SCES582H July 2004 – April 2015 SN74AVCH2T45
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (Continued)
- 6 Pin Configurations and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 7.6 Switching Characteristics: VCCA = 1.2 V
- 7.7 Switching Characteristics: VCCA = 1.5 V
- 7.8 Switching Characteristics: VCCA = 1.8 V
- 7.9 Switching Characteristics: VCCA = 2.5 V
- 7.10 Switching Characteristics: VCCA = 3.3 V
- 7.11 Operating Characteristics
- 7.12 Typical Characteristics
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
- 9 Detailed Description
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
封装选项
请参考 PDF 数据表获取器件具体的封装图。
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
- DCU|8
- YZP|8
- DCT|8
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
订购信息
7 Specifications
7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCCA
VCCB |
Supply voltage | –0.5 | 4.6 | V | |
| VI | Input voltage(2) | I/O ports (A port) | –0.5 | 4.6 | V |
| I/O ports (B port) | –0.5 | 4.6 | |||
| Control inputs | –0.5 | 4.6 | |||
| VO | Voltage range applied to any output in the high-impedance or power-off state(2) |
A port | –0.5 | 4.6 | V |
| B port | –0.5 | 4.6 | |||
| VO | Voltage range applied to any output in the high or low state(2)(3) | A port | –0.5 | VCCA + 0.5 | V |
| B port | –0.5 | VCCB + 0.5 | |||
| IIK | Input clamp current | VI < 0 | –50 | mA | |
| IOK | Output clamp current | VO < 0 | –50 | mA | |
| IO | Continuous output current | ±50 | mA | ||
| Continuous current through VCCA, VCCB, or GND | ±100 | mA | |||
| TJ | Junction temperature | –40 | 150 | °C | |
| Tstg | Storage temperature | –65 | 150 | °C |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, which do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
(2) The input voltage and output negative-voltage ratings may be exceeded if the input and output current ratings are observed.
(3) The output positive-voltage rating may be exceeded up to 4.6 V maximum if the output current rating is observed.
7.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ±8000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | ±1000 | |||
| Machine Model (MM), Per JEDEC specification JESD22-A115-A | ±200 | |||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(3)(4)(5)| VCCI(1) | VCCO(2) | MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCCA | Supply voltage | 1.2 | 3.6 | V | ||||
| VCCB | Supply voltage | 1.2 | 3.6 | V | ||||
| VIH | High-level input voltage |
Data inputs(4) | 1.2 V to 1.95 V | VCCI(1) × 0.65 | V | |||
| 1.95 V to 2.7 V | 1.6 | |||||||
| 2.7 V to 3.6 V | 2 | |||||||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage |
Data inputs(4) | 1.2 V to 1.95 V | VCCI(1) × 0.35 | V | |||
| 1.95 V to 2.7 V | 0.7 | |||||||
| 2.7 V to 3.6 V | 0.8 | |||||||
| VIH | High-level input voltage |
DIR (referenced to VCCA)(5) |
1.2 V to 1.95 V | VCCA × 0.65 | V | |||
| 1.95 V to 2.7 V | 1.6 | |||||||
| 2.7 V to 3.6 V | 2 | |||||||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage |
DIR (referenced to VCCA)(5) |
1.2 V to 1.95 V | VCCA × 0.35 | V | |||
| 1.95 V to 2.7 V | 0.7 | |||||||
| 2.7 V to 3.6 V | 0.8 | |||||||
| VI | Input voltage | 0 | 3.6 | V | ||||
| VO | Output voltage | Active state | 0 | VCCO(2) | V | |||
| 3-state | 0 | 3.6 | ||||||
| IOH | High-level output current | 1.2 V | –3 | mA | ||||
| 1.4 V to 1.6 V | –6 | |||||||
| 1.65 V to 1.95 V | –8 | |||||||
| 2.3 V to 2.7 V | –9 | |||||||
| 3 V to 3.6 V | –12 | |||||||
| IOL | Low-level output current | 1.2 V | 3 | mA | ||||
| 1.4 V to 1.6 V | 6 | |||||||
| 1.65 V to 1.95 V | 8 | |||||||
| 2.3 V to 2.7 V | 9 | |||||||
| 3 V to 3.6 V | 12 | |||||||
| Δt/Δv | Input transition rise or fall rate | 5 | ns/V | |||||
| TA | Operating free-air temperature | –40 | 85 | °C | ||||
(1) VCCI is the voltage associated with the input port supply VCCA or VCCB.
(2) VCCO is the voltage associated with the output port supply VCCA or VCCB.
(3) All unused data inputs of the device must be held at VCCI or GND to ensure proper device operation. Refer to the TI application report, Implications of Slow or Floating CMOS Inputs, SCBA004.
(4) For VCCI values not specified in the data sheet, VIH min = VCCI × 0.7 V, VIL max = VCCI × 0.3 V.
(5) For VCCI values not specified in the data sheet, VIH min = VCCA × 0.7 V, VIL max = VCCA × 0.3 V.
7.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | SN74AVCH2T45 | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DCT (SSOP) | DCU (VSSOP) | YZP (DSBGA) | |||
| 8 PINS | 8 PINS | 8 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 194.4 | 199.3 | 105.8 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 124.7 | 76.2 | 1.6 | |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 106.8 | 80.6 | 10.8 | |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 49.8 | 7.1 | 3.1 | |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 105.8 | 80.1 | 10.8 | |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the IC Package Thermal Metrics application report, SPRA953.
7.5 Electrical Characteristics
over recommended operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(5)(6)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | VCCA | VCCB | TA = 25°C | –40°C to 85°C | UNIT | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIN | TYP | MAX | MIN | TYP | MAX | |||||||
| VOH(7) | IOH = –100 μA | VI = VIH | 1.2 V to 3.6 V | 1.2 V to 3.6 V | VCCO – 0.2 | V | ||||||
| IOH = –3 mA | 1.2 V | 1.2 V | 0.95 | |||||||||
| IOH = –6 mA | 1.4 V | 1.4 V | 1.05 | |||||||||
| IOH = –8 mA | 1.65 V | 1.65 V | 1.2 | |||||||||
| IOH = –9 mA | 2.3 V | 2.3 V | 1.75 | |||||||||
| IOH = –12 mA | 3 V | 3 V | 2.3 | |||||||||
| VOL(7) | IOL = 100 μA | VI = VIL | 1.2 V to 3.6 V | 1.2 V to 3.6 V | 0.2 | V | ||||||
| IOL = 3 mA | 1.2 V | 1.2 V | 0.15 | |||||||||
| IOL = 6 mA | 1.4 V | 1.4 V | 0.35 | |||||||||
| IOL = 8 mA | 1.65 V | 1.65 V | 0.45 | |||||||||
| IOL = 9 mA | 2.3 V | 2.3 V | 0.55 | |||||||||
| IOL = 12 mA | 3 V | 3 V | 0.7 | |||||||||
| II(7) | DIR input | VI = VCCA or GND | 1.2 V to 3.6 V | 1.2 V to 3.6 V | ±0.025 | ±0.25 | ±1 | μA | ||||
| IBHL(1) | VI = 0.42 V | 1.2 V | 1.2 V | 25 | μA | |||||||
| VI = 0.49 V | 1.4 V | 1.4 V | 15 | |||||||||
| VI = 0.58 V | 1.65 V | 1.65 V | 25 | |||||||||
| VI = 0.7 V | 2.3 V | 2.3 V | 45 | |||||||||
| VI = 0.8 V | 3.3 V | 3.3 V | 100 | |||||||||
| IBHH(2) | VI = 0.78 V | 1.2 V | 1.2 V | –25 | μA | |||||||
| VI = 0.91 V | 1.4 V | 1.4 V | –15 | |||||||||
| VI = 1.07 V | 1.65 V | 1.65 V | –25 | |||||||||
| VI = 1.6 V | 2.3 V | 2.3 V | –45 | |||||||||
| VI = 2 V | 3.3 V | 3.3 V | –100 | |||||||||
| IBHLO(3) | VI = 0 to VCC | 1.2 V | 1.2 V | 50 | μA | |||||||
| 1.6 V | 1.6 V | 125 | ||||||||||
| 1.95 V | 1.95 V | 200 | ||||||||||
| 2.7 V | 2.7 V | 300 | ||||||||||
| 3.6 V | 3.6 V | 500 | ||||||||||
| IBHHO(4) | VI = 0 to VCC | 1.2 V | 1.2 V | –50 | μA | |||||||
| 1.6 V | 1.6 V | –125 | ||||||||||
| 1.95 V | 1.95 V | –200 | ||||||||||
| 2.7 V | 2.7 V | –300 | ||||||||||
| 3.6 V | 3.6 V | –500 | ||||||||||
| Ioff(8) | A port | VI or VO = 0 to 3.6 V | 0 V | 0 V to 3.6 V | ±0.1 | ±1 | ±5 | μA | ||||
| B port | 0 V to 3.6 V | 0 V | ±0.1 | ±1 | ±5 | |||||||
| IOZ(8) | B port | VO = VCCO or GND, VI = VCCI or GND |
0 V | 3.6 V | ±0.5 | ±2.5 | ±5 | |||||
| A port | 3.6 V | 0 V | ±0.5 | ±2.5 | ±5 | μA | ||||||
| ICCA(8) | VI = VCCI or GND, IO = 0 | 1.2 V to 3.6 V | 1.2 V to 3.6 V | 10 | μA | |||||||
| 0 V | 3.6 V | –2 | ||||||||||
| 3.6 V | 0 V | 10 | ||||||||||
| ICCB(8) | VI = VCCI or GND, IO = 0 | 1.2 V to 3.6 V | 1.2 V to 3.6 V | 10 | μA | |||||||
| 0 V | 3.6 V | 10 | ||||||||||
| 3.6 V | 0 V | –2 | ||||||||||
| ICCA + ICCB | VI = VCCI or GND, IO = 0 | 1.2 V to 3.6 V | 1.2 V to 3.6 V | 20 | μA | |||||||
| Ci | Control inputs |
VI = 3.3 V or GND | 3.3 V | 3.3 V | 2.5 | pF | ||||||
| Cio | A or B port | VI = 3.3 V or GND | 3.3 V | 3.3 V | 6 | pF | ||||||
(1) The bus-hold circuit can sink at least the minimum low sustaining current at VIL maximum. IBHL should be measured after lowering VIN to GND and then raising it to VIL maximum.
(2) The bus-hold circuit can source at least the minimum high sustaining current at VIH mininum. IBHH should be measured after raising VIN to VCC and then lowering it to VIH minimum.
(3) An external driver must source at least IBHLO to switch this node from low to high.
(4) An external driver must sink at least IBHHO to switch this node from high to low.
(5) VCCO is the voltage associated with the output port supply VCCA or VCCB.
(6) VCCI is the voltage associated with the input port supply VCCA or VCCB.
(7) VOH: Output High Voltage; VOL: Output Low Voltage; II: Control Input Current.
(8) Ioff: Partial Power Down Output current; IOZ: Hi-Z Output Current; ICCA: Supply A Current; ICCB: Supply B Current.
7.6 Switching Characteristics: VCCA = 1.2 V
over recommended operating free-air temperature range, VCCA = 1.2 V (see Figure 7)| PARAMETER | FROM (INPUT) |
TO (OUTPUT) |
VCCB = 1.2 V | VCCB = 1.5 V | VCCB = 1.8 V | VCCB = 2.5 V | VCCB = 3.3 V | UNIT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TYP | TYP | TYP | TYP | TYP | ||||
| tPLH(2) | A | B | 3.1 | 2.6 | 2.4 | 2.2 | 2.2 | ns |
| tPHL(2) | 3.1 | 2.6 | 2.4 | 2.2 | 2.2 | |||
| tPLH(2) | B | A | 3.4 | 3.1 | 3 | 2.9 | 2.9 | ns |
| tPHL(2) | 3.4 | 3.1 | 3 | 2.9 | 2.9 | |||
| tPHZ(2) | DIR | A | 5.2 | 5.2 | 5.1 | 5 | 4.8 | ns |
| tPLZ(2) | 5.2 | 5.2 | 5.1 | 5 | 4.8 | |||
| tPHZ(2) | DIR | B | 5 | 4 | 3.8 | 2.8 | 3.2 | ns |
| tPLZ(2) | 5 | 4 | 3.8 | 2.8 | 3.2 | |||
| tPZH(2)(1) | DIR | A | 8.4 | 7.1 | 6.8 | 5.7 | 6.1 | ns |
| tPZL(2)(1) | 8.4 | 7.1 | 6.8 | 5.7 | 6.1 | |||
| tPZH(2)(1) | DIR | B | 8.3 | 7.8 | 7.5 | 7.2 | 7 | ns |
| tPZL(2)(1) | 8.3 | 7.8 | 7.5 | 7.2 | 7 |
(1) The enable time is a calculated value derived using the formula shown in the Enable Times section.
(2) tPLH: Low-to-high Propagation Delay; tPHL: High-to-Low Propagation Delay; tPHZ: High-to-Hi-Z Propagation Delay; tPLZ: Low-to-Hi-Z Propagation Delay; tPZH: Hi-Z-to-High Propagation Delay; tPZL: Hi-Z-to-Low Propagation Delay
7.7 Switching Characteristics: VCCA = 1.5 V
over recommended operating free-air temperature range, VCCA = 1.5 V ± 0.1 V (see Figure 7)| PARAMETER | FROM (INPUT) |
TO (OUTPUT) |
VCCB = 1.2 V | VCCB = 1.5 V ± 0.1 V |
VCCB = 1.8 V ± 0.15 V |
VCCB = 2.5 V ± 0.2 V |
VCCB = 3.3 V ± 0.3 V |
UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TYP | MIN | MAX | MIN | MAX | MIN | MAX | MIN | MAX | ||||
| tPLH(2) | A | B | 2.8 | 0.7 | 5.4 | 0.5 | 4.6 | 0.4 | 3.7 | 0.3 | 3.5 | ns |
| tPHL(2) | 2.8 | 0.7 | 5.4 | 0.5 | 4.6 | 0.4 | 3.7 | 0.3 | 3.5 | |||
| tPLH(2) | B | A | 2.7 | 0.8 | 5.4 | 0.7 | 5.2 | 0.6 | 4.9 | 0.5 | 4.7 | ns |
| tPHL(2) | 2.7 | 0.8 | 5.4 | 0.7 | 5.2 | 0.6 | 4.9 | 0.5 | 4.7 | |||
| tPHZ(2) | DIR | A | 3.9 | 1.3 | 8.5 | 1.3 | 7.8 | 1.1 | 7.7 | 1.4 | 7.6 | ns |
| tPLZ(2) | 3.9 | 1.3 | 8.5 | 1.3 | 7.8 | 1.1 | 7.7 | 1.4 | 7.6 | |||
| tPHZ(2) | DIR | B | 4.7 | 1.1 | 7 | 1.4 | 6.9 | 1.2 | 6.9 | 1.7 | 7.1 | ns |
| tPLZ(2) | 4.7 | 1.1 | 7 | 1.4 | 6.9 | 1.2 | 6.9 | 1.7 | 7.1 | |||
| tPZH(2)(1) | DIR | A | 7.4 | 12.4 | 12.1 | 11.8 | 11.8 | ns | ||||
| tPZL(2)(1) | 7.4 | 12.4 | 12.1 | 11.8 | 11.8 | |||||||
| tPZH(2)(1) | DIR | B | 6.7 | 13.9 | 12.4 | 11.4 | 11.1 | ns | ||||
| tPZL(2)(1) | 6.7 | 13.9 | 12.4 | 11.4 | 11.1 | |||||||
(1) The enable time is a calculated value derived using the formula shown in the Enable Times section.
(2) tPLH: Low-to-high Propagation Delay; tPHL: High-to-Low Propagation Delay; tPHZ: High-to-Hi-Z Propagation Delay; tPLZ: Low-to-Hi-Z Propagation Delay; tPZH: Hi-Z-to-High Propagation Delay; tPZL: Hi-Z-to-Low Propagation Delay
7.8 Switching Characteristics: VCCA = 1.8 V
over recommended operating free-air temperature range, VCCA = 1.8 V ± 0.15 V (see Figure 7)| PARAMETER | FROM (INPUT) |
TO (OUTPUT) |
VCCB = 1.2 V | VCCB = 1.5 V ± 0.1 V |
VCCB = 1.8 V ± 0.15 V |
VCCB = 2.5 V ± 0.2 V |
VCCB = 3.3 V ± 0.3 V |
UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TYP | MIN | MAX | MIN | MAX | MIN | MAX | MIN | MAX | ||||
| tPLH(2) | A | B | 2.7 | 0.5 | 5.2 | 0.4 | 4.3 | 0.2 | 3.4 | 0.2 | 3.1 | ns |
| tPHL(2) | 2.7 | 0.5 | 5.2 | 0.4 | 4.3 | 0.2 | 3.4 | 0.2 | 3.1 | |||
| tPLH(2) | B | A | 2.4 | 0.7 | 4.7 | 0.5 | 4.4 | 0.5 | 4 | 0.4 | 3.8 | ns |
| tPHL(2) | 2.4 | 0.7 | 4.7 | 0.5 | 4.4 | 0.5 | 4 | 0.4 | 3.8 | |||
| tPHZ(2) | DIR | A | 3.7 | 1.3 | 8.1 | 0.7 | 6.9 | 1.4 | 5.3 | 1.1 | 5.2 | ns |
| tPLZ(2) | 3.7 | 1.3 | 8.1 | 0.7 | 6.9 | 1.4 | 5.3 | 1.1 | 5.2 | |||
| tPHZ(2) | DIR | B | 4.4 | 1.3 | 5.8 | 1.3 | 5.9 | 0.8 | 5.7 | 1.5 | 5.9 | ns |
| tPLZ(2) | 4.4 | 1.3 | 5.8 | 1.3 | 5.9 | 0.8 | 5.7 | 1.5 | 5.9 | |||
| tPZH(2)(1) | DIR | A | 6.8 | 10.5 | 10.3 | 9.7 | 9.7 | ns | ||||
| tPZL(2)(1) | 6.8 | 10.5 | 10.3 | 9.7 | 9.7 | |||||||
| tPZH(2)(1) | DIR | B | 6.4 | 13.3 | 11.2 | 8.7 | 8.3 | ns | ||||
| tPZL(2)(1) | 6.4 | 13.3 | 11.2 | 8.7 | 8.3 | |||||||
(1) The enable time is a calculated value derived using the formula shown in the Enable Times section.
(2) tPLH: Low-to-high Propagation Delay; tPHL: High-to-Low Propagation Delay; tPHZ: High-to-Hi-Z Propagation Delay; tPLZ: Low-to-Hi-Z Propagation Delay; tPZH: Hi-Z-to-High Propagation Delay; tPZL: Hi-Z-to-Low Propagation Delay
7.9 Switching Characteristics: VCCA = 2.5 V
over recommended operating free-air temperature range, VCCA = 2.5 V ± 0.2 V (see Figure 7)| PARAMETER | FROM (INPUT) |
TO (OUTPUT) |
VCCB = 1.2 V | VCCB = 1.5 V ± 0.1 V |
VCCB = 1.8 V ± 0.15 V |
VCCB = 2.5 V ± 0.2 V |
VCCB = 3.3 V ± 0.3 V |
UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TYP | MIN | MAX | MIN | MAX | MIN | MAX | MIN | MAX | ||||
| tPLH(2) | A | B | 2.6 | 0.4 | 4.9 | 0.2 | 4 | 0.2 | 3 | 0.2 | 2.6 | ns |
| tPHL(2) | 2.6 | 0.4 | 4.9 | 0.2 | 4 | 0.2 | 3 | 0.2 | 2.6 | |||
| tPLH(2) | B | A | 2.1 | 0.6 | 3.8 | 0.5 | 3.4 | 0.4 | 3 | 0.3 | 2.8 | ns |
| tPHL(2) | 2.1 | 0.6 | 3.8 | 0.5 | 3.4 | 0.4 | 3 | 0.3 | 2.8 | |||
| tPHZ(2) | DIR | A | 2.4 | 0.7 | 7.9 | 0.8 | 6.4 | 0.8 | 5 | 0.5 | 4.3 | ns |
| tPLZ(2) | 2.4 | 0.7 | 7.9 | 0.8 | 6.4 | 0.8 | 5 | 0.5 | 4.3 | |||
| tPHZ(2) | DIR | B | 3.8 | 1 | 4.3 | 0.6 | 4.3 | 0.5 | 4.2 | 1.1 | 4.1 | ns |
| tPLZ(2) | 3.8 | 1 | 4.3 | 0.6 | 4.3 | 0.5 | 4.2 | 1.1 | 4.1 | |||
| tPZH(2)(1) | DIR | A | 5.9 | 8.5 | 7.7 | 7.2 | 6.9 | ns | ||||
| tPZL(2)(1) | 5.9 | 8.5 | 7.7 | 7.2 | 6.9 | |||||||
| tPZH(2)(1) | DIR | B | 5 | 12.8 | 10.4 | 8 | 6.9 | ns | ||||
| tPZL(2)(1) | 5 | 12.8 | 10.4 | 8 | 6.9 | |||||||
(1) The enable time is a calculated value derived using the formula shown in the Enable Times section.
(2) tPLH: Low-to-high Propagation Delay; tPHL: High-to-Low Propagation Delay; tPHZ: High-to-Hi-Z Propagation Delay; tPLZ: Low-to-Hi-Z Propagation Delay; tPZH: Hi-Z-to-High Propagation Delay; tPZL: Hi-Z-to-Low Propagation Delay
7.10 Switching Characteristics: VCCA = 3.3 V
over recommended operating free-air temperature range, VCCA = 3.3 V ± 0.3 V (see Figure 7)| PARAMETER | FROM (INPUT) |
TO (OUTPUT) |
VCCB = 1.2 V | VCCB = 1.5 V ± 0.1 V |
VCCB = 1.8 V ± 0.15 V |
VCCB = 2.5 V ± 0.2 V |
VCCB = 3.3 V ± 0.3 V |
UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TYP | MIN | MAX | MIN | MAX | MIN | MAX | MIN | MAX | ||||
| tPLH(2) | A | B | 2.5 | 0.3 | 4.7 | 0.2 | 3.8 | 0.2 | 2.8 | 0.2 | 2.4 | ns |
| tPHL(2) | 2.5 | 0.3 | 4.7 | 0.2 | 3.8 | 0.2 | 2.8 | 0.2 | 2.4 | |||
| tPLH(2) | B | A | 2.1 | 0.6 | 3.6 | 0.4 | 3.1 | 0.3 | 2.6 | 0.3 | 2.4 | ns |
| tPHL(2) | 2.1 | 0.6 | 3.6 | 0.4 | 3.1 | 0.3 | 2.6 | 0.3 | 2.4 | |||
| tPHZ(2) | DIR | A | 2.9 | 1.1 | 8 | 1 | 6.5 | 1.3 | 4.7 | 1.2 | 4 | ns |
| tPLZ(2) | 2.9 | 1.1 | 8 | 1 | 6.5 | 1.3 | 4.7 | 1.2 | 4 | |||
| tPHZ(2) | DIR | B | 3.4 | 0.5 | 6.6 | 0.3 | 5.6 | 0.3 | 4.6 | 1.1 | 4.2 | ns |
| tPLZ(2) | 3.4 | 0.5 | 6.6 | 0.3 | 5.6 | 0.3 | 4.6 | 1.1 | 4.2 | |||
| tPZH(2)(1) | DIR | A | 5.5 | 10.2 | 8.7 | 7.2 | 6.6 | ns | ||||
| tPZL(2)(1) | 5.5 | 10.2 | 8.7 | 7.2 | 6.6 | |||||||
| tPZH(2)(1) | DIR | B | 5.4 | 12.7 | 10.3 | 7.5 | 6.4 | ns | ||||
| tPZL(2)(1) | 5.4 | 12.7 | 10.3 | 7.5 | 6.4 | |||||||
(1) The enable time is a calculated value derived using the formula shown in the Enable Times section.
(2) tPLH: Low-to-high Propagation Delay; tPHL: High-to-Low Propagation Delay; tPHZ: High-to-Hi-Z Propagation Delay; tPLZ: Low-to-Hi-Z Propagation Delay; tPZH: Hi-Z-to-High Propagation Delay; tPZL: Hi-Z-to-Low Propagation Delay
7.11 Operating Characteristics
TA = 25°C| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS |
VCCA = VCCB = 1.2 V |
VCCA = VCCB = 1.5 V |
VCCA = VCCB = 1.8 V |
VCCA = VCCB = 2.5 V |
VCCA = VCCB = 3.3 V |
UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TYP | TYP | TYP | TYP | TYP | ||||
| CpdA(1) | A-port input, B-port output |
CL = 0, f = 10 MHz, tr(2) = tf(2) = 1 ns |
3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | pF |
| B-port input, A-port output |
13 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 15 | |||
| CpdB(1) | A-port input, B-port output |
CL = 0, f = 10 MHz, tr(2) = tf(2) = 1 ns |
13 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 15 | pF |
| B-port input, A-port output |
3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | |||
(1) Power dissipation capacitance per transceiver
(2) tr: Rise time; tf: Fall time
7.12 Typical Characteristics
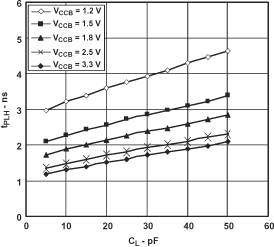
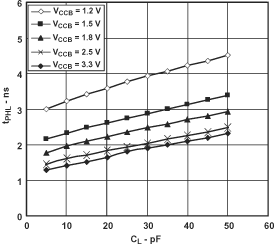
7.12.1 Typical Propagation Delay (A to B) vs Load Capacitance, TA = 25°C, VCCA = 1.8 V
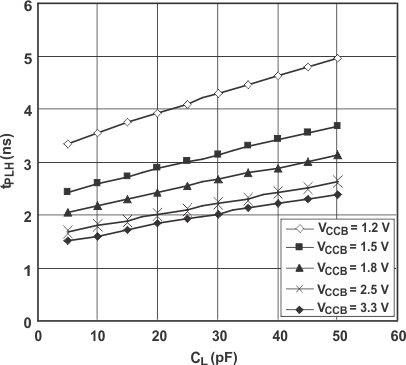
7.12.2 Typical Propagation Delay (A to B) vs Load Capacitance, TA = 25°C, VCCA = 2.5 V
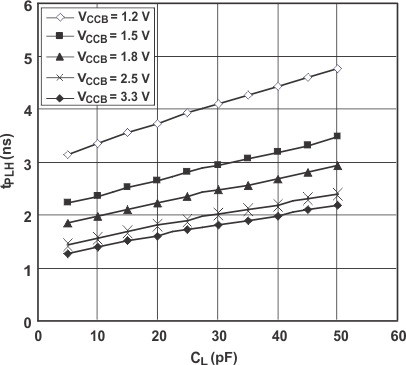
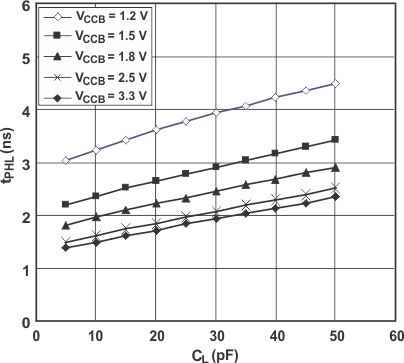
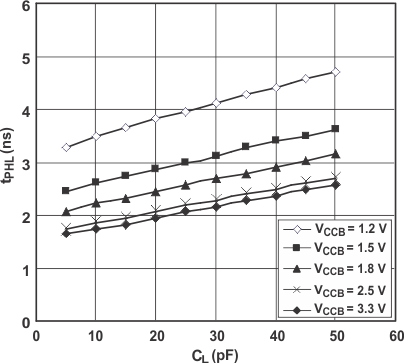
7.12.3 Typical Propagation Delay (A to B) vs Load Capacitance, TA = 25°C, VCCA = 3.3 V