SLLA515 November 2020 SN6501-Q1
4.1 SOT-23 (5) Package
Figure 4-1 shows the SN6501-Q1 pin diagram for the SOT-23 (5) package. For a detailed description of the device pins please refer to the Pin Configuration and Functions section in the SN6501-Q1 data sheet.
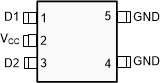 Figure 4-1 Pin Diagram (SOT-23 (5))
Package
Figure 4-1 Pin Diagram (SOT-23 (5))
PackageTable 4-2 Pin FMA for Device Pins
Short-Circuited to Ground
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | 1 | D1 pin stuck low creates short circuit path between Vcc and ground through transformer winding, causing high current to flow and possible damage to transformer. Output voltage out of designed spec. | A |
| VCC | 2 | No power to the device. No isolated output voltage. | B |
| D2 | 3 | D2 pin stuck low creates short circuit path between Vcc and ground through transformer winding, causing high current to flow and possible damage to transformer. Output voltage out of designed spec. | A |
| GND | 4 | Device continues to function as expected. Normal operation. | D |
| GND | 5 | Device continues to function as expected. Normal operation. | D |
Table 4-3 Pin FMA for Device Pins
Open-Circuited
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | 1 | With D1 open, one primary transformer winding does not store energy. Isolated output supply out of intended set-point. | B |
| VCC | 2 | No power to device, so no switching action of D1/D2. Isolated output voltage does not build up. | B |
| D2 | 3 | With D2 open, one primary transformer winding does not store energy. Isolated output supply out of intended set-point. | B |
| GND | 4 | Device gets return ground through pin5. Thermal performance may reduce. | C |
| GND | 5 | Device gets return ground through pin4. Thermal performance may reduce. | C |
Table 4-4 Pin FMA for Device Pins
Short-Circuited to Adjacent Pin
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Shorted to | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | 1 | VCC | D1 stuck high. Makes potential difference between one transformer winding zero. When D1 FET switches on, high current flows from supply to ground. Isolated output supply out of intended set-point. | A |
| VCC | 2 | D2 | D2 stuck high. Makes potential difference between one transformer winding zero. When D2 FET switches on, high current flows from supply to ground. Isolated output supply out of intended set-point. | A |
| D2 | 3 | GND | Not considered. Corner pin. | D |
| GND | 4 | GND | No effect. Normal operation. | D |
| GND | 5 | D1 | Not considered. Corner pin. | D |
Table 4-5 Pin FMA for Device Pins Short-Circuited to
supply
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | 1 | D1 stuck high. Makes potential difference between one transformer winding zero. When D1 FET switches on, high current flows from supply to ground. Isolated output supply out of intended set-point. | A |
| VCC | 2 | No effect. Normal operation. | D |
| D2 | 3 | D2 stuck high. Makes potential difference between one transformer winding zero. When D2 FET switches on, high current flows from supply to ground. Isolated output supply out of intended set-point. | A |
| GND | 4 | This creates potential difference between pin4 and pin5, causing high current to flow with possible device damage. | A |
| GND | 5 | This creates potential difference between pin4 and pin5, causing high current to flow with possible device damage. | A |