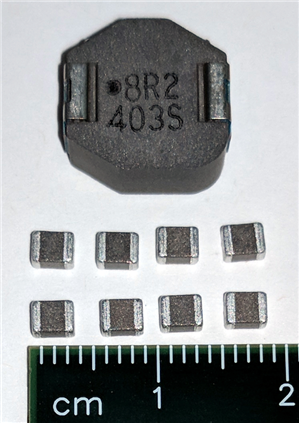 Figure 3 Inductor Size Comparison
Figure 3 Inductor Size ComparisonAnother key feature of the TPA6404-Q1 that helps contribute to a small four-channel amplifier solution size is its “flow-through” audio signal design. Figure 4 illustrates how the analog input signals come into the amplifier device on one side of the chip; then amplification of the audio signal takes place on the opposite side of the device where the signals flow into the external output filters.
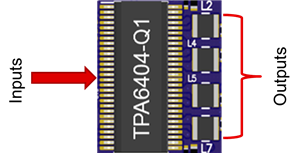 Figure 4 Flow-through Design of the TPA6404-Q1
Figure 4 Flow-through Design of the TPA6404-Q1Combining metal-alloy 3.3µH inductors along with flow-through design yields the industry’s smallest four-channel automotive Class-D amplifier size. Figure 5 shows that the TPA6404-Q1 complete solution (including amplifier and all required passive components) measures just 4.5cm2.
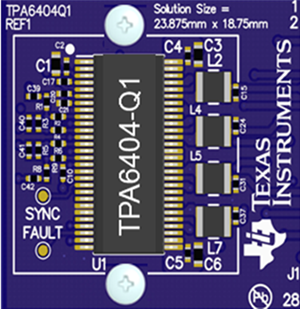 Figure 5 Four-channel Class-D Amplifier Solution Size
Figure 5 Four-channel Class-D Amplifier Solution SizeIf you need to focus on reducing overall solution size and the heat generated in your entry-level infotainment head unit system, then I invite you to learn more details about how the TPA6404-Q1 2.1-MHz Class-D amplifier can significantly help. You can also reduce the development time with the TPA6404-Q1 evaluation module (EVM), as well as the schematics, design files and layout guidance, to kick-start your design.
Additional Resources
- Check out the TAS6424-Q1, the digital input companion device to the TPA6404-Q1, and watch a video to learn more about its features.
- Read the blog post, “How switching above the AM band eases automotive Class-D amplifier EMC designs.”
- Explore additional mid-power audio amplifiers to suit your design needs.
- Learn more about TI’s automotive infotainment and cluster solutions.