SLOS520A August 2007 – March 2016 TPA2013D1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 DC Characteristics
- 7.6 Boost Converter DC Characteristics
- 7.7 Class D Amplifier DC Characteristics
- 7.8 AC Characteristics
- 7.9 Class D Amplifier AC Characteristics
- 7.10 Dissipation Ratings
- 7.11 Typical Characteristics
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
- 9 Detailed Description
-
10Application and Implementation
- 10.1 Application Information
- 10.2
Typical Applications
- 10.2.1
TPA2013D1 With Differential Input Signal
- 10.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 10.2.1.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 10.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 10.2.2 Bypassing the Boost Converter
- 10.2.3 Stereo Operation Application
- 10.2.4 LED Driver for Digital Still Cameras
- 10.2.5 Design Requirements
- 10.2.6 Detailed Design Procedure
- 10.2.7 Application Curves
- 10.2.1
TPA2013D1 With Differential Input Signal
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
封装选项
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
- RGP|20
订购信息
8 Parameter Measurement Information
All parameters are measured according to the conditions described in Specifications. Figure 31 shows the setup used for the typical characteristics of the test device.
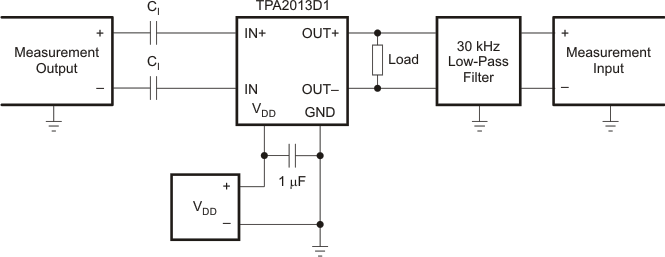
1. CI was shorted for any common-mode input voltage measurement. All other measurements were taken with a 1-μF CI (unless otherwise noted).
2. A 33-μH inductor was placed in series with the load resistor to emulate a small speaker for efficiency measurements.
3. The 30-kHz low-pass filter is required, even if the analyzer has an internal low-pass filter. An RC low-pass filter (100-Ω, 47-nF) is used on each output for the data sheet graphs.
4. L = 4.7 μH is used for the boost converter unless otherwise noted.
Figure 31. Test Set-Up for Graphs