SBAA051A January 1994 – April 2015 MSC1210Y2 , MSC1210Y3 , MSC1210Y4 , MSC1210Y5
5 Digital Codes
One final consideration in data acquisition and conversion systems is the digital coding of the data at the output of the A/D converter. Data is usually encoded in either binary or binary-coded-decimal (BCD) form.
Binary encoded data formats are most commonly employed for digital computer-oriented applications where the processing is normally performed in binary notation. BCD data encoding is usually required in applications where the data is fed to decimal end devices such as digital readouts and printers. The majority of applications require binary encoding.
The most commonly used binary codes in A/D converters are:
- Unipolar Straight Binary (USB) — used for unipolar ana- log signal ranges, i.e., 0 to ±5 V, 0 to ±10 V, etc.
- Bipolar Offset Binary (BOB) — used for bipolar analog signal ranges, i.e., ±5 V, ±10 V, etc.
- Bipolar Two’s Complement (BTC) — used for bipolar analog signal ranges in many digital computer applications.
Two BCD codes, unipolar BCD and sign-magnitude BCD (SMD) are used in A/D converters. The definition of these codes is shown in Table 4 and Table 5.
Table 4. Definition of Binary Codes
| DEFINITION | OUTPUT DIGITAL CODE | USB CODE | BOB CODE(2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MSB ...... LSB | |||
| +Full Scale | 111....11Φ (1) | +VFSR –1/2LSB | 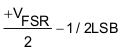 |
| Mid Scale | 100....00Φ | +VFSR /2 | Zero |
| –Full Scale | 000....00Φ | +1/2LSB | 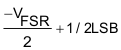 |
| One Least Significant Bit | 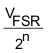 |
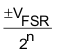 |
Table 5. Definition of Decimal Codes
| DEFINITION | OUTPUT DIGITAL CODE
(3 DIGITS) |
DECIMAL VALUE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BCD CODE | SMD CODE | ||
| Sign | MSD(1).............LSD | ||
| + Full Scale | 1 1001 1001 1001 | 999 | +999 |
| Zero | 1 0000 0000 0000 | 000 | +000 |
| –Full Scale | 0 1001 1001 1001 | N/A | –999 |
| One Least Significant Bit | 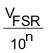 (2) (2) |
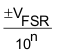 (2) (2) |
|