SBOA550 October 2022 OPA1671 , OPA2990 , SN74HCS04 , SN74HCS164 , SN74HCS30 , SN74LVC1G00 , SN74LVC1G123 , TLC04 , TLC14 , TS5A9411
- Abstract
- Trademarks
- 1 Introduction
- 2 The Davies Generator
- 3 Optimizing Standard Resistance Values for THD Performance
- 4 Simulation Examples
- 5 Compensating for Shift Register Output Resistance
- 6 Voltage-Mode Thevenin Equivalent
- 7 Harmonic Filtering
- 8 Tracking Harmonic Filter
- 9 Multiphase Output
- 10Conclusion
- 11Acknowledgment
- 12References
- A Analytical Solution for Resistance Network Values
- B Forbidden States of the Johnson Counter
5 Compensating for Shift Register Output Resistance
The SN74HCS164 8-Bit Parallel-Out Serial Shift Registers With Schmitt-Trigger Inputs data sheet provides insight into the output resistance of the flip-flops, with the output driver specifications shown in Figure 5-1.
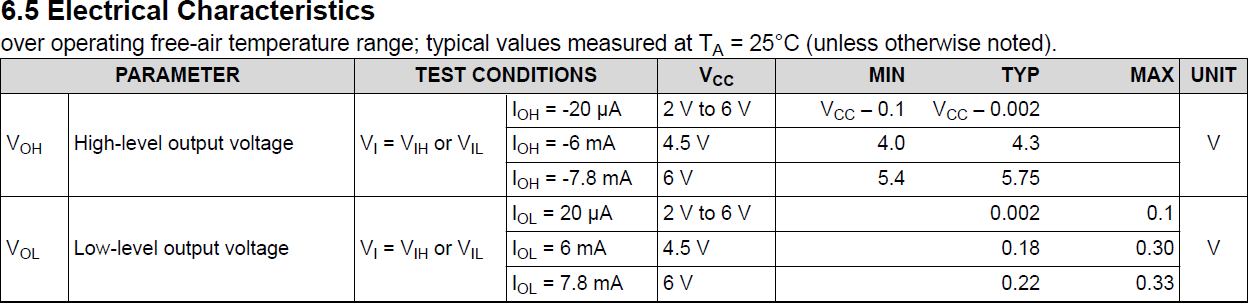
For sourcing current, the output resistance typically is (4.5 V – 4.3 V) / 0.006 A ≈ 33.3 Ω. For sinking current, the typical output resistance is 0.18 V / 0.006 A ≈ 30.0 Ω. The average output resistance is then approximately 31.7 Ω, which is about 1% of the value of the inner resistors of the previous idealized case; significant given the level of THD so far in question. Note that the worse case MIN, MAX values are dramatically different and result in much higher and more asymmetric output resistance values.
Recalculating the resistor network by assuming the previously discussed typical output resistance, the following network and an overall Thevenin output resistance of 597.6 Ω is determined. Using the same FFT analysis the THD for this compensated version is < 0.06%, and the 3rd harmonic is 65 dB below the fundamental. This is nearly a 8-dB improvement in 3rd harmonic performance compared to Figure 4-3, obtained simply by optimizing the resistor values to account for average output resistance.
Alternatively, the effects of output resistance can be reduced (though not eliminated) by simply scaling up the Thevenin resistance of the whole network – the previous example uses a relatively low Thevenin resistance to accentuate the impact of flip-flop resistance on THD.